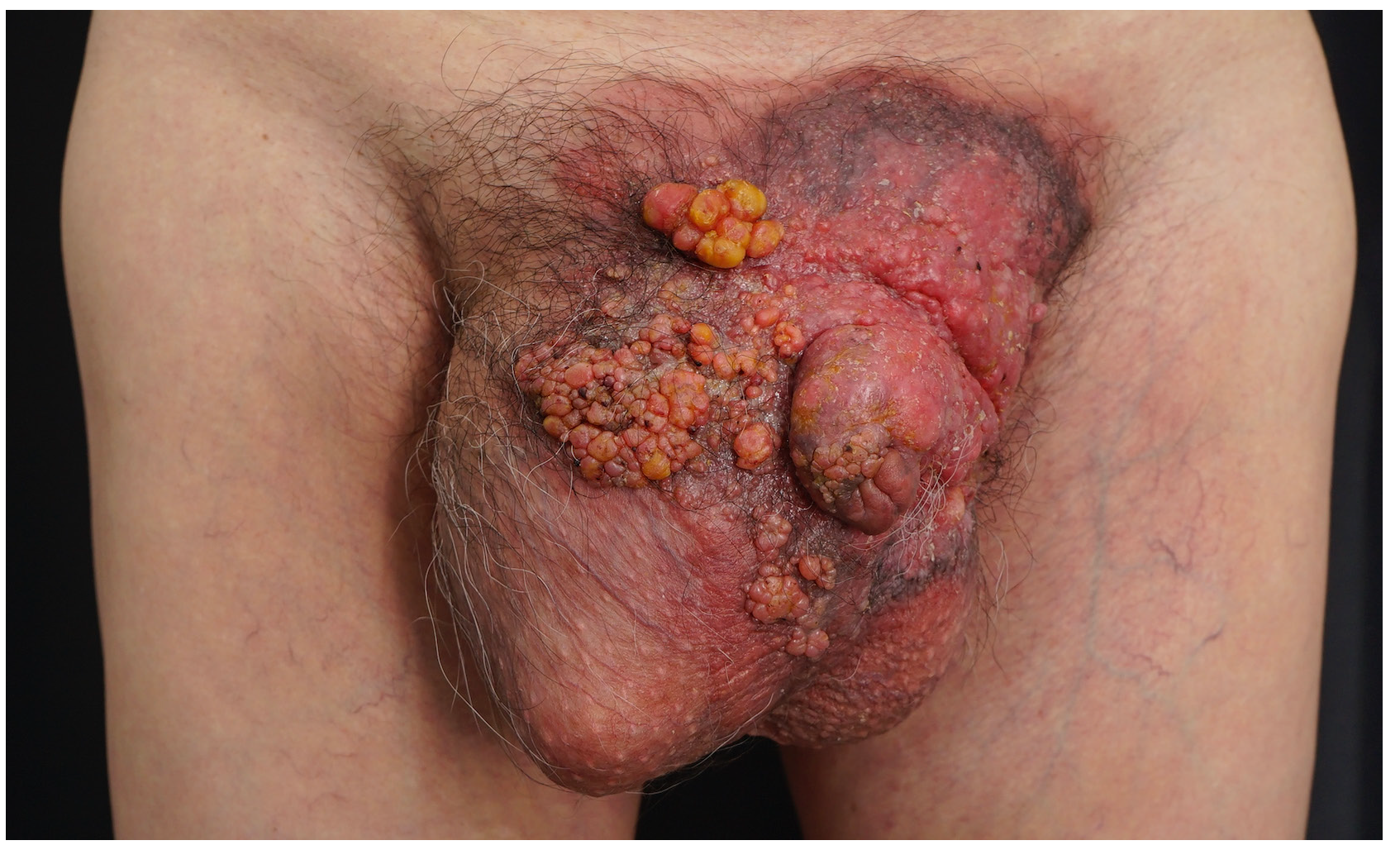
A 63-year-old man presented with multiple, asymptomatic, erythematous coalescing nodules over his scrotum and penis [Figure 1]. Skin biopsy from a nodule revealed atypical epithelioid cells with foamy and eosinophilic cytoplasm infiltrating the epidermis, dermis and lymphovascular structures, and stained positive for cytokeratin (CK)7 and negative for P40 [Supplementary Figures], consistent with Paget cells.
Export to PPT
Extramammary Paget’s disease, generally presenting as an intraepithelial adenocarcinoma, typically appears as erosive, crusted, or eczematous plaques. Differential diagnoses for multiple nodules on the scrotum include condyloma acuminatum, squamous cell carcinoma, and sebaceous carcinoma, necessitating histopathological examination for confirmation. The nodules in this patient probably resulted from the lymphatic stasis secondary to the invasion of lymphatic vessels by Paget cells.
留言 (0)