A diffuse erythematous, oedematous and tender swelling with a distinct border and local rise in temperature suggests a morphological diagnosis of erysipelas, while an indistinct border indicates cellulitis. Certain dermatological conditions mimic erysipelas and cellulitis which are labelled as erysipelas-like eruption and pseudocellulitis, respectively. It is vital to have comprehensive knowledge about the different causes of erysipelas-like eruptions and pseudocellulitis to decide on appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
MethodsA detailed search was performed in ‘PubMed’ and ‘Google Scholar’ and the search terms used were ‘erysipelas’, OR ‘erysipelas-like reaction’, OR ‘erysipeloid’, OR ‘erysipelas-like erythema’, OR ‘cellulitis’ OR ‘pseudocellulitis’. The mimickers of erysipelas and cellulitis are mentioned in Table 1.
Table 1: List of diseases that mimic erysipelas and cellulitis.
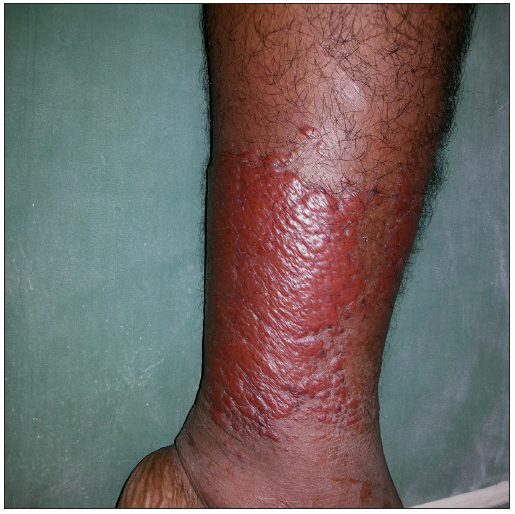
Erysipelas-like eruption Pseudocellulitis Infections Erysipeloid Necrotising fasciitis Dermatophytid Lymphangitis Histoplasmosis Drugs Injection site reaction Drug-induced [docetaxel, pemetrexed and gemcitabine] Covid-19 vaccine-induced erysipelas-like eruption Non-pigmented fixed drug eruption Tick bite Lymes disease Erysipeloid leishmaniasis Inflammatory conditions Sweet syndrome Erythema nodosum Metastatic Crohn’s disease Allergic contact dermatitis Nephrotic syndrome and its crisis Eosinophilic cellulitis Dermatomyositis Gout Familial Mediterranean fever Relapsing polychondritis Malignancy Carcinoma erysipeloides Superficial thrombophlebitis Diffuse large B cell lymphoma Paraneoplastic phenomenon in renal cell carcinoma Erysipeloid carcinomatosum [malignant melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma] Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Stasis related Acute lipodermatosclerosis Deep vein thrombosis Lymphedema Stasis dermatitis Iatrogenic Erysipelas-like eruption of mercury exanthem Ruptured Baker’s cyst Erysipelas and erysipelas-like eruption ErysipelasIt is usually caused by streptococcus (Group A β-haemolytic streptococcus) or staphylococcal species. The break in the barrier due to eczema, tinea pedis, folliculitis or ulcer leads to the entry of bacilli. This results in the development of a clearly demarcated erythematous, oedematous, tender, and smooth plaque [Figure 1].1 Ideally, aspirate from the bullae of erysipelas, blood, urine and stool are to be sent for culture as bullous erysipelas-like septic vasculitis due to Pseudomonas and Yersinia enterocolitica septicaemia have been reported.2,3 Treatment of erysipelas includes flucloxacillin and other penicillin group of antibiotics and in case of penicillin allergy, clarithromycin and clindamycin can be considered.1,3
Export to PPT
ErysipeloidErysipeloid is an occupational dermatosis in breeders, butchers and slaughterhouse workers due to traumatic penetration of gram-positive, non-sporing, non-motile bacilli Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Usually, it is transmitted by sheep, pigs, turkeys, ducks, lobsters and scorpions. Two clinical varieties of erysipeloid include localised and diffuse and generalised types. The localised and diffuse type is characterised by bluish-red to purplish, well-defined, raised plaque located over the fingers, palms, forearms, arms, legs and face. A generalised variant is associated with fever, joint pain and myalgia. Endocarditis, encephalitis, meningitis, peritonitis and sepsis are the complications.4 Histopathology reveals papillary dermal oedema, dilated vessels and mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of neutrophils, lymphocytes and eosinophils. Treatment includes antibiotics.5
Erysipelas-like dermatophytidDevelopment of recurrent erysipelas and cellulitis in lower extremities in patients of tenia pedis is a well-known entity and the pathomechanism is presumed to be the invasion of haemolytic streptococci along lymphatics due to the penetration of bacteria through fissures and erosions in soles and toes. As per this concept, the fungi act as passive media for penetration. According to a few authors, this may be a hypersensitivity response to fungal toxins. However, the long duration of the disease, neutrophilic leukocytosis, systemic symptoms and successful treatment with antibiotics are against the theory of erysipelas-like dermatophytid. The distinguishing feature is the sequelae; erysipelas-like dermatophytids recur repeatedly and heal without gross changes, whereas tinea with recurrent cellulitis overlap results in lymphedema. Treatment includes systemic antifungals for tinea infection.6
HistoplasmosisIt is caused by dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum var capsulatum in America and tropical countries and Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisii in Africa.7 Cutaneous features have diverse presentations, such as papules, ulcers, umbilicated lesions, erysipelas-like lesions and ecthyma-like lesions.8 Unresponsive to conventional antibiotics and immunocompromised patients must be evaluated for non-bacterial cellulitis such as deep fungal infection. Biopsy shows ill-formed granuloma with intracellular yeasts within histiocytes and retraction of cytoplasm of histocytes gives a pseudocapsule appearance. The organism is highlighted by the periodic acid Schiff and Gomori methenamine silver stain.9 It usually responds to itraconazole, fluconazole and amphotericin B.10
Non-pigmented fixed drug eruption (NPFDE)FDE is a delayed hypersensitivity response with a reaction recurrently appearing in the same area due to the intake of suspected drugs. It has multiple variants such as bullous, non-pigmented, eczematous and erythema dyschromicans-like, etc. NPFDE is characterised by tender symmetrical salmon to the erythematous plaque [Figure 2]. Histopathology reveals basal vacuolar degeneration, keratinocyte necrosis, melanin incontinence and lichenoid infiltration of lymphocytes. Treatment includes the withdrawal of the offending drug and systemic steroids.11
Export to PPT
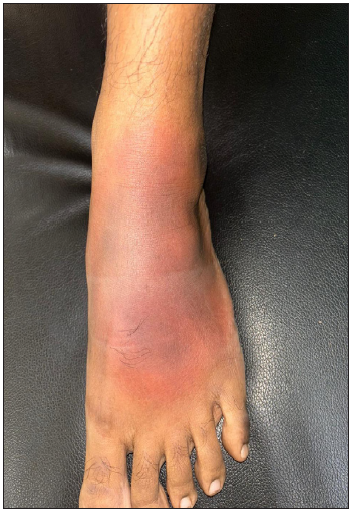
Injection site reactionDiphtheria, pertussis and tetanus vaccines can cause local site reactions characterised by redness, swelling and pain [Figure 3] which can be localised or extensive and may be associated with fever. The exact pathomechanism is unknown, but the possible theory is a cellular response against vaccine proteins. It is differentiated from erysipelas by the appearance of the lesion within a few hours following the vaccination, attains maximum size in 1–2 days and spontaneously subsides within a week.12 Treatment recommendations include analgesia, cold compression and encouraging the mobilisation of limbs.13
Export to PPT
COVID-19 vaccine-induced erysipelas-like eruptionIt is seen within 1–4 days of vaccination and characterised by an oedematous, erythematous rash over the extremities. Histopathology reveals marked papillary oedema with no inflammation in the oedematous area and perivascular mild lymphocytic infiltrate. It is differentiated from cellulitis by symmetry of lesions, absence of constitutional symptoms, temporal correlation with the vaccine and absence of neutrophilic infiltrate in the biopsy. Treatment includes oral steroids and subsidence of the lesion is noted within 1 week.14
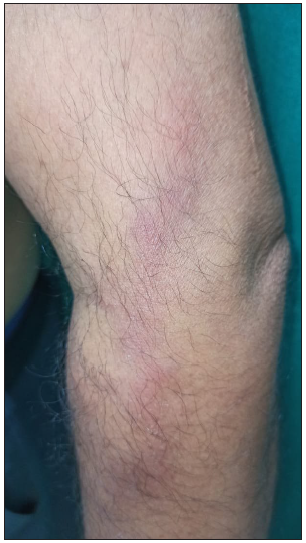
Lyme diseaseLyme disease is transmitted through Ixodes tick bite by the species Borrelia burgdorferi. It has three stages: early localised, disseminated and chronic disease. The early localised type is also known as erythema chronicum migrans [Figure 4] and occurs at the site of a tick bite. It is characterised by centrifugally spreading macule erythematous oedematous patch with central clearing, giving a ‘bull’s eye’ or ‘target appearance.’ It is delineated from erysipelas by the presence of a central tick bite mark.15 Cultivation of B. burgdorferi from Barbour–Stoenner–Kelly medium and elevated IgG or IgM antibodies by western blot immunoassay may help in definitive diagnosis. Histopathology reveals superficial and deep perivascular coat sleeve lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with or without plasma cells and eosinophils.16 Treatment includes doxycycline 100 mg BD for 2–3 weeks.17
Export to PPT
Erysipeloid leishmaniasisCutaneous leishmaniasis classically presents as papules and nodulo-ulcerative lesions. Atypical morphologies such as paronychial, chancriform, lupus-like, verrucous, sporotrichoid, mucocutaneous, panniculitis and erysipelas-like presentations are described. Erysipeloid leishmaniasis is generally reported in Pakistan, Iran, Tunisia and Turkey. Hence, travel history is important.18 A direct smear reveals amastigotes; histopathology reveals mixed inflammatory infiltrate with histiocytes demonstrating leishmania donovani bodies.19 Treatment includes sodium stibogluconate, meglumine antimoniate, amphotericin B and miltefosine.20
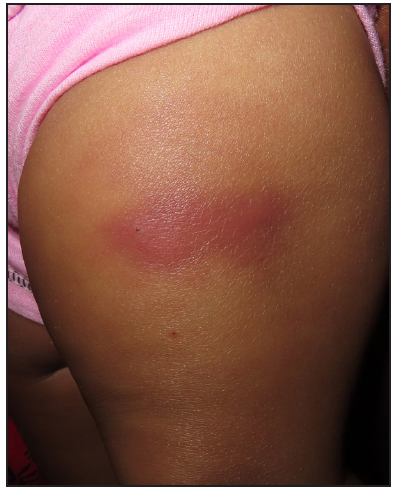
Sweet syndromeIt is characterised by erythematous infiltrated papules and plaques that give a pseudovesicular look [Figure 5] over the face, upper trunk and upper limbs. It is differentiated from erysipelas by presence of coalescing papules which form giant irregularly shaped plaque with relapsing, chronic course and is unresponsive to antibiotics. Histopathology reveals papillary dermal oedema with dense mature neutrophils. Oral prednisone is considered as the treatment of choice. Dapsone, colchicine and cyclosporine are alternative therapy to steroids.21
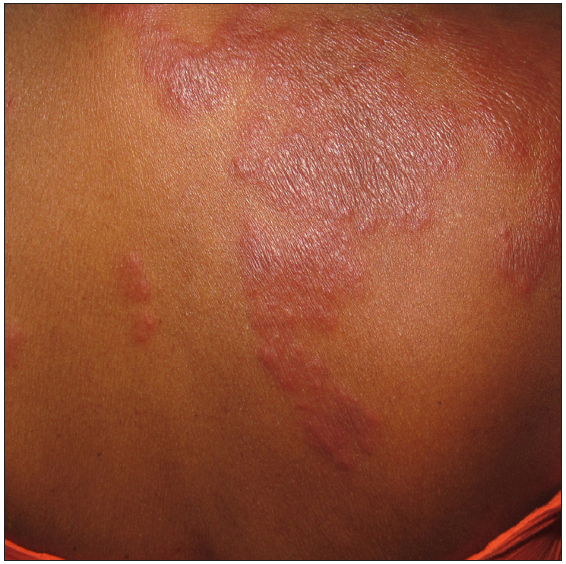
Export to PPT
Metastatic Crohn’s disease (MCD)Clinical presentation of MCD includes genital and extragenital involvement. Extragenital presentation varied from papules, nodules, abscesses, polypoidal plaques and erysipelas-like lesions. Associated symptoms are oral aphthosis, ocular symptoms, erythema nodosum-like lesions and they should raise the suspicion of MCD.22 Histopathology of MCD demonstrates non-caseating granulomas in papillary and reticular dermis and may extend into the subcutis. Treatment of MCD include oral prednisolone (0.5 mg/kg), metronidazole (800 to 1500 mg/day), methotrexate, azathioprine, cyclosporine, thalidomide, and TNF alfa inhibitors.23
Migrating erysipelas-like erythemas due to nephrotic crisisNephrotic crisis is a serious and dreaded complication of nephrotic syndrome with various stages, such as painful abdominal crisis, migrating erysipelas-like erythemas and ultimately hypovolemic shock. It is an emergency condition and needs fluid correction, salt restriction and diuretics.24
Erysipelas-like eruption in dermatomyositis (DM)It presents as facial erysipelas or cellulitis-like rash the malar and mandibular areas, along with Gottron papules over the dorsal aspect of proximal and distal interphalangeal joints and extensors of elbows.25 Histopathology of these lesions shows lobular lymphocytic panniculitis. Investigations such as creatinine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and myositis profile are done in suspected cases. Oral steroids and immunosuppressants are considered depending on the severity of the disease.26
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)FMF is a monogenic autoinflammatory disease due to the mutation of pyrin encoding the MEditerranean FeVer (MEFV) gene, characterised by increased activity and secretion of IL1β. FMF was diagnosed based on family history, recurrent fever associated with pleuritis, peritonitis or serositis, erysipelas-like erythema, amyloidosis of AA type and good response to colchicine. It is differentiated from classical erysipelas by family history, early age of onset, acute recurrent episodes with spontaneous resolution and associated serositis.27
Carcinoma Erysipeloides (CE)CE is a cutaneous metastasis either through contiguous spread or distant metastasis. It presents as well-demarcated erythematous indurated plaque, mostly originating from underlying breast cancer [Figure 6] or metastasis from the lung, pancreas or ovaries.28 Histopathology reveals infiltration of dermis and vascular and lymphatic channels with emboli of malignant cells. It has a poor survival rate ranging from 3 to 6 months.29
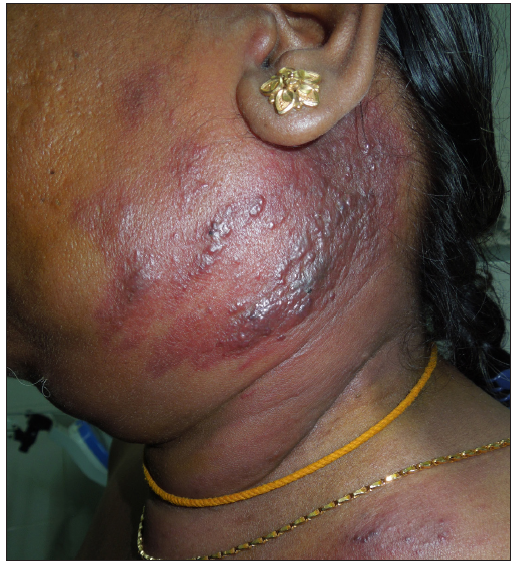
Export to PPT
Erysipelas-like erythema as a paraneoplastic eruption of renal cell carcinomaParaneoplastic cutaneous manifestations of renal cell carcinoma are rare. Erythema gyratum repens, angiosarcoma-like presentation, bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA disease and erysipelas-like lesions are described to date as cutaneous manifestations which may appear prior or simultaneously or proceeding renal cell carcinoma. Malignancies should be suspected when unexpected and unexplained skin lesions appear in the elderly.30
Erysipelas melanomatosum and Erysipelas carcinomatosumAs described previously, superficial dermal invasion by malignancies leads to erysipelas-like presentation and it was described earlier in metastasis from breast, lung, gastric and ovarian adenocarcinoma. There are reports of malignant melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma presenting as erysipelas-like lesions, labelled as erysipelas melanomatosum and erysipelas carcinomatosum, respectively.31,32 Histopathology shows infiltration of dermal and subcutaneous lymphatics and vasculature by atypical tumour emboli.33
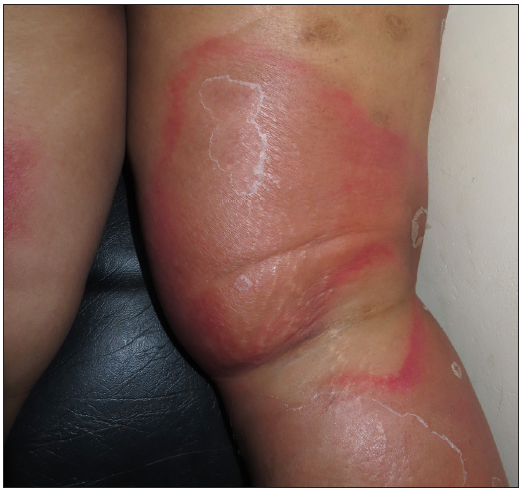
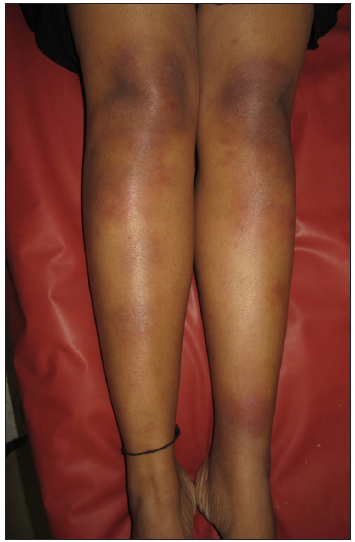
Acute lipodermatosclerosis (LDS)LDS can be subdivided into acute (<1 month), subacute (1–12 months) and chronic (>12 months) types. Acute, painful, erythematous, tender, indurated plaques on one or both legs, associated with the binding down of skin [Figure 7], should prompt the dermatologist to look into the possibility of acute LDS.34 Histopathology reveals sparse septal lymphocytic infiltrates, ischemic necrosis at the centre of fat lobules, lipomembranous changes and septal sclerosis.34,35 Imaging such as venous Doppler and duplex are done to check underlying venous insufficiency. Treatment of acute LDS includes topical steroids, limb elevation and compression stockings once DVT is ruled out.35
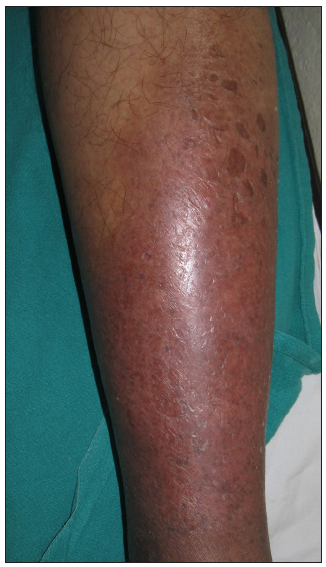
Export to PPT
Erysipelas-like eruption of mercury exanthemIn patients with mercury-filled dental amalgam, the release of mercury is associated with erysipelas-like nummular dermatitis, Baboon syndrome and lichen planus. There are case reports of erysipelas-eruptions in patients with dental fillers and metal hip replacement.36 Suspicion should be raised when a recent procedure history is found and a patch test with suspected metal alloys should be done to confirm the possibility. Treatment includes removal and replacement of the inciting metal.37
Many haematological malignancies, such as diffuse large B cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, present as erysipelas-like eruptions.38
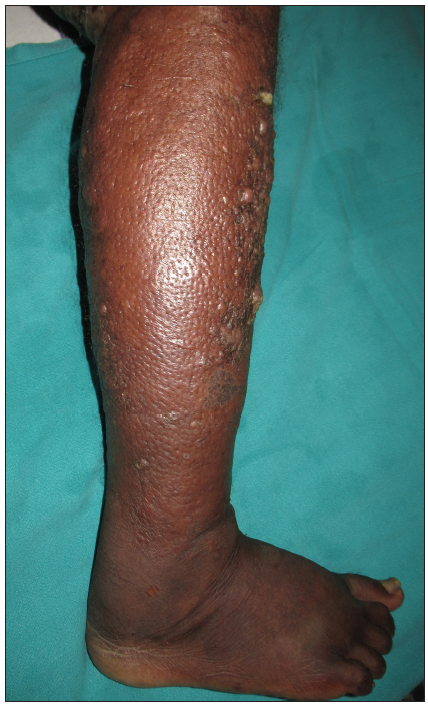
Cellulitis and pseudo cellulitis CellulitisFacial cellulitis in children is caused by Haemophilus influenzae and following a dog bite by Pasteurella.39,40 Erysipelas is distinguished from cellulitis by a well-demarcated elevated border [Figure 8] and superficial location of infection. Erysipelas in the face is delineated from cellulitis by characteristic sparing of ear lobule due to uninvolved fat tissue referred to as the ‘Milian ear sign’.41 Histopathology reveals marked dermal oedema, dilated vascular and lymphatic channels with neutrophils and mononuclear cell infiltration.42 Investigations reveals elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and c-reactive protein, leukocytosis and a positive aspirate culture from the bullae of erysipelas and blood in around 25% and 15%, respectively.43 Treatment includes antibiotics, preferably the penicillin group, and resolution is noted within 1–2 weeks.1 In case of recurrent cellulitis, a preventive prophylactic dose of penicillin V 500 mg daily is administered for a period of 6 months.44
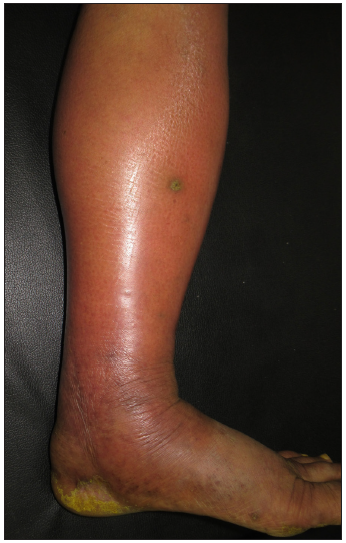
Export to PPT
Necrotising fasciitis (NF)NF is a rapidly spreading infection of deeper soft tissues along with systemic signs of sepsis. Based on aetiological agents, four types have been considered: the first type is polymicrobial, the second is monomicrobial (streptococcal> staphylococcal origin), the third type is vibrio vulnificans and the fourth is based on fungal origin. The plain X-ray may show soft tissue gas and computed tomography depicts fascial thickening with subcutaneous infiltration (in 80% of cases). Magnetic resonance imaging shows a high signal on contrast-enhanced T1 and T2-weighted images and is better appreciated with fat saturation. It is considered a surgical emergency and debridement and adequate antibiotic and/or antifungal coverage are considered the mainstay of management.45
LymphangitisInflammation of the lymphatic channels, either by infectious or non-infectious aetiologies, is referred to as lymphangitis which presents as a linear erythematous streak along the lymphatic channel extending towards a respective lymph node resembling a comet tail [Figure 9]. Bacterial lymphangitis has constitutional symptoms that mimic cellulitis clinically which is distinguished by a cord-like feeling during palpation. Treating the underlying aetiology remains the mainstay of management.46
Export to PPT
Drug-induced pseudocellulitisIt is described in association with gemcitabine, docetaxel and pemetrexed. These chemotherapeutic agents are commonly used in solid organ malignancies.47 Pseudocellulitis is usually encountered within 2 days after gemcitabine, 1–2 weeks following pemetrexed and within 4 weeks of docetaxel therapy.48,49 Radiotherapy and lymphedema are suspected to be the risk factors, but there are certain reports where gemcitabine led to pseudocellulitis without any triggering factors.48
Erythema nodosum (EN)EN is indistinguishable from cellulitis when typical nodular presentation is not seen. It is differentiated by the presence of multiple, bilaterally symmetrical, painful erythematous plaques and nodules over the anterior aspect of the legs [Figure 10]. Extensive evaluation for the underlying aetiologies should be made. Biopsy shows neutrophil predominant septal panniculitis with Miescher’s microgranuloma. It is usually self-limiting; treatment includes NSAIDs, steroids and TNFα inhibitors.50
Export to PPT
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD)ACD is a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. Acute-onset ACD can be confused with cellulitis as it has an abrupt onset due to exposure to plants, hair dye, adhesives such as resins and ultraviolet light exposure. It presents as an intensely itchy erythematous plaque with micro-vesiculation or bullae. Linear streaks, geometric patterns and pruritus help delineate it from cellulitis. Patch tests and features of acute spongiotic dermatitis on histopathology confirm the diagnosis. Removal of offending agents and steroids remains the mainstay of treatment.51
Eosinophilic cellulitis or Wells syndromeIt clinically presents as tender urticated papules and plaques, vesicles and nodules which later progress to form a morphea-like plaque and resolve without scarring. It is associated with fever and joint pains.52 Investigations reveal peripheral eosinophilia and histopathology shows the characteristic flame figures and eosinophilic granulomatous infiltration without evidence of vasculitis. Clinically, it closely mimics cellulitis or erysipelas, but presence of eosinophilia and being unresponsive to antibiotics should raise the suspicion of Wells syndrome. It is successfully treated with steroids, dapsone, ciclosporin or methotrexate.53
GoutWithout a background of hyperuricaemia, it is quite difficult to delineate an acute attack of gout from cellulitis. Risk factors of gout include increased age, male gender, drugs that inhibit the uric acid pathway and intake of red meat and alcohol. Delta neutrophilic index (DNI) represents the fraction of immature granulocytes that can predict the burden of bacterial infection. DNI >1.7% and <0.6% correspond to cellulitis and gout, respectively.54 Demonstration of monosodium urate crystal in affected tissue under polarised microscopy is considered the gold standard. Treatment involves NSAIDs, steroids, colchicine and uricosurics.55
Relapsing polychondritisRelapsing polychondritis is an immune-mediated disease that primarily affects cartilaginous structures and also the inner ears, heart and eyes. Inflammation of the ear closely mimics cellulitis, differentiated by the involvement of the cartilaginous area and sparing the ear lobule. Histopathology reveals a basophilic satined cartilage matrix infiltrated with lymphocytic infiltrates in perichondrium. Treatment is based on the severity and responds to NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, dapsone and colchicine.56
Superficial venous thrombophlebitis (SVT)SVT can be due to hypercoagulable state, trauma, drugs and malignancy. Trousseau syndrome is a paraneoplastic phenomenon that is commonly misdiagnosed as cellulitis. It is distinguished by the presence of cord-like tender erythematous swelling along with purpura over the surrounding area. SVT is commonly seen in greater and short saphenous veins of lower limbs. A visible echogenic non-compressible thrombus is seen on the duplex scan. Treatment includes administration of heparin or coumarin.57
LymphedemaLymphedema clinically presents as erythema, non-pitting unilateral oedema starting over the toes and progressing proximally and later shows hyperkeratotic warty dyspigmentation [Figure 11]. Patients with lymphedema are prone to superficial and deep cutaneous infections due to loss of natural skin barrier and impaired lymphatic drainage.58 Differentiation of uncomplicated lymphedema from secondary bacterial infection is done based on the recent increase in erythema, pain and the presence of warmth.
Export to PPT
Stasis dermatitisStasis eczema can result from chronic venous insufficiency and acute exacerbation manifests as erythematous papules and plaques with scaling and pruritus which mimics cellulitis. Pruritus, scaly oozy papules in a background of lichenification without systemic symptoms and involvement of both lower limbs, helps delineate it from cellulitis. Venous Doppler shows evidence of varicosities and a skin biopsy reveals an acute spongiotic reaction. Treatment includes antihistamines, topical steroids, limb elevation and compression stockings.59
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)DVT can be a complication of cellulitis (incidence rate is 2%–3%) or can present as a cellulitis-like lesion.60 It is differentiated from cellulitis by the absence of constitutional symptoms such as fever, chills and leukocytosis. Other bedside tests such as the Homan sign (tenderness in the calf muscle on dorsiflexion of the foot), Lisker sign (tenderness on percussion of shin) and Mose’s sign (calf tenderness on compression) can help in delineating it from cellulitis, but these tests are obsolete now.61 A duplex scan is a diagnostic tool that confirms a diagnosis. Anticoagulants (low molecular weight heparin, factor Xa inhibitors) and vitamin K antagonists are therapeutic options.60,61
Ruptured Baker’s CystBaker’s cyst or popliteal cyst is due to fluid accumulation in the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa, characterised by minimally painful palpable swelling over the popliteal fossa. Direct or iatrogenic trauma leads to rupture of baker’s cyst and can have a presentation similar to deep vein thrombosis or cellulitis over the calf region. Ultrasound reveals a collection of fluid over the intermuscular plane and crescent sign due to haemorrhage. Treatment includes analgesics for pain and surgical intervention for drainage of collection.62
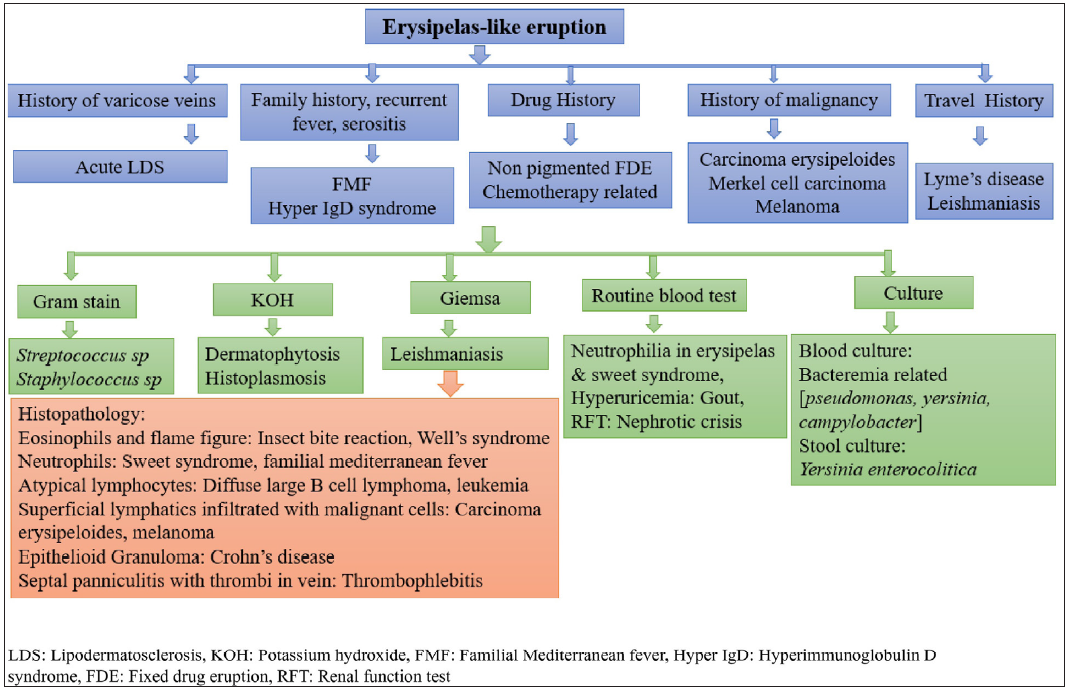
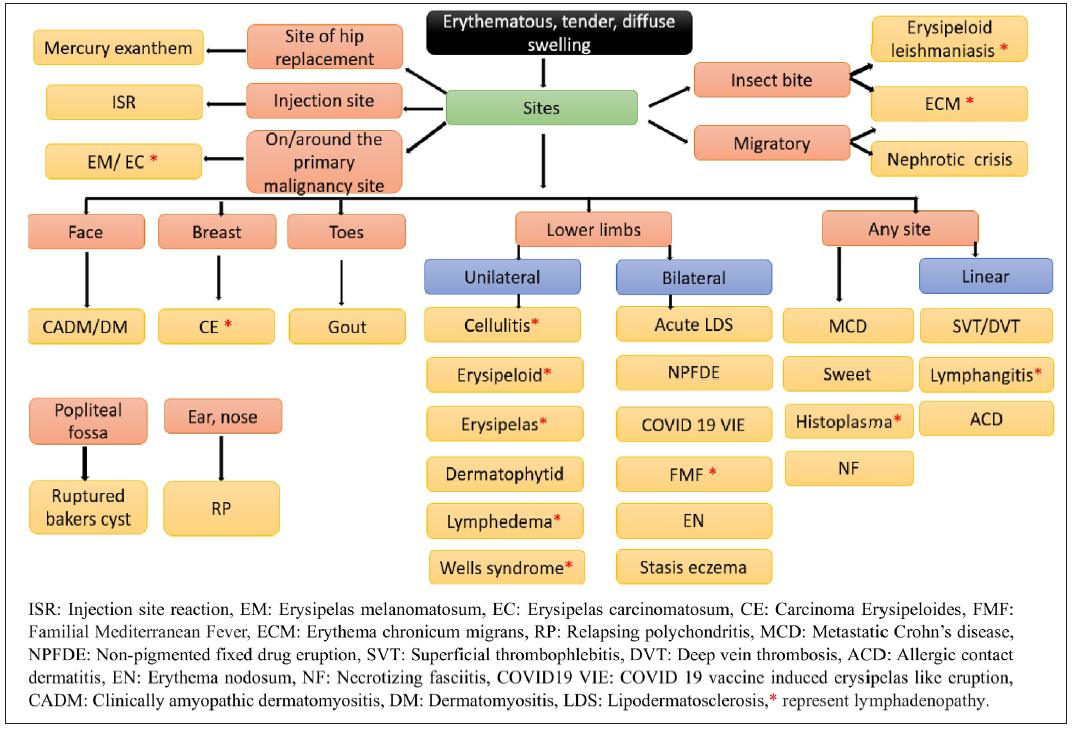
Flowchart 1 and 2 summarises the approach to erysipelas and cellulitis mimickers.
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
ConclusionTo conclude, even though erysipelas and cellulitis are more frequently encountered, a straightforward diagnosis of erysipelas should not be made. A strong suspicion of non-infectious erysipelas-like rash should be considered in atypical presentations, such as lack of response to conventional antibiotics, and a relapsing and recurrent course.
留言 (0)