In the published article, there was an error in the article title. Instead of “Shifting the paradigm of type 1 diabetes: a narrative review of disease modifying therapies”, it should be “Shifting the paradigm of type 1 diabetes: a narrative review of disease-modifying therapies”.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
In the published article von Herrath M, Bain SC, Bode B, Clausen JO, Coppieters K, Gaysina L, et al. Anti-interleukin-21 antibody and liraglutide for the preservation of β-cell function in adults with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(4):212-224. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00019-X was not cited in the article.
In the published article McGuire HM, Walters S, Vogelzang A, Lee CMY, Webster KE, Sprent J, et al. Interleukin-21 is critically required in autoimmune and allogeneic responses to islet tissue in murine models. Diabetes (2011) 60:867–75. doi: 10.2337/db10-1157 was not cited in the article.
The citation has now been inserted in Disease Modifying Therapies, Anti-IL-21 Monoclonal Antibodies & GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (Liraglutide), Paragraph 1 and should read:
“Anti-IL-21 and GLP-1 Agonists (Liraglutide)
Interleukin-21 (IL-21), a cytokine produced by T cells, plays an important role in the trafficking and activation of autoreactive CD8+ T cells in the beta cell (72, 73), thus making it a potential therapy target in the prevention of T1D. In this study, Anti-IL-21, considered a milder, well-tolerated immunomodulatory agent, was tested alone and in combination with a GLP-1 agonist, liraglutide, which has been associated with decreased beta cell stress and preservation of insulin secretion. To test the isolated and synergistic effects on beta cell preservation, a randomized 4-arm placebo-controlled, double-dummy, double-blind phase 2 clinical trial evaluated the impact of IL-21 and liraglutide on C-peptide secretion over 54 weeks. Adults with T1D diagnosed within 20 weeks with at least two known T1D autoantibodies and residual beta cell function were included. Participants were randomly assigned equally to liraglutide, anti-IL-21, both, or placebo, receiving treatment over 54 weeks and monitored for another 26 weeks after the cessation of treatment. During the treatment period, C-peptide secretion decreased by 10% in the group receiving anti-IL-21 and liraglutide, compared to a 39% decrease with placebo. Further, C-peptide secretion was 48% higher in the combination group when compared to the placebo group. No difference in C-peptide secretion was found when comparing single therapy with liraglutide or anti-IL-21 to placebo. During the 26-week observation period after cessation of therapy, no significant differences in C-peptide secretion, HbA1c, or total daily insulin dose were noted (72).”
In the published article, there was an error in Table 1 as published. We neglected to include a relevant study to the table, which also includes the newly added citation by von Herrath above. The corrected Table 1 and its caption appear below.
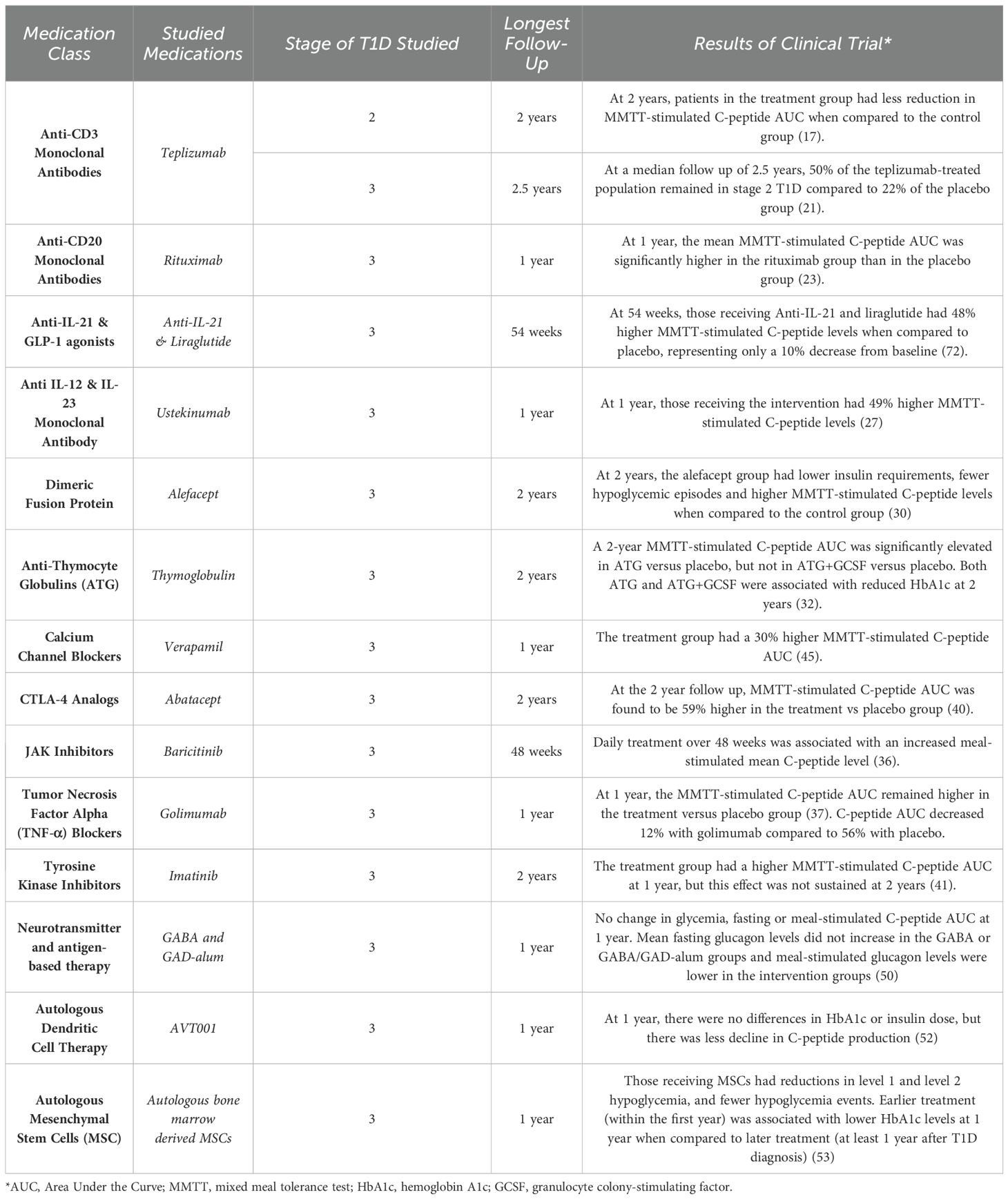
Table 1. Published clinical trials of disease modifying therapies in type 1 diabetes.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: type 1 diabetes, stage 1 type 1 diabetes, stage 2 type 1 diabetes, stage 3 type 1 diabetes, teplizumab, disease-modifying therapies
Citation: O’Donovan AJ, Gorelik S and Nally LM (2025) Corrigendum: Shifting the paradigm of type 1 diabetes: a narrative review of disease-modifying therapies. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1548761. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1548761
Received: 20 December 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 28 January 2025.
Copyright © 2025 O’Donovan, Gorelik and Nally. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Laura M. Nally, bGF1cmEubmFsbHlAeWFsZS5lZHU=
留言 (0)