While HHD has been managed by varied topical, systemic and procedural methods, the drugs administered either in sequence or isolation largely disregard the pathogenesis. The drugs seem to be directed at either the trigger factors or inflammatory mediators. In the absence of good-quality evidence, the clinician is at a loss to arrive at the ideal drug regimen for HHD.
We comprehensively searched the literature for the varied medical therapies used in HHD, align them with the existing knowledge on the pathogenetic aspects of the disease and encapsulate the existing drugs which can be used by the clinicians for the treatment of HHD.
MethodsThis narrative review was conducted by searching database using PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), using the keywords, ‘Hailey–Hailey Disease AND treatment, pathogenesis, trigger factors’. Grey literature was avoided due to the lack of veracity of the published data.
Using the keywords ‘Hailey–Hailey Disease and ‘therapy’, sorted by Most Recent,’ from July 1984 to May 2024, 364 articles were found. Search was focussed on the active therapy arm as a monotherapy and included papers which were studies, Double blinded (DB) randomised control trials (RCT), DB placebo-controlled studies, case series and also case reports if a novel drug had been administered. Papers that looked at the molecular aspects of HHD and the rationale of the treatment were particularly looked into. This data was then used to divide various therapies into broad mechanistic categories and the drugs were categorised depending on the level of evidence as first-line, second-line and third-line . First-line drugs were chosen from studies, DB RCT and placebo-controlled studies. Second-line drugs were added from case series and third-line drugs were from case reports.
Overview & PathogenesisHailey–Hailey disease (HHD) is a genetic disorder of keratinocyte adhesion with autosomal dominant inheritance and incomplete penetrance. The diagnosis may therefore be delayed in mild cases.
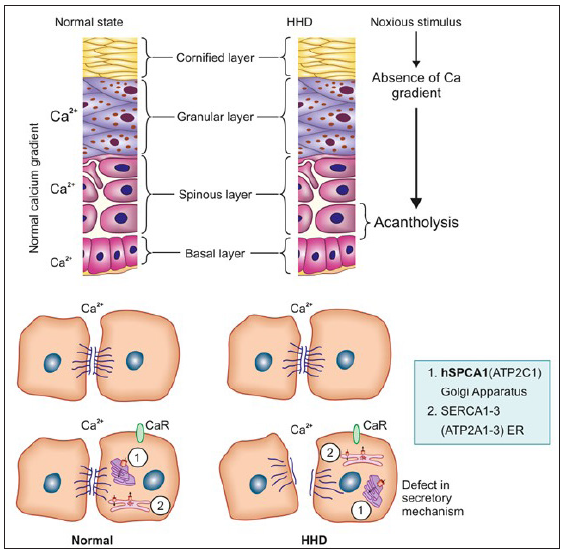
The defect is due to mutations in ATP2C1, a gene at chromosome 3q21-24 which encodes for the human secretory pathway Ca2+/Mn2+ ATPase isoform 1 (SPCA1), a calcium pump of the Golgi apparatus membrane. SPCA1 and sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase2 (SERCA2), encoded by ATP2C1 and ATP2A2 genes, respectively, are two essential calcium pumps necessary for Ca2+ homeostasis in keratinocytes. The specific defect in HHD is linked to hSPCA1, the function of which is to transport Ca2+ and Mn2+ into the Golgi lumen.1 ATP2C1 is highly expressed in the basal layer of the epidermis. In normal epidermis, there is a calcium gradient with the highest levels in the basal layer and granular layer, both intra- and extracellularly. This gradient appears to be a key element for the differentiation process in the epidermis and helps in counter-talk between keratinocytes and the extracellular space which has a calcium-sensing receptor (CaR). In the case of external stressors, this gradient is disturbed but reverses within 24 hours and the normally functioning hSPCA1 compensates with increased Ca2+ levels and prevents acantholysis. In HHD, there is an impaired Ca2+ gradient and sequestration which causes a depletion of Ca2+ within the Golgi lumen and this leads to a dysfunction in the processing and translocation of junctional proteins that function in cell–cell adhesion leading to suprabasal acantholysis [Figure 1].
Export to PPT
Recent studies have reported that apart from the low levels of hSPCA1 in HHD patients, there is an increase of miR-203 level and a decrease of p63 and HKII levels.2 A novel pathogenic mechanism involving SPCA1, p63 and IRF6 may play a role in the skin lesions occurring in HHD.3
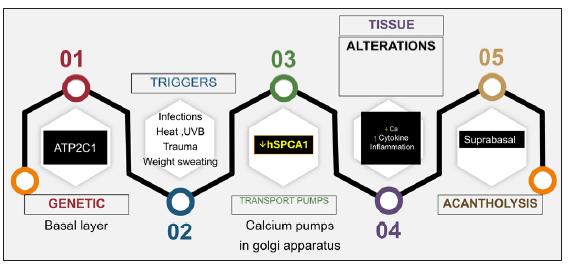
Various triggers have been implicated including excessive heat, menstruation, pregnancy, sweating, friction, exposure to sunlight and superficial infections with bacteria, viruses, candida, and scabies.4–6 Contact allergy to topical agents (e.g. crotamiton)7 or application of occlusive dressings8 can also flare the condition. The series of events resulting in acantholysis is depicted in Figure 2.
Export to PPT
There has been a renewed focus on certain pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-8 which play a role in HHD and Ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation has been implicated in reducing SPCA1 to critical levels.6 The addition of IL-6 antibody prevents the UVB-induced suppression of ATP2A2 and ATP2C1 mRNA; in contrast, the addition of an anti-IL-8 antibody accelerates the suppression. The reduction of ATP2C1 mRNA expression by UVB irradiation in keratinocytes is reversed by retinoids, corticosteroids, ciclosporin, tacrolimus, and vitamin D3.9 The role of newer drugs like dupilumab and JAK inhibitors (JAKibs) revolve around their inhibitory effect on the Th2 cytokines.
Clinical FeaturesThe onset of the disease is in young adult life and involves the sites of maceration and friction such as the axillae, groins, perianal region, and lateral aspect of the neck. Classic morphology is of ‘a dirt road drying out after a rainstorm.’
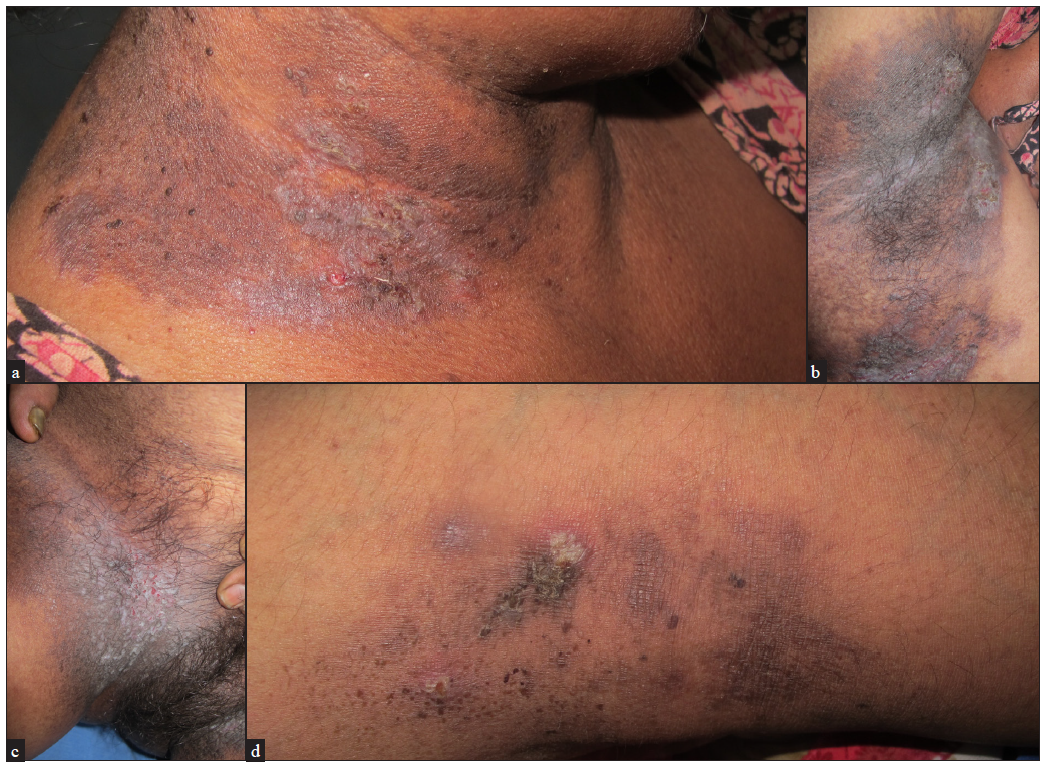
The initial lesion is a broad flaccid blister which ruptures to form plaques with crusts and fissures. The lesions are usually symmetric, round, oval, or circinate and can ooze, become foul-smelling, and develop papillomatous morphology. Unlike Darier’s disease, pruritus is not common. In less occluded areas, like the trunk and neck, the lesions are vesico-pustular with flaccid bullae or may be crusted [Figures 3a–3d]. Occasionally, palmar pits as well as longitudinal nail stripes can be seen.
Export to PPT
Differentials mainly include other conditions which can lead to erosive and oozing lesions in the intertriginous areas, such as Darier disease, pemphigus vegetans, inverse psoriasis, and intertriginous candidiasis.
The histology is characterised by prominent acantholysis, reminiscent of a ‘dilapidated brick wall’, affecting whole rete pegs and continues over the papilla tips. Dyskeratoses is only occasionally seen and the dermis has relatively dense lymphocyte-dominated inflammatory infiltrate.10
TreatmentThe disorder is an inherited acantholytic disorder and hence has a chronic course with recurrent crops of lesions appearing intermittently. One of the basic pillars of therapy is to avoid triggers.
General MeasuresPatients should avoid heat or friction, lose weight and wear loose-fitting cotton clothes, and avoid tight-fitting jeans. Adhesives and occlusive dressings should be avoided. There is a high chance of secondary infections. Hence, occasional topical and/or systemic antimicrobial and antifungal agents are indicated and long-term antimicrobial cleansers can be used as a preventive measure.11 Another useful option is bleach baths that can be used twice a week to reduce superficial infection.
Topical AgentsTopical agents are best described as adjunctive agents and include topical steroids, tacrolimus 0.03–0.1% or pimecrolimus 1% cream, and topical vitamin D analogues like calcitriol and talcalcitol.11 The various topical antimicrobial agents used include aminoglycosides (gentamicin 0.1% gel), fusidic acid, Castellani paint, and imidazoles.12 Tacrolimus has been used on a long-term basis to prevent flares.13 Here, it must be noted that the use of tacrolimus can itself lead to infections, including herpes with a report of SCC following prolonged use in vulvar HHD.14 A recent report used topical 15% aluminium chloride twice a week in an aqueous solution which is based on the perceived role of hyperhidrosis in aggravating HHD.15 Gentamicin in vitro can induce translational read-through of nonsense mutations in ATP2C1,16 though this might not be consistently seen in all genotypes of HHD. Steroids are advised only during acute flares and for a short course, as excessive use can lead to side effects including steroid atrophy, secondary infections, and contact dermatitis.
There are single case reports of topical fluorouracil 5% cream (thrice weekly for 3 months, then once weekly for 3 months) in groin involvement.17 This is based on the previous successful use of topical fluorouracil 5% cream in Darier’s disease with the hypothesis that 5-FU restores normal intracytoplasmic calcium concentrations.18 Topical cadexomer iodine, a sterile formulation of 0.9% elemental iodine bound to hydrophilic matrix cadexomer starch molecules with anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, absorbent, and wound-healing properties has also been successfully tried in a single case.19
There are isolated case reports of the beneficial effect of topical timolol 0.5% and topical cinacalcet 3% ointment, the former being a beta adrenergic blocker restoring calcium homeostasis, the latter being a CaR agonist.20,21 The purported action would be to increase the intracellular calcium levels.
Systemic AgentsThe systemic agents include oral corticosteroids, retinoids (acitretin 10–25 mg daily, etretinate 25–60 mg daily, alitretinoin 20–30 mg daily or Isotretinoin)22–24 and immunomodulatory drugs such as cyclosporine (2.8 to 3.4 mg/kg per day),25 methotrexate (7.5 mg weekly),26,27 azathioprine28 and dapsone (50–200 mg per day).29 All retinoids except isotretinoin have demonstrated resolution of patients’ symptoms, although failure with retinoids does occur.24
Broad-spectrum antibiotics such as oral flucloxacillin, erythromycin, or tetracyclines may be helpful, but the ideal antimicrobial agent to be used should be guided by the skin swabs for bacterial, fungal, and yeast culture and viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR).11,9 Painful, recalcitrant disease is suggestive of superinfection by herpes simplex and systemic antiviral treatment should be considered. Long-term antibiotics have also been tried including oral erythromycin (500 mg twice daily, 600 mg thrice daily ) or doxycycline (100 mg per day for 3 months) while a recent report has used the antibiotic and anti-inflammatory properties of minocycline (100 mg/day).30,31
Other drugs tried include low-dose naltrexone with/without oral magnesium,32–36 oral magnesium chloride,35–40 vitamin D,39,40 afamelanotide,41 oral glycopyrrolate42 and liraglutide43 [Table 1]. Biologicals like adalimumab,44 etanercept45 and dupilumab,46–49 have also been reported to be useful. Apremilast,50–52 and oral thalidomide53 have been used in isolated cases. Lately, JAK inhibitors (upadacitinib, abrocitinib) have been reported to be useful in HHD.54,55 Dupilumab and JAKibs possibly work via their inhibitory effect on IL-4 and IL-13 which have been shown to lead to a significant decrease in the peak amplitude of Ca2+ influx.56
Table 1: Overview of the salient systemic agents and their level of evidence
Systemic agents Mechanism of action in HHD Comments/Dose Level of evidence Doxycycline30 Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory property, anticollagenase activity via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases Recurrence is seen after stoppage of therapy Case series Oral corticosteroidsAnti-inflammatory action
Reduces protease activity
Reduces expression of ATP2C1
Recurrence after stoppage of the drug is seen and hence good as a ‘rescue therapy’ Retrospective study and large case series Oral retinoids22–24Normalise the epidermal turnover, reduce the inflammation
Reduces expression of ATP2C1
Acitretin 25 mg/day (10–50 mg/day)
Used alone, in adjunct with cyclosporine, NB UVB
Etretinate 25–60 mg daily, Alitretinoin 20–30 mg daily or isotretinoin
Case series Cyclosporine25Anti-inflammatory
Reduces expression of ATP2C1
Rapid control of flare,
2.8–3.4 mg/kg/day
Cannot be used on a long-term basis
Case reports Methotrexate26,27 Anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory (especially at low doses) 7.5–15 mg weekly Case reports Thalidomide53 Thalidomide inhibits TNF alpha that causes downregulation of NOTCH 1 signalling (upregulated in HHD), thereby reducing ROS formation and leading to proper terminal differentiation of keratinocytesRefractory HHD
Started on oral thalidomide 50 mg once daily (OD) for 24 weeks
Case report Low-dose naltrexone32–36 Modulates calcium transportation dysfunction by inhibiting toll like receptor (TLR) 4, leading to further reduction in Interleukin (IL) 6, TNF alpha and nitric oxide levels The dose varies from 9 mg to 50 mg. A better option seems to be to use 0.1 mg/kg/day Case reports and small case series Magnesium chloride35–40 Mg2+ inhibits the extrusion of Ca2+ ion via inhibiting the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase pump on the human RBC, thereby increasing the intracellular Ca2+ stores and preventing acantholysis Has been used alone and in combination with high-dose oral vitamin D (8,000 IU) & low-dose oral naltrexone Case reports Vitamin D39–40 Increases intracellular calcium levels, thus reducing acantholysis High-dose oral vitamin D (up to 800–8,000 IU) has been tried Case reports Afamelanotide41Anti-oxidative effects
Restores defective keratinocyte proliferative activity
Injection, 16 mg sustained release implant, 30 days apart Case report Glycopyrrolate42 Reduces hyperhidrosis by blocking M3 muscarinic receptors on eccrine sweat glands and thereby reducing Ach release from the presynaptic terminal Combination of topical mid-potent steroid, oral minocycline 50 mg BD and oral glycopyrrolate 1 mg OD (combination for 1 month) à Thereafter glycopyrrolate monotherapy Case report Liraglutide43 GLP 1 agonist, used as an adjunct for HHD for weight reduction and decreasing frictionUseful in the case of concomitant obesity and diabetes
(Formulation–subcutaneous injection 1.8 mg)
Single case report Apremilast50–52 Specific inhibition of PDE-4, leading to Th1 and Th17 inhibition and a decrease in CXCL10 release by the keratinocytes which mediates inflammations and flares in HHD Has been used in dose of 30 mg BD either alone or in combination with dermabrasion and BTX-A Case reports Dupilumab46–49 Fully humanised monoclonal Ab against IL-4a receptor subunit that interferes with signalling of IL-4 and IL-13. IL-4 acts via CCR1 and CCR5 (which inhibit increase in intracellular calcium and actin depolarisation) Given as subcutaneous injection 600 mg loading dose, thereafter 300 mg every other weekCase series
Case reports
Adalimumab44
Etanercept45
TNF alpha modifies intracellular calcium signalling, induces inositol phosphate turnover and also has a role in secondary infection in HHDAdalimumab: 40 mg every other week
Etanercept: 25 mg/week for 1 month, then 50 mg/week for 6 months, then 75 mg/week
Case report Oral JAKibs54–55 Skin barrier defect in HHD leads to Th2-mediated inflammation via IL-4 and IL-13. These cytokines mediate their action via JAK1 and STAT6, hence JAK1 inhibitors play a role in reducing inflammationUpadacitinib (15 mg daily)
Abrocitinib (100 mg/day)
Case report Azathioprine28 Dose not mentioned Case reports Procedural Therapy and Surgical InterventionSome authors report positive results with intralesional botulinum toxin type A, as a result of reduced lesional sweating, reducing chances of maceration and secondary infections.57,58 The modality has been shown to have good tolerance and minimal adverse effects. Combination treatment using Narrow Band (NB) UVB along with prednisolone59/acitretin60/alitretinoin61 has been shown to achieve resolution in refractory cases. Surgical modalities used for limited extent disease include dermabrasion62 and ablative lasers (CO2 & erbium: YAG).58,63 Surgical excision should ideally be done with split skin grafts.64 If so performed, a mid-dermis depth should be achieved. Other locally directed interventions include electron beam therapy and 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)-Photodynamic therapy (PDT).65–67
Mechanistic Targets of Existent Therapeutic AgentsThe varied therapeutic agents in HHD aim to target various proven and possible pathogenetic mechanisms. An overview of the sequential steps that lead to HHD is given in Figure 2. Some of the agents address the trigger factors and thus combinations or sequential oral antimicrobial agents have been tried as an initial step in the management of HHD. Of these, doxycycline seems to have the maximum evidence.30 This is followed by agents that reduce sweating including botulinum toxin injections,47,48 followed by measures to reduce weight and friction. The diverse triggers result in a shift in the tissue cytokine environment, which appears to be limited to Th2 cytokines, along with impaired calcium metabolism caused by defects in the Golgi apparatus’s secretory pathway Ca2+/Mn2+ ATPase.
Thus, after addressing the triggers, drugs are needed to target the local cytokine-mediated inflammation and secretory defects. Of the drugs listed in Table 2, there is a need to explore drugs that can address both the cytokine dysfunction and the secretory defect. This includes retinoids, corticosteroids, ciclosporin, tacrolimus, and vitamin D3 analogues which have been shown to address the activity of the ATP2C1 gene and counteract the reduced calcium levels.9 Naltrexone has been a novel addition though the ideal dose needs to be rationalised.33–35 Lately, drugs that target the cytokines have been used in HHD and include dupilumab46–49 and JAK inhibitors56 both of which target the Th2 cytokines5,6,9,56 which are implicated in the process of calcium imbalance in HHD. While many other drugs have been tried, they are usually effective in combination which itself is a reflection on their relative inferiority in monotherapy of HHD. The various agents are listed according to their level of evidence in Table 3.
Table 2: Overview of mechanistic targets of drugs used to treat HHD
Infectious triggers Topical antibiotics, systemic antibiotics (tetracycline, minocycline, doxycycline, dapsone, erythromycin, flucloxacillin), topical antifungals (miconazole) Inflammation Oral corticosteroids, dapsone, immunosuppressive agents (cyclosporine, methotrexate) Sweating Topical aluminium chloride, oral glycopyrrolate, oral oxybutynin, botulinum toxin A Weight LiraglutideKeratinocyte
Differentiation
Afamelanotide, oral retinoids, thalidomide Cytokines Dupilumab, TNF alpha inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept), JAK inhibitorsCalcium-dependent
secretory Defect
Low-dose naltrexone, vitamin D analogues, oral magnesium chloride Tissue removal techniques NB-UVB, PDT, EBRT, dermabrasion, ablative lasers (CO2 & Er: YAG), split skin graftsTable 3: Line of management
Topical Systemic Surgical First line Topical corticosteroids and antimicrobial agents Oral doxycycline 100 mg/day × 3 months Second lineCalcitriol 3 mcg/g ointment
Tacrolimus, 0.1% ointment
Topical aluminium chloride
Dapsone: 100 to 200 mg daily to as low as 50 mg every other day Cyclosporine: 2.5 mg/kg/day Oral glycopyrrolate: 1 mg daily Third line Methotrexate: 15 mg/week Excision followed by split-thickness skin grafting Acitretin: 0.25–0.5 mg/kg/day mg EBRT, PDT, LASER Dupilumab: 600 mg loading dose F/B 300 mg every 2 weeks Liraglutide: 0.6–1.2 mg daily Upadacitinib: 15 mg daily Magnesium Chloride: 300 mg Naltrexone: 3– 4.5 mgSurgical modalities, including lasers, remove the involved tissue62–64 which is an inelegant method of treating HHD. In most cases, surgery should be the last resort because ir is fraught with the possibility of local recurrence and sequelae.
ConclusionWhile the basic defect in HHD is known and the resultant pathology is that of a decrease in intracellular calcium levels (decreased CaR response and/or defective protein processing in the ER/Golgi apparatus), drugs that address this pivotal defect have yet not been rigorously tested. As triggers can upset calcium homeostasis, they should be addressed in all cases. To date, the exact link between cytokines and the defect in the secretory mechanism is not known though possibly a cause-and-effect hypothesis is probable and accounts for the efficacy of JAKis and dupilumab. Certain drugs that act on multiple pathways would make them superior to the existing drugs. There is as yet no double-blinded randomised controlled trial or real-world comparison of drugs to arrive at an ideal drug regimen so that treatment can be guided based on the existing level of evidence. There is an urgent need for therapeutic agents that address the basic pathogenetic pathway in HHD and we hope that future studies will address this concern with pre- and post-treatment proteomic and mutational expression studies that can determine the ideal drug for HHD. But, it is important to reiterate that being a genetic disorder long-term remissions off therapy are difficult to achieve at the present time.
留言 (0)