Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an invasive and most common pathological type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, accounting for approximately 30% to 40% of all cases. However, it is rare for the uterus and reproductive organs to be affected, which has not been well documented. Primary lymphomas of the female genital tract account for 0.2% to 1.1% of all extranodal lymphomas (1). Most cases of uterine lymphoma are caused by secondary involvement of the disease (2). Due to its rarity and non-specific clinical presentation, the diagnosis of uterine DLBCL is difficult. There are few studies at present, and therefore, there is currently no standard treatment for uterine DLBCL. However, several studies on DLBCL have investigated the efficacy of various treatment regimens, which were not specific to the female reproductive tract. For patients with DLBCL, the current standard treatment regimen is rituximab, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine and prednisone (R-CHOP), which has a cure rate of about 60%-70% and a relapse/refractory rate of 30%-40% (3, 4).
ResultsCase reportIn this case a 72-year-old woman experienced abdominal pain and urinary tract obstruction due to a large tumor in the uterus. The woman was in good general conditions had no hypertension, diabetes and dyslipidemia in her past medical History. Ultrasonography showed the presence of a large uterine mass, without clear evidence of local infiltration or lymphadenopathy. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed that significant increase in uterine volume and slightly longer T1 and T2 signals were seen in the anterior wall and bottom of the uterine body. The lesion in the anterior wall of the uterine body was relatively large, with a size of about 34mm×47mm×43mm. After enhanced scanning, the arterial phase enhancement of the lesion was significantly uneven, the degree of venous phase enhancement was lower than that of the normal uterine myometrium, the boundary was clear, and the leading edge of the lesion was incomplete. Diffusion weighted imaging showed a significant high signal, which is due to the tight arrangement of tumor cells, small extracellular space, and limited cytoplasm, resulting in limited diffusion of water molecules inside and outside the cell. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value of 0.751×10-3 mm2/s was significantly decreased (Figure 1). Computed tomography (CT) showed that the uterine volume increased, soft tissue density shadow could be seen in the anterior wall of the uterus, with unclear boundary, the size was about 34mmx47mm, and the enhanced scan showed uneven enhancement, lower than the myometrium, and liquid density shadow could be seen in the pelvic cavity (Figure 2). An incisional biopsy was taken from the anterior wall of the uterus. Histological examination showed a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the uterus. Immunohistological examination revealed CD20(+), Bcl6(+), CD10(+),P40(-), CK7(-), P16(+), ER(-), PR(-), Vim(+), P53(mutant type, +), Ki67approximately 90%(+), HNF1-β(-), CK(-), WT1(-), NapsinA(-), PAX8(-), CA125(-), LCA(+), CD3(-), PAX5 (+), P504S(-), Desmin(-), Caldesmon(-), EBV(-), MUM(+), Bcl2(+) and c-Myc approximately 30-40%(+) suggested a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma from the uterus (Figure 3). A bone marrow biopsy was performed, and the results showed normal bone marrow cells without evidence of lymphoma involvement. The patient’s International Prognosric Index (IPI) score was 2. Under the supervision of the hematology department, a series of chemotherapy treatments including rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) were initiated. According to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guideline, the patients in stage IV was planned to receive 6 cycles of RCHOP chemotherapy, and intrathecal methotrexate (IT-MTX) was given for Central Nervous System (CNS) prophylaxis, which were monitored every 3-6 monthly. A comparative CT scan was performed, and the results showed that after 3 courses of chemotherapy, all tumor locations significantly regressed. Before CT enhancement, the lesion density was relatively uniform, and obvious enhanced nodular shadow of about 6mm in diameter in the anterior wall of the uterus after the enhanced scan. The uterus is of normal shape and size. A small amount of fluid-like density shadow is seen in the pelvic cavity. Unfortunately, the patient died of heart failure after 3 cycles of RCHOP chemotherapy. The limitation is that interim positron emission tomography (PET)/CT scan was not done for the patient.
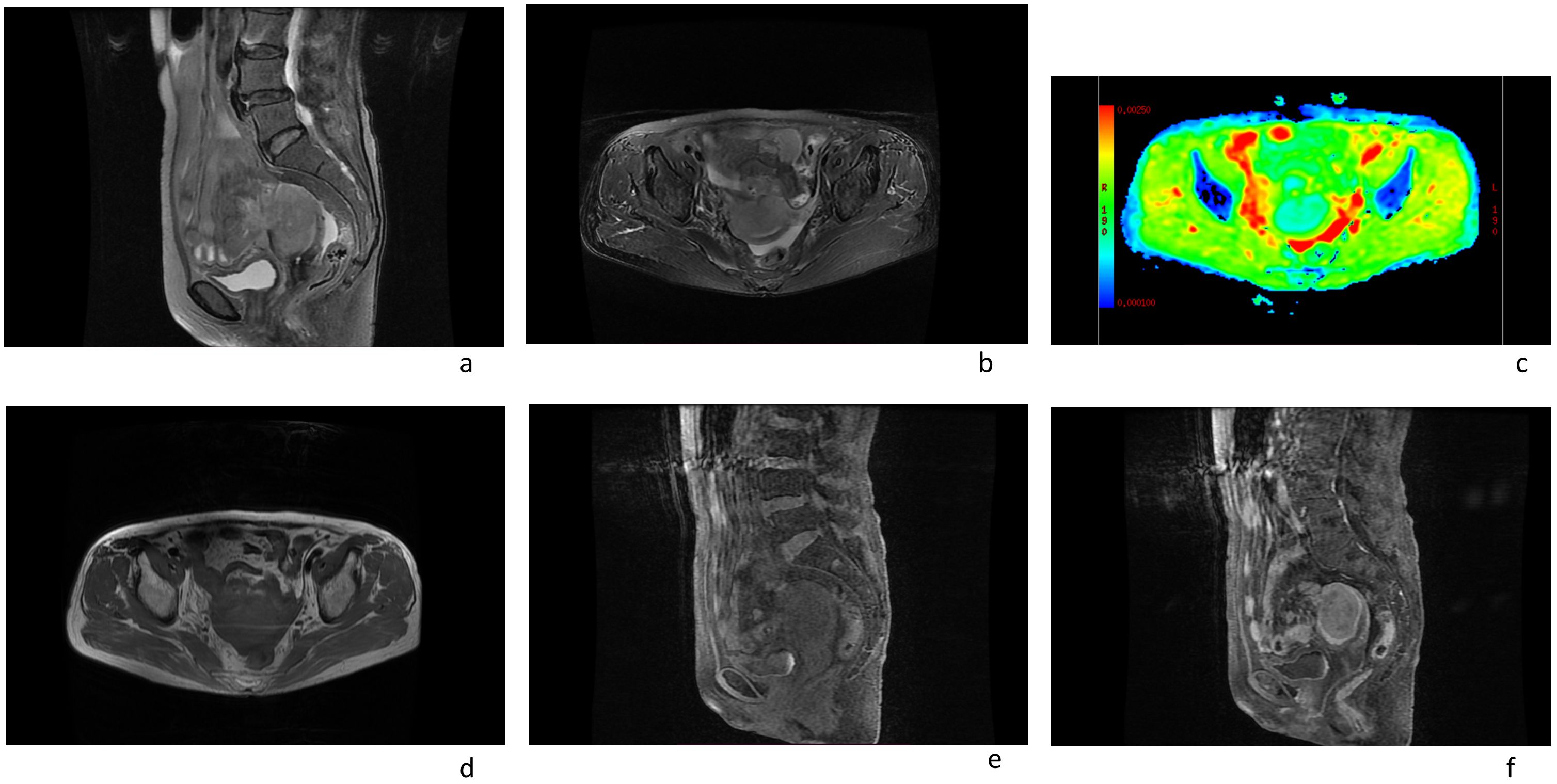
Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging scans of an 72-year-old female patient with a pelvic mass showed the following: (A, B, D, E) an enlarged uterus; (F) the arterial phase enhancement of the lesion was significantly uneven, the degree of venous phase enhancement was lower than that of the normal uterine myometrium. (C) The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value of uterine mass was 0.751×10-3 mm2/s.
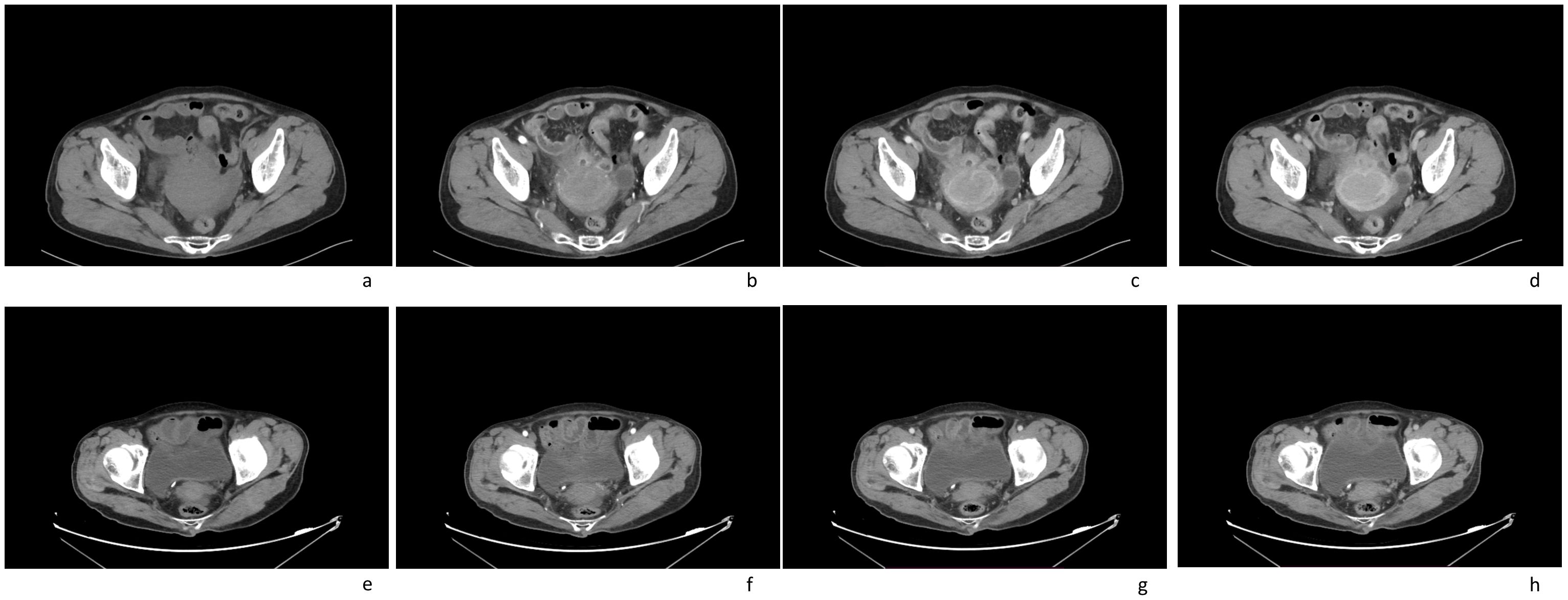
Figure 2. Computed tomography (CT) imaging scans of an 72-year-old female patient with a pelvic mass for more than 1 month: (A) plain CT imaging showed an enlarged uterine volume, soft tissue density shadow in the anterior wall of the uterus, with unclear boundary; (B–D) enhanced CT imaging(arterial phase[b]; venous phase[c]; delay phase[d]) showed that the lesion were slightly enhanced, the boundary was clear; (E–H) after treatment, enhanced CT imaging(arterial phase[f]; venous phase[g]; delay phase[h]) showed that the volume of the uterus had significantly reduced(plain CT imaging[e]).
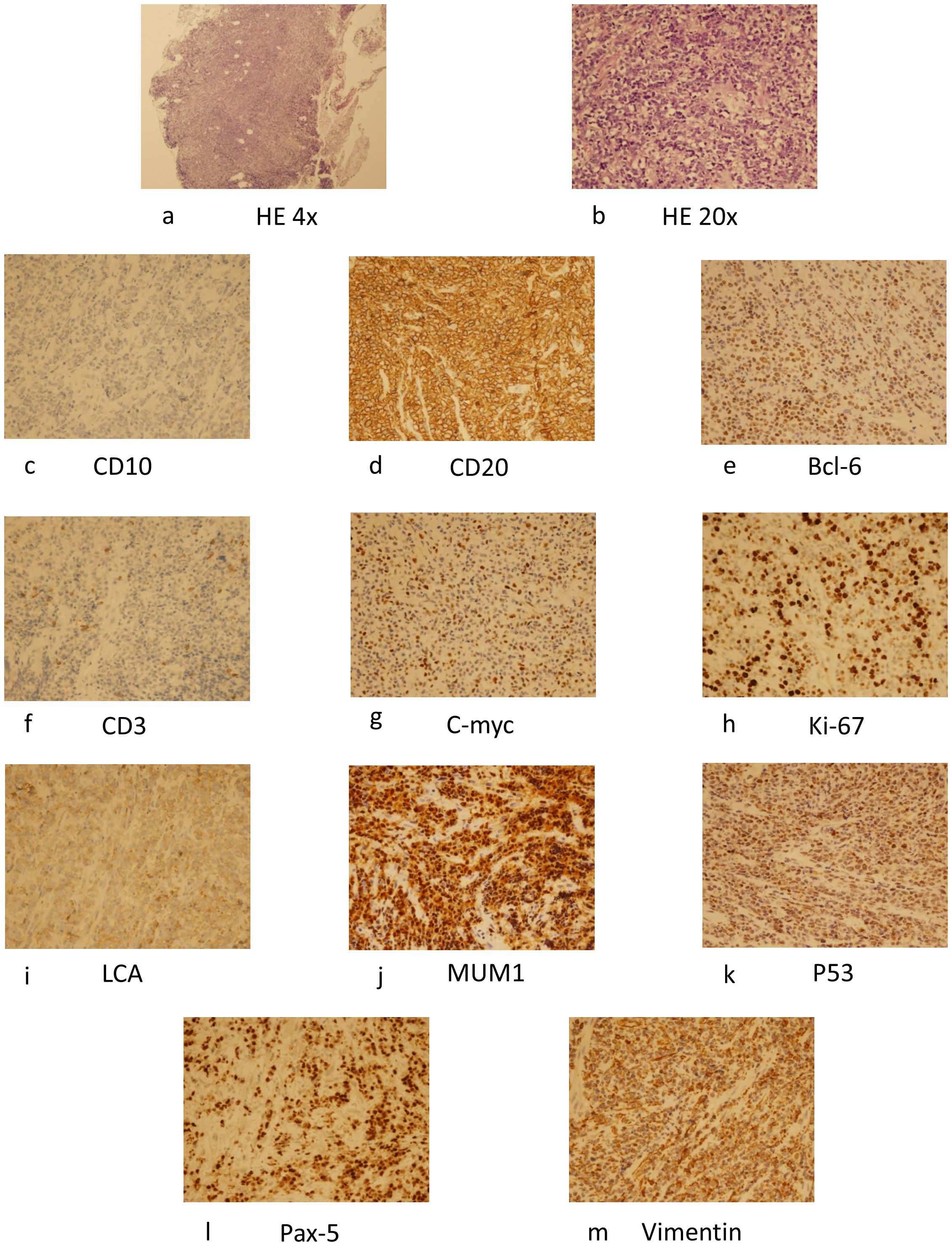
Figure 3. HE staining of the specimen (×40) (A), (×200) (B), and immunohistochemical examination revealed CD10 (+) (C), CD20 (+) (D), Bcl-6 (+) (E), CD3(+) (F), C-myc(+) (G), Ki-67(+) (H), LCA(+) (I), MUM1(+) (J), P53(+) (K), Pax-5(+) (L), Vimentin(+) (M) and suggested a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. HE, hematoxylin.
DiscussionThe table displays detailed information of 141 patients with primary uterine lymphoma (2, 10–63).
The uterine body, cervix, and vagina are rarely the origin sites of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Primary Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas (NHL) of the uterus is a very rare disease, with non-specific clinical manifestations. Fox and More (4) defined three criteria for primary uterine lymphoma: (1) clinical limitation to the uterus; (2) There is no evidence of leukemia; (3) The interval between primary uterine lymphoma and secondary tumors is very long. If diagnosed with lymphoma, bone marrow biopsy must be performed to rule out leukemia.
Primary uterine and vaginal lymphoma usually present with non-specific symptoms such as abnormal vaginal or uterine bleeding, perineal discomfort, persistent vaginal discharge, abdominal pain, and urinary obstruction. These symptoms occur in many more diseases, such as cervical or endometrial carcinoma, adenomyosis, endometriosis and uterine fibroids, complicating the determination of a definitive differential diagnosis. The appearance of symptoms is not a characteristic of uterine lymphoma, therefore, making a correct diagnosis may take longer.
The age and pathological type of patients with uterine lymphoma are related, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is most common in women aged 35 to 45; Follicular lymphoma is more likely to occur in women over the age of 50 (1). Burkitt’s lymphoma usually occurs most often in children aged 5 and 10 (5). The current patients are elderly individuals with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which is relatively rare in clinical practice.
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the most effective method for distinguishing lymphoma from cervical carcinoma, due to the fact that uterine DLBCL is a stromal rather than epithelial disease. The signal intensity of the uterine stroma and mucosa is usually intact and not invaded, which is different from cervical cancer. The Uterine lymphoma presents as a large mass within the uterus, and has similar signal intensity with that of other tumors, which is of low signal on T1 -weighted images, and high signal on T2 -weighted images. The contrast enhancement is common. The apparent diffusion coefficient values showed certain characteristics, which showed its ability to make a definitive differential diagnosis. The ADC of primary uterine lymphoma (0.696× 10-3 mm2/s) (6) was much lower than uterine fibroids and cervical cancer (1.15± 0.18× 10-3 mm2/s and 0.99± 0.18×10-3 mm2/s, respectively) (7).
CT is usually the preferred method for detecting and staging non Hodgkin lymphoma. The size and extent of the tumor can be accurately measured by CT. Moreover, CT can develop appropriate treatment plans and track treatment responses. CT can not only detect the lesions in the cervix, but also the involvement of the vagina, bladder, rectum and adjacent lymph nodes, which often presented as a large enhanced mass within the cervix, invasion of the vagina, bladder, rectum, and enlarged lymph nodes. No calcification is detected. CT is valuable for evaluating response to treatment, identifying active residual masses and assessing recurrence. Diagnosis invariably requires a core biopsy.
Currently, rituximab has been approved for monotherapy and when used in combination with CHOP, they are commonly referred to as R-CHOP (8). In several studies, the adding rituximab to CHOP therapy can improved complete response rate and prolonged event-free survival and overall survival (OS) in DLBCL patients (9) Szanto et al. found that using chemotherapy instead of radiotherapy can protect ovarian function, prevent micro metastasis (10). This has been proven to be effective in our patient.
In conclusion, elderly patients with primary uterine non Hodgkin lymphoma are relatively rare in clinical practice. When elderly patients develop pelvic masses, the physicians should consider the possibility of lymphoma and make a differential diagnosis.
Data availability statementThe original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statementEthical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributionsJW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
FundingThe author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We were supported by Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of china (No.2024MS08006, No.2020MS08128).
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s noteAll claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary materialThe Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1462353/full#supplementary-material
References1. Nasioudis D, Kampaktsis PN, Frey M, Witkin SS, Holcomb K. Primary lymphoma of the female genital tract: an analysis of 697 cases. Gynecol Oncol. (2017) 145:305–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.02.043
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Frey NV, Svoboda J, Andreadis C, Tsai DE, Schuster SJ, Elstrom R, et al. Primary lymphomas of the cervix and uterus: the University of Pennsylvania’s experience and a review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma. (2006) 47:1894–901. doi: 10.1080/10428190600687653
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
4. Hamlin PA, Satram-Hoang S, Reyes C, Hoang KQ, Guduru SR, Skettino S. Treatment patterns and comparative effectiveness in elderly diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results-medicare analysis. Oncologist. (2014) 19:1249–57. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0113
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
5. Pinto E, Batista S, Lourenc C, Gonçalves J, Ramalho G. Gynecological lymphomas Linfomas ginecologicos. Acta Obstet Ginecol Port. (2014) 8:201–5.
6. Mabray MC, Cohen BA, Villanueva-Meyer JE, Valles FE, Barajas RF, Rubenstein JL, et al. Performance of apparent diffusion coefficient values and conventional MRI features in differentiating tumefactive demyelinating lesions from primary brain neoplasms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2015) 205:1075–85. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.13970
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
7. Lee EY, Yu X, Chu MM, Ngan HY, Siu SW, Soong IS, et al. Perfusion and diffusion characteristics of cervical cancer based on intraxovel incoherent motion MR imaging – a pilot study. Eur Radiol. (2014) 24:1506–13. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3160-7
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
8. Salles G, Barrett M, Foà R, Maurer J, O'Brien S, Valente N, et al. Rituximab in B-cell hematologic Malignancies: a review of 20 years of clinical experience. Adv Ther. (2017) 34:2232–73. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0612-x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
9. Coiffier B, Lepage E, Brière J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2002) 346:235–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011795
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
10. Szánthó A, Bálega JJ, Csapó Z, Sréter LL, Matolcsy A, Papp Z. Primary non -Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix successfully treated by neoadjuvant chemotherapy: case report. Gynecol Oncol. (2003) 89:171–4. doi: 10.1016/s0090-8258(03)00057-x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
11. Chorlton I, Karnei RF Jr, King FM, Norris HJ. Primary Malignant reticuloendothelial disease involving the vagina, cervix, andcorpus uteri. Obstet Gynecol. (1974) 44:735–8.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
12. Harris NL, Scully RE. Malignant lymphoma and granulocytic sarcoma of the uterus and vagina. A clinicopathologic analysis of 27cases. Cancer. (1984) 53:2530–45. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840601)53:11<2530::AID-CNCR2820531127>3.0.CO;2-J
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
13. Komaki R, Cox J, Hansen R, Gunn W, Greenberg M. Malignant lymphoma of the uterus and cervix. Cancer. (1984) 54:1699–704. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841015)54:8<1699::AID-CNCR2820540836>3.0.CO;2-E
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
14. Muntz HG, Ferry JA, Flynn D, Fuller AF Jr, Tarraza HM. StageIE primary Malignant lymphomas of the uterine cervix. Cancer. (1991) 68:2023–32. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19911101)68:9<2023::AID-CNCR2820680930>3.0.CO;2-V
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
15. Broekmans FJ, Swartjes JM, van der Valk P, Schutter EM. Primary Malignant lymphoma of the uterus: localization in a cervicalpolyp. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (1993) 48:215–9. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(93)90090-Y
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
16. Kuo HC, Chou CY, Chang CH, Liu MT, Tzeng CC, Huang KE. Primary Malignant lymphoma of the uterine cervix shows favorable response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. (1994) 52:408–10. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1994.1070
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
17. Awwad JT, Khalil AM, Shamseddine AI, Mufarrij AA. Primarymalignant lymphoma of the uterine cervix: is radiotherapy thebest therapeutic choice for stage IE? Gynecol Oncol. (1994) 52:91–3. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1994.1017
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
18. Stroh EL, Besa PC, Cox JD, Fuller LM, Cabanillas FF. Treatment of patients with lymphomas of the uterus or cervix with combination chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Cancer. (1995) 75:2392–9. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950501)75:9<2392::AID-CNCR2820750932>3.0.CO;2-Y
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
19. Chandy L, Kumar L, Dawar R. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting as a primary lesion in uterine cervix: case report. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. (1998) 24:183–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1998.tb00073.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
20. Lee KM, Seah ES, Sethi VK. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix: case report of long-term survival of two patients treated with surgery and radiotherapy. Australas Radiol. (1998) 42:126–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.1998.tb00587.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
21. Nasu K, Yoshimatsu J, Urata K, Miyakawa I. A case of primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix treated by combination chemotherapy (THP-COP). J Obstet Gynaecol Res. (1998) 24:157–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1998.tb00068.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
22. Grace A, O’Connell N, Byrne P, Prendiville W, O’Donnell R, Royston D, et al. Malignant lymphoma of the cervix: an unusual presentation and a rare disease. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. (1999) 20:26–8.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
24. Vang R, Medeiros LJ, Ha CS, Deavers M. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas involving the uterus: a clinicopathologic analysis of 26cases. Mod Pathol. (2000) 13:19–28. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880005
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
25. Pham DC, Guthrie TH, Ndubisi B. HIV-associated primarycervical non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and two other cases of primary pelvic non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Gynecol Oncol. (2003) 90:204–6. doi: 10.1016/S0090-8258(03)00223-3
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
26. Venizelos ID, Zafrakas M, Dragoumis K, Mandala E, Bondis J. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma involving the uterine cervix after treatment for Hodgkin disease. Leuk Lymphoma. (2003) 44:2155–7. doi: 10.1080/1042819031000116643
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
27. Gabriele A, Gaudiano L. Primary Malignant lymphoma of the cervix. A case report. J Reprod Med. (2003) 48:899–901.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
29. Engin H, Türker A, Abali H, Uner A, Günalp S. Successful treatment of primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the vagina with chemotherapy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2004) 269:208–10. doi: 10.1007/s00404-002-0350-3
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
30. Chan JK, Loizzi V, Magistris A, Hunter MI, Rutgers J, Disaia PJ, et al. Clinicopathologic features of six cases of primary cervicallymphoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2005) 193:866–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2005.04.044
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
31. Garavaglia E, Taccagni G, Montoli S, Panacci N, Ponzoni M, Frigerio L, et al. Primary stage I-IIE non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of uterine cervix and upper vagina: evidence for a conservative approach in a study on three patients. Gynecol Oncol. (2005) 97:214–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.07.065
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
32. Heredia F, Bravo M, Pierotic M, Majlis A, Carmona L. Neoadjuvant combined chemotherapy followed by external whole pelvicirradiation in two cases of primary extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix. Gynecol Oncol. (2005) 97:285–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.12.018
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
33. Dursun P, Gultekin M, Bozdag G, Usubutun A, Under A, Celik NY, et al. Primary cervical lymphoma: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. (2005) 98:484–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.04.040
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
34. Hariprasad R, Kumar L, Bhatla N, Kukreja M, Papaiah S. Primary uterine lymphoma: Report of 2 cases and review of literature. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2006) 195:308–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2006.04.002
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
35. Semczuk A, Skomra D, Korobowicz E, Balon B, Rechberger T. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix mimicking leiomyoma: Case report and review of the literature. Pathol Res Pract. (2006) 202:61–4. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2005.10.009
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
36. González-Cejudo C, Martínez-Maestre MA, Peregrín-Álvarez I, Daza-Manzano C. Primary lymphoma of the cervix: Unusual location for a common disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2006) 125:268–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.09.020
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
37. Lorusso D, Ferrandina G, Pagano L, Gagliardi ML, Scambia G. Successful pregnancy in stage IE primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of uterine cervix treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and conservative surgery. Oncology. (2007) 72:261–4. doi: 10.1159/000113018
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
38. Signorelli M, Maneo A, Cammarota S, Isimbaldi G, Garcia Parra R, Perego P, et al. Conservative management in primary genital lymphomas: The role of chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. (2007) 104:416–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.08.024
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
39. Ferreri AJ, Verona C, Bolognesi A, Taccagni G, Ponzoni M, Ferrari S. Successful pregnancy after chemo-immuno-radiation therapy for aggressive lymphoma of the uterus. Br J Haematol. (2008) 142:141–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07083.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
40. Wuntakal R, Janga D, Satyanarayana D, Reynolds K, Hollingworth A. An unusual cause of postmenopausal bleeding. J Low Genit Tract Dis. (2008) 12:130–3. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0b013e3181571ae2
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
41. Ab Hamid S, Wastie ML. Primary non -Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting as a uterine cervical mass. Singapore Med J. (2008) 49:e73.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
42. Baijal G, Vadiraja BM, Fernandes DJ, Vidyasagar MS. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the uterine cervix: A rare case managed novelly. J Cancer Res Ther. (2009) 5:140–2. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.52784
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
43. Upanal N, Enjeti A. Primary lymphoma of the uterus and cervix: two case reports and review of the literature. Aust New Z J Obstetrics Gynaecology. (2011) 51:559–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2011.01365.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
45. Parva M, Lamb K, Savior DC, Gilman P, Belden M. Full-term pregnancy and vaginal delivery after treatment for nonHodgkin’s lymphoma of the cervix and lower uterine segment: A case report. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. (2011) 33:620–4. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)34911-8
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
48. Vasudev DS, Kaler AK. Non-hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix. Online J Health Allied Sci. (2012) 11:13.
49. Mouhajir N, Diakité A, Toulba A, Hemmich M, Saadi I. Primary non-hodgkin’s lymphoma of the uterine cervix: case report of long-term survival patient. J Obstet Gynecol India. (2014) 64:S145–7. doi: 10.1007/s13224-013-0483-2
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
50. Cao XX, Li J, Zhang W, Duan MH, Shen T, Zhou DB. Patients with primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of female genital tract have high risk of central nervous system relapse. Ann Hematol. (2014) 93:1001–5. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-2003-y
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
51. Chen R, Yu Z, Zhang H, Ding J, Chen B. Primary malignant lymphoma of the uterus and broad ligament: a case report and review of literature. OncoTargets Ther. (2015) 8:265–8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S78171
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
52. Pósfai É, Nagy K, Marton I, Bánfalvi A, Kocsis L, Cserni G. Incidentally discovered diffuse large B-cell lymphoma limited to the endocervical mucosa in a young female patient. Gynecol Obstet Investig. (2015) 80:134–8. doi: 10.1159/000369388
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
53. Cubo AM, Soto ZM, Cruz MÁ, Doyague MJ, Sancho V, Fraino A, et al. Primary diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the uterine cervix successfully treated by combined chemotherapy alone: A case report. Medicine. (2017) 96:e6846. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006846
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
54. Boussios S, Zerdes I, Vassou A, Bareta E, Seraj E, Papoudou-Bai A, et al. Extranodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas: A retrospective case series and review of the literature. Hematol Rep. (2018) 10:7070. doi: 10.4081/hr.2018.7070
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
56. Gui W, Li J, Zhang Z, Wang L, Zhao J, Ma L, et al. Primary hematological Malignancy of the uterine cervix: A case report. Oncol Lett. (2019) 18:3337–41. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10652
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
57. Goda JS, Gaikwad U, Narayan A, Kurkure D, Yadav S, Khanna N, et al. Primary diffuse large B cell lymphoma of Uterine Cervix: Treatment outcomes of a rare entity with literature review. Cancer Rep. (2020) 3:e1264. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1264
留言 (0)