Due to a lack of a Western screening program, gastric cancer is often discovered at an advanced stage with distant metastases. Historically, patients with gastric cancer were managed with palliative chemotherapy with a median overall survival of 9.9 months (1). The results of the FLOT-3 trial (2) have changed this paradigm. In a group of oligometastatic gastric cancer patients treated with the FLOT regimen (fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel), 36 patients emerged with a good response to systemic treatment and became surgical candidates. These patients with limited metastatic disease exhibited a promising median survival of 31.3 months compared to 15.9 months for patients who did not proceed to surgery. The notion of oligometastatic disease came to light. According to current literature, esophagogastric cancer that has spread to a single organ with ≤3 metastases or to one extraregional lymph node station is classified as an oligometastatic disease. Local treatment for oligometastatic disease has been associated with improved overall survival compared to systemic therapy alone (3). Ongoing efforts are focused on refining the definition of oligometastatic disease through the prospective OligoCare trial (NCT03818503) (4). Besides chemotherapy, immunotherapy has shown encouraging results in palliative metastatic situations. Currently, chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy is the standard first-line treatment for metastatic HER2-negative, programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1)-positive gastric cancers based on the positive results of the CheckMate 649 trial (5). Recently, new players have entered the treatment landscape for this condition, such as anti-claudin 18 therapies (6). Patients who are HER2-positive with PD-L1 >1 can also now benefit from a combination treatment of immunotherapy, trastuzumab, and chemotherapy (7). As a result, the therapeutic landscape for gastric cancer has evolved significantly. However, patients with peritoneal involvement remain underserved by immunotherapy, and deep responses are rare in this population (8). We present the case of a patient with a microsatellite-stable (MSS) oligometastatic gastric adenocarcinoma who despite bad prognosis factors like liver and peritoneal metastases achieved a complete histological response after “neoadjuvant” chemoimmunotherapy.
Case presentationA 54-year-old patient was addressed to our department with the diagnosis of MSS gastric adenocarcinoma. He had a history of weight loss, dysphagia, and epigastric pain for the last 3 months. He underwent gastroscopy which found an ulcerative lesion in the antrum (Figures 1, 2) and a pangastritis of moderate intensity and activity, with slight atrophy caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. The pathological examination confirmed an adenocarcinoma HER2-negative, MSS, and a PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) of 5. The patient underwent thoraco-abdominal tomography, laparoscopy, and liver MRI, revealing a single suspected liver metastasis between segments V and VII (Figure 3). Peritoneal lavage cytology was positive showing suspicious cells. The disease was classified as cT4 cN+cM1 according to the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC 8th edition) (9), and the multidisciplinary tumor board (MDT) proposed a metastatic systemic treatment with chemoimmunotherapy. The patient received four cycles of FOLFOX–nivolumab (leucovorin 400 mg/m², day 1; fluorouracil 400 mg/m², day 1 and 1,200 mg/m², days 1–2; and oxaliplatin 85 mg/m², day 1 and every 2 weeks; nivolumab 240 mg, every 2 weeks).
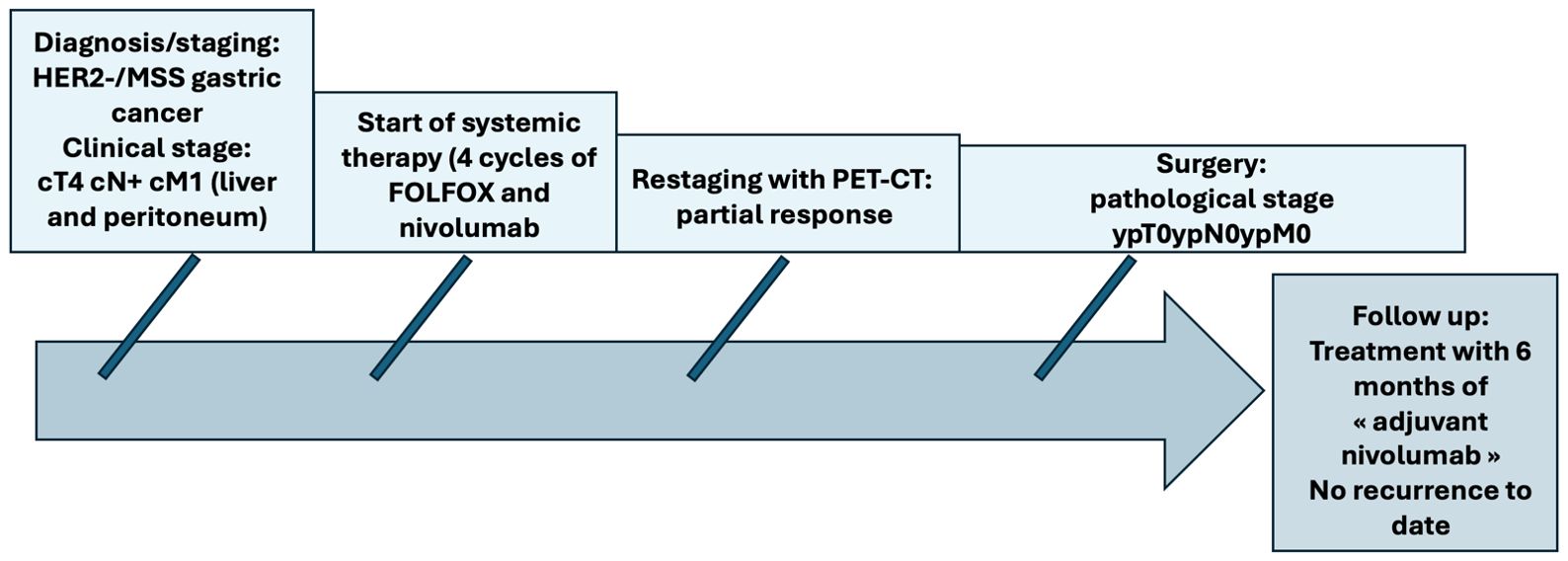
Figure 1. Patient care timeline.
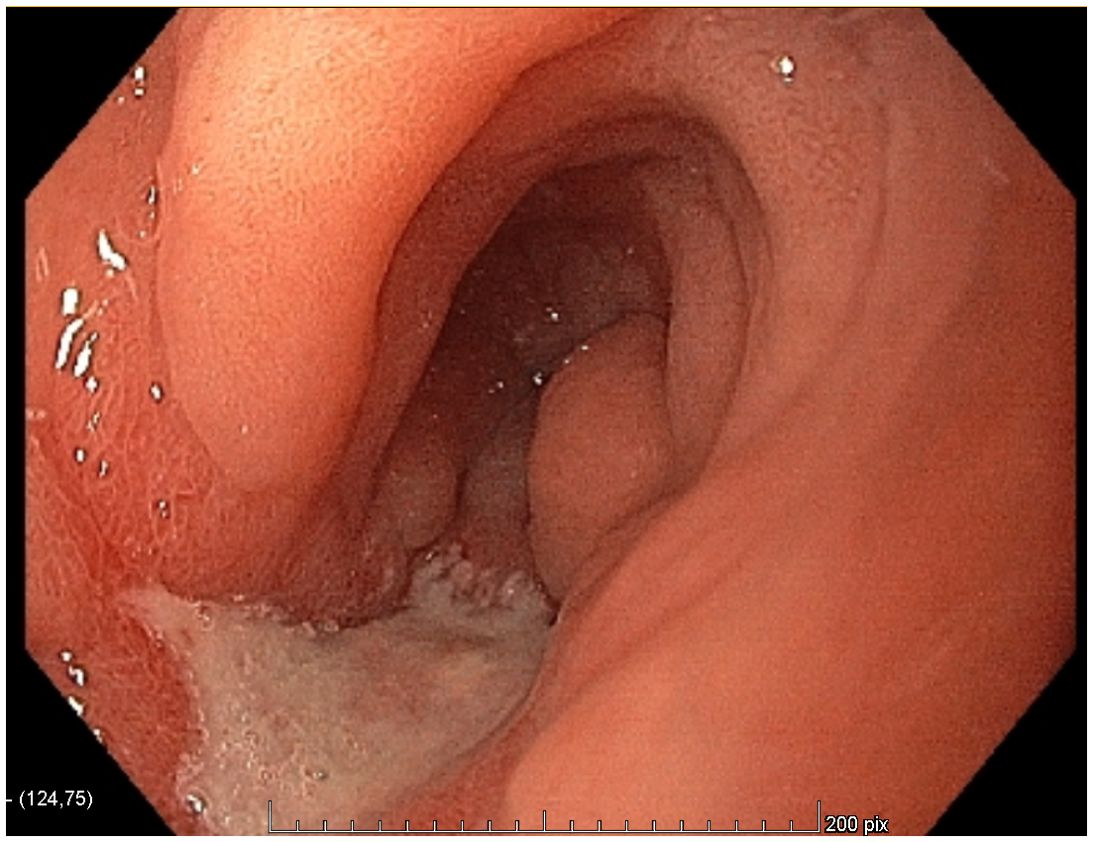
Figure 2. Endoscopic view of the antrum before the neoadjuvant treatment.
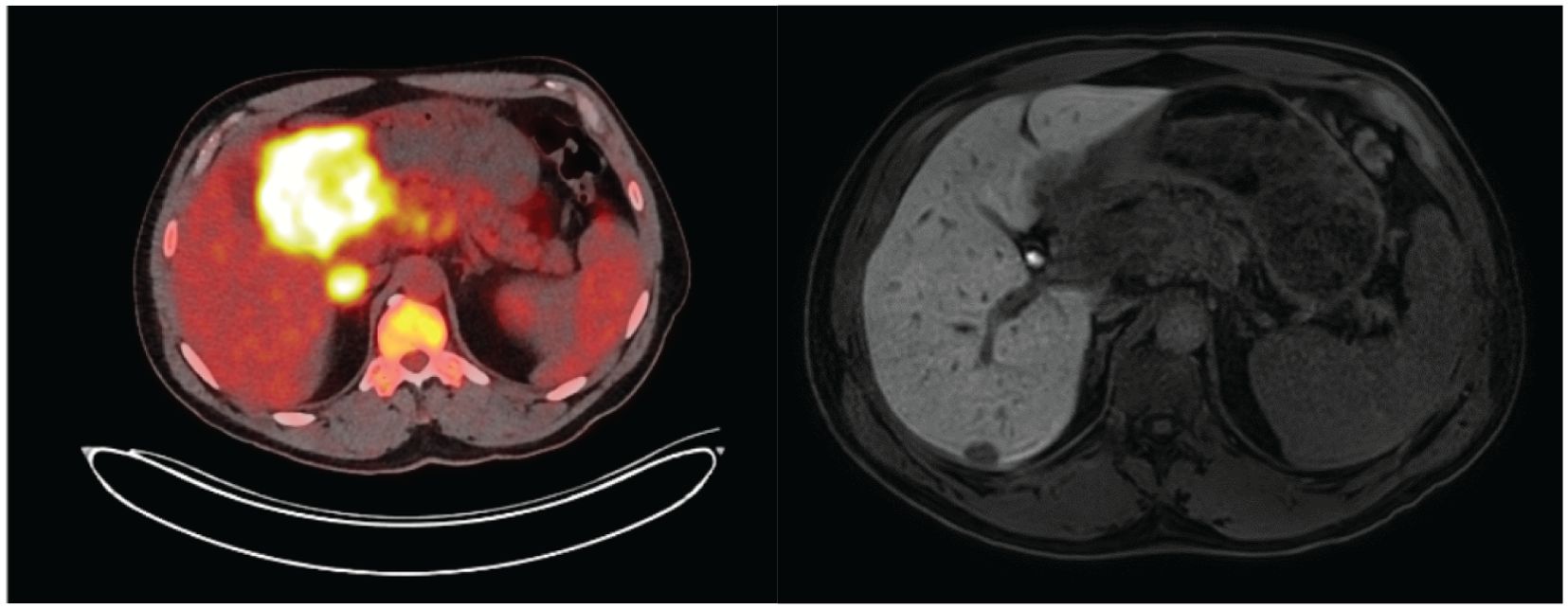
Figure 3. Preliminary staging with PET scan (left) and liver MRI (right). The PET scan shows a clear uptake of the primary tumor with regional lymph nodes. On MRI, a suspicion of liver metastasis is seen just at the junction between segments V and VI.
Restaging with a PET scanner and liver MRI 2 weeks after the fourth cycle showed a partial response (−37%) with downsizing of the gastric lesion, lymph nodes, and liver metastasis (10). An endoscopy examination confirmed macroscopic abnormality, but no biopsy was taken.
Due to the good partial response, our MDT suggested to conduct a laparoscopic restaging and possible surgery if no carcinomatosis was seen and the primary lesion was resectable. No sign of peritoneal disease was observed, and a hardened lesion at the level of the antrum was palpated but with a possible dissection from the pancreatic plane. In liver segment VI, we found an infracentimetric subcapsular lesion corresponding to the metastasis. We performed a total gastrectomy with a D2 lymphadenectomy and liver metastasectomy with a 1-cm margin. The postoperative course was uneventful, and the patient was discharged on postoperative day 13. On histologic examination of the specimen, a complete pathological response at the primary tumor localization was found with granulomatosis reactions, necrosis, and fibrous inflammatory remnants, conferring a tumor regression grade of 0 (Figure 4). Moreover, we found complete pathological regression in 15 out of the 24 examined lymph nodes, as well as in the liver metastasis (Figure 5). The final tumor classification was ypT0 ypN0 ypM0 R0. After discussion with the MDT, it was decided to continue with adjuvant nivolumab for a 6-month duration. At the 1-year follow-up, the chest and abdominal scan revealed no evidence of recurrence.
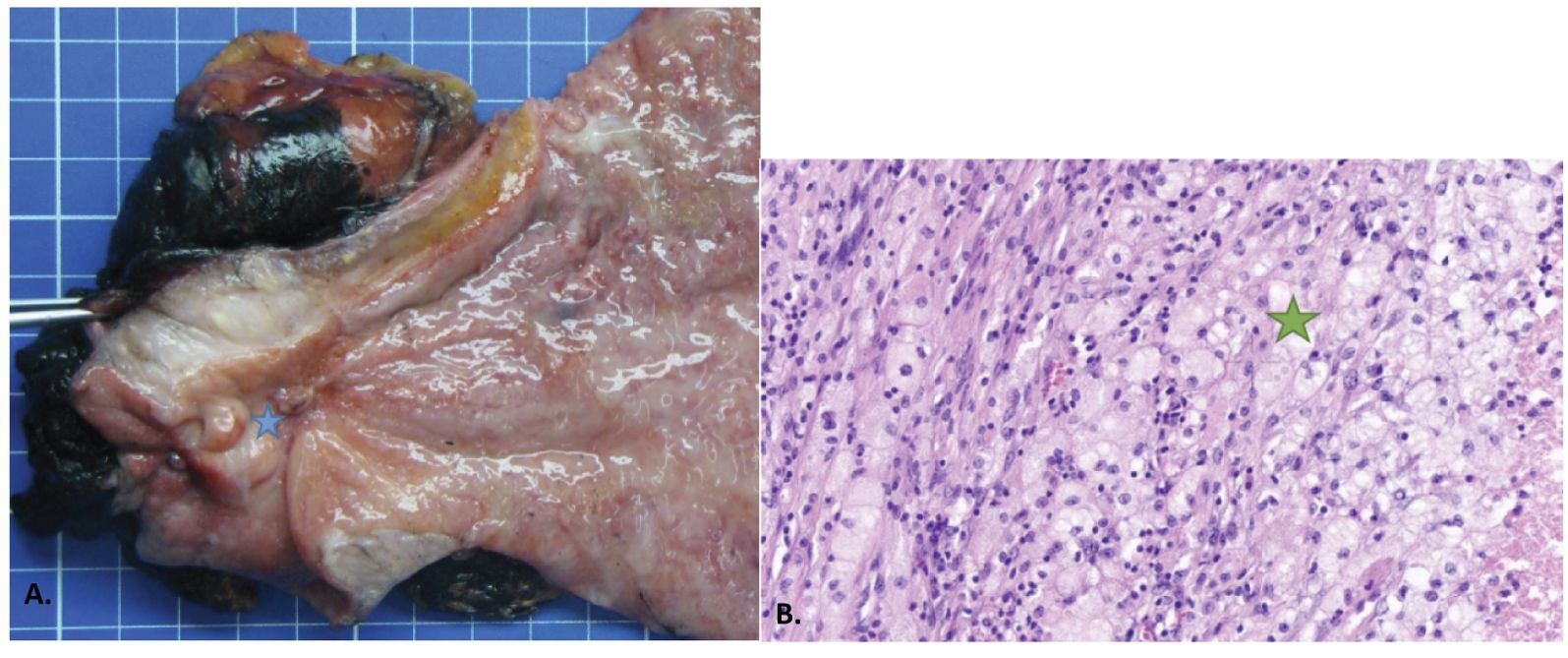
Figure 4. Histopathologic findings. (A) Macroscopic appearance with the distal part of the stomach with the tumoral bed (blue star). (B) Microscopic appearance with necrosis (orange star) surrounded by a xanthogranulomatous reaction with foamy macrophages (green star), fibrosis, and lymphocytes.

Figure 5. Lymph node with residual parenchyma (orange star) at the periphery, with central necrosis (blue star) and xanthogranulomatous (green star) reaction, which suggests a metastasis regression.
The patient was satisfied with his care and did not experience any significant complications following surgery or adjuvant immunotherapy.
DiscussionWe present the case of an oligometastatic MSS gastric adenocarcinoma with complete pathological response after four cycles of FOLFOX–nivolumab therapy. To our knowledge, this is the first report of such a complete response in a metastatic situation. Despite presenting with two unfavorable criteria (liver metastasis and peritoneal positive cytology) (11), the patient presented a complete regression of the primary and distant tumors. Several case reports of conversion to surgery for metastatic or unresectable gastric cancer have been published (Table 1). The distinction in our case lies in the use of a combined chemoimmunotherapy as the initial treatment, with a complete pathological response observed, including in the metastatic sites. The role of immunotherapy in patients carrying microsatellite instability (MSI) is well known in digestive tumors with a median overall survival of 44.8 months for MSI-high patients versus 14.3 months in MSS patients in the CheckMate 649 trial (5). However, our case shows that even patients with MSS status can achieve impressive responses.
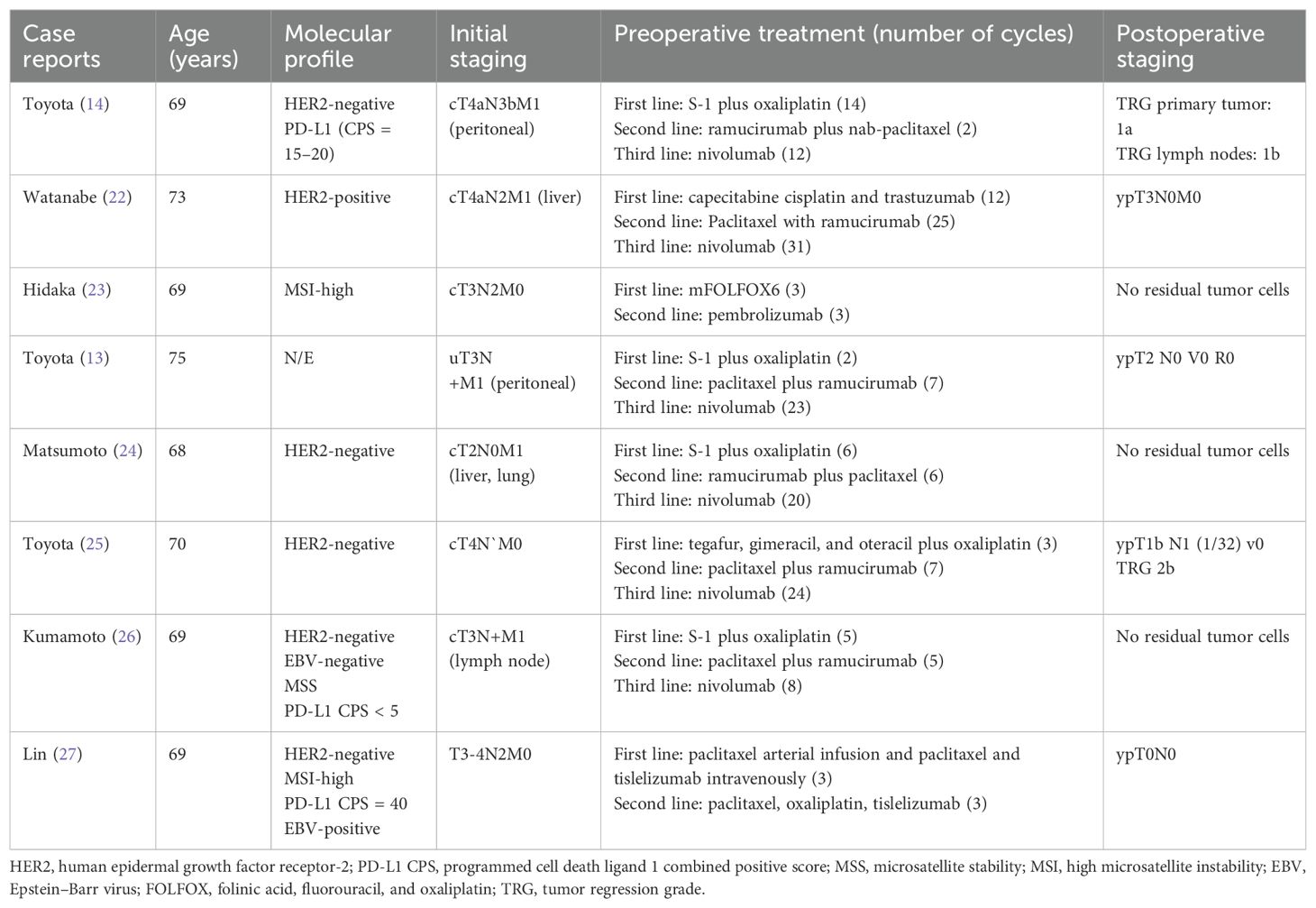
Table 1. Conversion to surgery case reports for metastatic or unresectable gastric cancer.
The updated CheckMate 649 results showed that in the MSS CPS ≥5 group, the overall response rate was high (60%) with 13 radiologic complete responses, and the outcome of these patients is unknown. Conversely, the presence of a liver metastasis was of poorer prognosis (12). This trend was already noticed in metastatic colon cancer, where the group with liver metastasis had almost no response to immunotherapy, suggesting a colder microenvironment in the liver (10). Regarding the location of the primary tumor, overall survival was higher in gastric cancers than in gastroesophageal junction cancers (15 months versus 13.4 months) (3). This observation is also true for other compounds such as zolbetuximab (antibody against claudin 18.2) in the SPOTLIGHT trial (6).
Peritoneal dissemination has always been the Achilles’ heel of advanced gastric cancer, but systemic immunotherapy seems to be able to control peritoneal carcinomatosis in certain cases (13, 14). In our case, despite a positive cytology, no sign of peritoneal invasion was noted during the surgery. The question of peritoneal penetrance or local control of immunotherapy to avoid peritoneal dissemination is yet to be answered.
Interestingly, our patient presented with H. pylori gastritis, which is a well-known carcinogenic agent of gastric cancer. Few studies have been carried out on the subject and patients were not stratified on this parameter in the main trials. Chronic H. pylori infection is the leading cause of gastric cancer, accounting for approximately 89% of gastric cancer cases worldwide, and is classified as a class 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization. Most of the existing data point toward a negative impact of the infection on the immunotherapy response (15).
Our patient therefore presented positive (CPS ≥ 5, gastric location) and negative (MSS status, liver metastasis) predictive factors of response to immunotherapy. In this population of patients who had a pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer, Cho et al. (16) have reported a 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate of up to 85%. In the KEYNOTE-585 trial, 12.9% of patients with localized gastric cancer who received chemoimmunotherapy achieved a pathological complete response. However, although the median event-free survival was longer in the pembrolizumab group (44.4 months versus 25.3 months), it did not reach the threshold for statistical significance (17). The second question raised concerns the continuation of immunotherapy following a pathological complete response. The literature on this subject is poor and no prospective study has assessed the issue. Some data exist for metastatic melanomas and show that if a complete response is obtained after systemic treatment, the response seems to be durable with a low probability of long-term recurrence. The place of immunotherapy rechallenge in recurrence is however unclear and deserves further prospective studies (18–20). However, its use earlier in the oncological management could be beneficial for the patient as more toxic treatment can be omitted. By reducing the impact of systemic treatment, patients could be in an enhanced condition to undergo a major surgical procedure.
Despite an improvement in systemic chemotherapy, the surgical principle regarding resection margins is still the same as described in 1980 (21) with a proximal margin of 5 to 8 cm. Patient’s quality of life has been proven to be better after subtotal compared to total gastrectomy. In addition to the benefits of improved survival and disease control, another advantage of immunotherapy treatment could be organ preservation during surgery, allowing for less radical interventions. Finally, if the positive efficacy of immunotherapy continues to be demonstrated, the next challenge will be to identify complete responders. One option, in the case of a complete radiological response, would be to continue with close radiological monitoring, which could potentially avoid the need for extensive surgery. However, for the moment, there is no infallible tool to assess the response. The immunotherapy-induced inflammatory response can appear as a non-response or even an uptake on a PET scan. Additional studies are needed to identify the optimal approach for identifying these patients and providing them with personalized therapeutic strategies.
ConclusionImmunotherapy represents a promising and rapidly evolving therapeutic approach for gastric cancer. In oligometastatic disease, a therapeutic approach with combined chemo and immunotherapy achieved local and distant control. Immunotherapy allows to improve outcomes while avoiding intensifying chemotherapy. Further research is needed to better select patients with oligometastatic MSS gastric cancer who will benefit from the triplet combination and could therefore be offered surgery with a chance of a long-lasting cure or possibly even more provocatively cure without surgery.
Data availability statementThe original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statementWritten informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributionsHM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FC: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. NC: Resources, Writing – review & editing. GP: Resources, Writing – review & editing. TK: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SM: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
FundingThe author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Open access funding by University of Geneva.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s noteAll claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References1. Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Coxon F, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. (2008) 358:36–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa073149
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Al-Batran S-E, Homann N, Pauligk C, Illerhaus G, Martens UM, Stoehlmacher J, et al. Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgical resection on survival in patients with limited metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: the AIO-FLOT3 trial. JAMA Oncol. (2017) 3:1237. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0515
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
3. Kroese TE, Van Laarhoven HWM, Nilsson M, Lordick F, Guckenberger M, Ruurda JP, et al. Definition of oligometastatic esophagogastric cancer and impact of local oligometastasis-directed treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. (2022) 166:254–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.02.018
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
4. Guckenberger M, Lievens Y, Bouma AB, Collette L, Dekker A, deSouza NM, et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: a European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:e18–28. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30718-1
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
5. Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M, Garrido M, Salman P, Shen L, et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2021) 398:27–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00797-2
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
6. Shitara K, Lordick F, Bang Y-J, Enzinger P, Ilson D, Shah MA, et al. Zolbetuximab plus mFOLFOX6 in patients with CLDN18.2-positive, HER2-negative, untreated, locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (SPOTLIGHT): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2023) 401:1655–68. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00620-7
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
7. Janjigian YY, Kawazoe A, Bai Y, Xu J, Lonardi S, Metges JP, et al. Pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: interim analyses from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-811 randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2023) 402:2197–208. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02033-0
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
8. Ruiz Hispán E, Pedregal M, Cristobal I, García-Foncillas J, Caramés C. Immunotherapy for peritoneal metastases from gastric cancer: rationale, current practice and ongoing trials. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:4649. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204649
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
9. Rice TW, Ishwaran H, Ferguson MK, Blackstone EH, Goldstraw P. Cancer of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: an eighth edition staging primer. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.10.016
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
10. Seymour L, Bogaerts J, Perrone A, Ford R, Schwartz LH, Mandrekar S, et al. iRECIST: guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:e143–52. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30074-8
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
11. Zhou Q, Lan X, Li N, Yuan D, Zhang J. Analysis of prognostic factors and design of prognosis model for patients with stage IV gastric cancer following first-line palliative chemotherapy. CMAR. (2020) 12:10461–8. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S263320
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
12. Harris. J. (2022). “Updated checkMate 649 results show sustain benefit of nivolumab plus chemo for gastric/GEJ cancer”, In ASCO GI cancer symposium.
13. Toyota S, Orita H, Fukuyama Y, Motoyoshi S, Kawanami S, Maeda S, et al. Successful conversion surgery following chylous ascites after nivolumab for advanced gastric cancer. In Vivo. (2020) 34:583–5. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11810
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
14. Toyota Y, Okamoto K, Tanaka N, Colvin HS, Takahashi Y, Inaba T. Conversion surgery of Stage IV gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination after nivolumab. Int Canc Conf J. (2021) 10:280–4. doi: 10.1007/s13691-021-00503-0
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
15. Plummer M, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Forman D, De Martel C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori: Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. (2015) 136:487–90. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28999
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
16. Cho H, Nakamura J, Asaumi Y, Yabusaki H, Sakon M, Takasu N, et al. Long-term survival outcomes of advanced gastric cancer patients who achieved a pathological complete response with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A systematic review of the literature. Ann Surg Oncol. (2015) 22:787–92. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4084-9
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
17. Shitara K, Rha SY, Wyrwicz LS, Oshima T, Karaseva N, Osipov M, et al. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in locally advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-585): an interim analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2024) 25:212–24. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00541-7
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
18. Betof Warner A, Palmer JS, Shoushtari AN, Goldman DA, Panageas KS, Hayes SA, et al. Long-term outcomes and responses to retreatment in patients with melanoma treated with PD-1 blockade. JCO. (2020) 38:1655–63. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01464
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
20. Gauci M-L, Lanoy E, Champiat S, Caramella C, Ammari S, Aspeslagh S, et al. Long-term survival in patients responding to anti–PD-1/PD-L1 therapy and disease outcome upon treatment discontinuation. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:946–56. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0793
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
21. Bozzetti F, Bonfanti G, Bufalino R, Menotti V, Persano S, Andreola S, et al. Adequacy of margins of resection in gastrectomy for cancer. Ann Surg. (1982) 196:685–90. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198212001-00012
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
22. Watanabe H, Fujikawa H, Komori K, Kano K, Takahashi K, Yamada T, et al. Successful conversion surgery for stage IV gastric cancer after nivolumab monotherapy as third-line chemotherapy. Case Rep Gastroenterol. (2021) 15:562–7. doi: 10.1159/000514396
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
23. Hidaka Y, Arigami T, Osako Y, Desaki R, Hamanoue M, Takao S, et al. Conversion surgery for microsatellite instability-high gastric cancer with a complete pathological response to pembrolizumab: a case report. World J Surg Onc. (2022) 20:193. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02661-8
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
24. Matsumoto R, Arigami T, Matsushita D, Okubo K, Tanaka T, Yanagita S, et al. Conversion surgery for stage IV gastric cancer with a complete pathological response to nivolumab: a case report. World J Surg Onc. (2020) 18:179. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01954-0
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
25. Toyota S, Naito H, Motoyoshi S, Nakanishi R, Oki E, Orita H, et al. Extended total gastrectomy after nivolumab for unresectable multivisceral invasive gastric cancer. Surg Case Rep. (2020) 6:298. doi: 10.1186/s40792-020-01040-3
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
26. Kumamoto T, Tomita T, Hojo Y, Nakamura T, Kurahashi Y, Ishida Y, et al. Pathological complete response and successful conversion surgery after nivolumab therapy for stage IV oesophagogastric junction cancer. In Vivo. (2021) 35:2247–51. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12497
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
27. Lin C-P, Sung Y-C, Wong J-U. Immunotherapy improves efficiency of conversion surgery for metastatic gastric cancer: A case report. Asian J Surg. (2020) 43:1039–40. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2020.06.016
留言 (0)