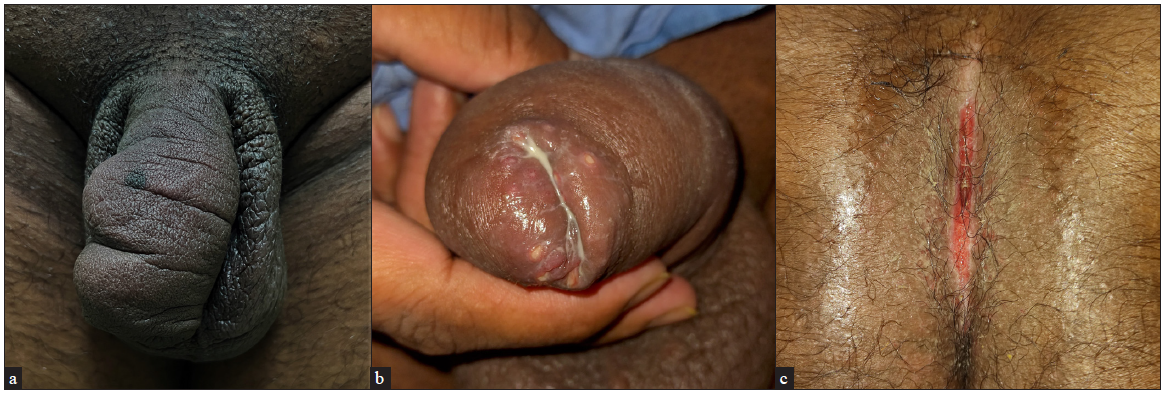
A 31-year-old man with no known comorbidities presented with 6-month-old penile enlargement. Dermatological examination revealed a non-tender, curved, and enlarged penis measuring 5 inches long and 4 inches in circumference [Figure 1a], multiple ulcers (0.5 x 0.5 cm) with sloping edges over the foreskin [Figure 1b], and a linear ulcer over the intergluteal region (8 x 2 cm) [Figure 1c]. Laboratory investigations including Gram and Giemsa-stained smears, and colonoscopy were normal. Fungal culture and GeneXpert for tuberculosis were negative. Ulcer biopsy showed lymphocytic aggregates, Langerhans giant cells, and epithelioid cell granulomas in the dermis, indicative of Crohn’s disease, and the patient was treated with oral prednisolone (40 mg/day) in tapering doses, azathioprine 50 mg twice daily and metronidazole 400 mg thrice daily. After 3-months, the patient exhibited a marked reduction in ulcer size and the size of the penis. Genital swelling with cutaneous Crohn’s disease is uncommon and arises from granulomas obstructing lymph vessels, leading to granulomatous lymphangiopathy that tends to persist and get exacerbated with each flare-up, gradually distorting the genital anatomy.
Export to PPT
留言 (0)