Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) comprising 80%–90% of primary lung malignancies. For patients with stage IV NSCLC, the standard treatment typically involves chemotherapy and palliative radiation therapy. Despite advancements in treatment options, including molecular targeted therapies and immunotherapy, the overall 5-year survival rate for stage IV NSCLC remains dismally low at 4%–6% (David et al., 2017).
Research has underscored the critical role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in tumor growth, progression, and metastasis, primarily by promoting angiogenesis (Apte et al., 2019). Targeting the VEGF signaling pathway has become a cornerstone in the development of anticancer therapies. Bevacizumab, a VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (VEGFR-TKI), effectively neutralizes VEGF, inhibiting the tumor’s blood supply and thereby showing significant clinical efficacy across various cancers, including breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and NSCLC (Al Kawas et al., 2022; Ahluwalia et al., 2014; Cardones and Banez, 2006). Similarly, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted therapies, such as cetuximab, have improved the prognosis for lung cancer patients (Le et al., 2021).
Despite the therapeutic benefits of antiangiogenic agents, these drugs are associated with increased risks of arterial thrombotic events and hemorrhagic complications. While hypertension represents another frequent adverse event, it can typically be managed with conventional antihypertensive medications (Krupitskaya and Wakelee, 2009). However, the precise magnitude of cardiovascular risks, particularly hypertension and thrombotic events, associated with antiangiogenic targeted therapies in NSCLC remains inadequately characterized (Castel et al., 2011).
Therefore, a comprehensive meta-analysis of contemporary randomized controlled trials could provide more robust evidence regarding the cardiovascular safety profile of antiangiogenic therapies in NSCLC, with particular emphasis on hypertensive and thrombotic complications.
MethodsLiterature searchA comprehensive search was conducted using the following terms: (“EGFR-TKI” OR “VEGF-TKI” OR “Gefitinib” OR “Erlotinib” OR “Icotinib” OR “Afatinib” OR “Dacomitinib” OR “Osimertinib” OR “ALK inhibitors” OR “Brigatinib” OR “Lorlatinib” OR “Alectinib”) AND (“NSCLC” OR “non-small-cell lung carcinoma” OR “non-small cell lung cancer”). Our search covered published articles from electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library, up to 1 June 2024. Additionally, we manually searched abstracts from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the World Congress on Lung Cancer to identify unpublished studies and ongoing clinical trials. Only studies published in English were included, and we also hand-searched the references of the included studies.
Inclusion criteriaStudies were eligible if they compared tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) combined with chemotherapy or other treatments versus TKIs alone. The criteria for inclusion were (David et al., 2017): prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing TKIs alone or in combination with chemotherapy in NSCLC patients (Apte et al., 2019); reported data on the number of patients with hypertension or thrombotic adverse reactions, as well as the total number of patients with adverse events; and (Al Kawas et al., 2022) original articles published in English. Exclusion criteria included (David et al., 2017): single-arm clinical trials (Apte et al., 2019); case reports or review articles; and (Al Kawas et al., 2022) clinical trials with fewer than 10 participants.
Data extractionData extracted from each study included the year of publication, first author, trial name, patient demographics (age, sex), ECOG score, disease status, smoking history, type of TKIs used, incidence of hypertension and thrombotic events, total number of subjects, and follow-up duration. Data extraction, study design, and results were reviewed by two independent reviewers. Disagreements were resolved through discussion, and if consensus was not reached, a third independent reviewer was consulted. Data were standardized according to pre-specified criteria to ensure consistency across studies. Data extraction was performed independently by two reviewers. In cases of discrepancies between reviewers, a third reviewer was consulted, and a consensus was reached through discussion. When necessary, we contacted the original authors for clarification or additional data. This process ensured the accuracy and completeness of the extracted data.
Risk of bias assessmentTwo researchers independently assessed the risk of bias using the Cochrane Handbook tool, evaluating the following domains: (David et al., 2017): random sequence generation, (Apte et al., 2019), allocation concealment, (Al Kawas et al., 2022), blinding of participants and personnel, (Ahluwalia et al., 2014), completeness of outcome data (Cardones and Banez, 2006), selective reporting, and (Le et al., 2021) other potential sources of bias. Trials were categorized into three levels: high risk, low risk, and unclear risk (Higgins et al., 2011).
Data analysisRandomized controlled trials (RCTs) conducted across various institutions frequently yield heterogeneous efficacy outcomes, challenging the establishment of definitive therapeutic hierarchies. Network meta-analysis emerges as a valuable methodological approach to facilitate comprehensive comparisons among diverse therapeutic agents evaluated in different RCTs. In this systematic review and network meta-analysis, we sought to evaluate and compare the cardiovascular safety profiles of various treatment strategies, specifically focusing on hypertensive and thrombotic risks in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma. The surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) probability was employed to establish a hierarchical ranking of therapeutic strategies based on their cardiovascular safety profiles (Sonbol et al., 2020). Statistical analysis was performed using R (version 4.2.1) with the gemtc and rjags packages. We used odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for dichotomous adverse reaction data. Network meta-analysis (NMA) and Bayesian aggregation were conducted using Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulations (Moher et al., 2015). Funnel plots, generated with Stata (version 15.0), assessed potential bias in network comparisons (Salanti et al., 2011). Stata also produced network diagrams depicting hypertension occurrences as an adverse event. These diagrams visually represent evidence, with nodes indicating different interventions and connecting lines showing direct comparisons. The size of each node and line width are proportional to the number of cases (Chaimani et al., 2013). The treatment effect was summarized using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA), where a higher SUCRA value indicates a better treatment effect (Daly et al., 2019). To assess the robustness of our findings, we conducted sensitivity analyses by excluding studies with high risk of bias. Additionally, we performed subgroup analyses based on patient characteristics and treatment duration to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. These analyses helped to evaluate the consistency of our results across different study conditions and patient populations.
ResultsStudy selectionFollowing an extensive search, a total of 30 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included, involving 11,375 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Eleven vascular-targeted drugs were compared, focusing primarily on adverse events such as hypertension and thrombotic events (venous and arterial thrombosis). Figure 1 illustrates the search process: initially, 1,487 articles containing the search terms were identified. After removing duplicates, 86 articles were selected for full-text review based on their titles and abstracts. Ultimately, 30 RCTs were chosen based on their randomization methodology and the relevance of their outcome measures (Table 1) (Nakagawa et al., 2019; Han et al., 2018; Garon et al., 2014; Akamatsu et al., 2021; Ramlau et al., 2012; Ninomiya et al., 2023; Piccirillo et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2021; Kato et al., 2018; Besse et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2018; Spigel et al., 2018; Cortot et al., 2020; Wakelee et al., 2017; Tiseo et al., 2017; Hanna et al., 2016; Karayama et al., 2016; Neal et al., 2016; Baggstrom et al., 2017; O'Brien et al., 2015; Pujol et al., 2015; Doebele et al., 2015; Twelves et al., 2014; Natale et al., 2011; Paz-Ares et al., 2012; Johnson et al., 2013; Herbst et al., 2011; Spigel et al., 2011; Heymach et al., 2008).
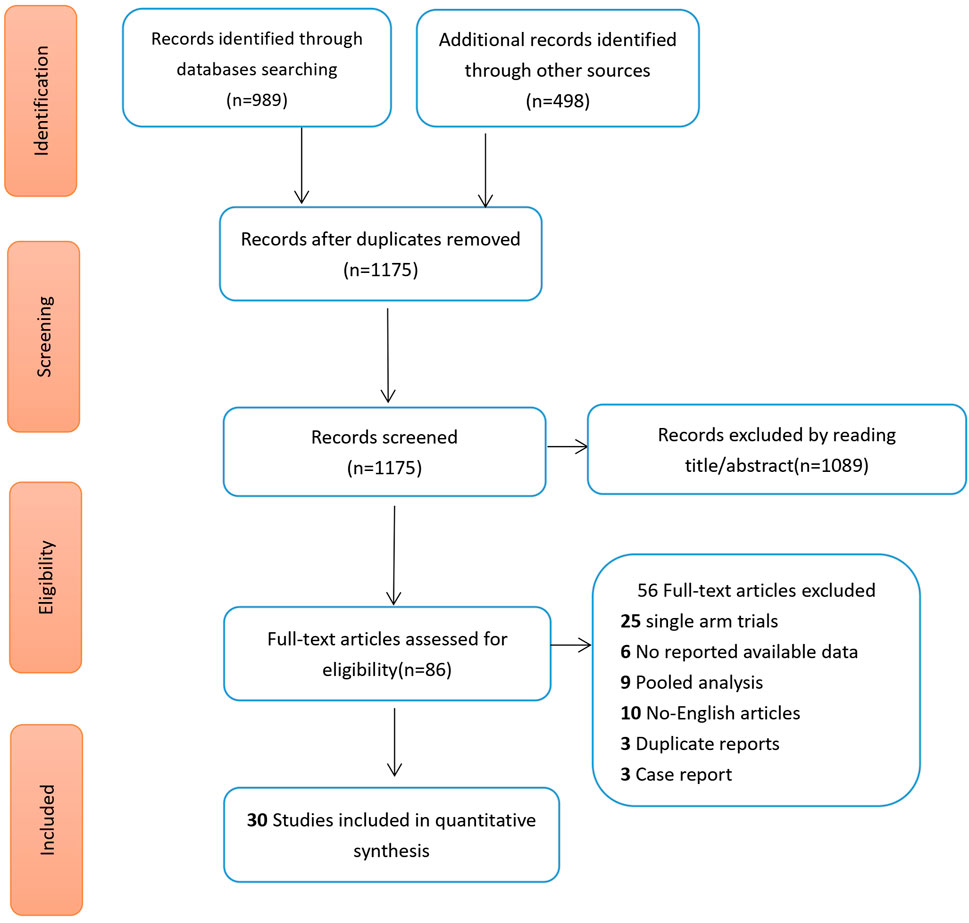
Figure 1. Literature screening flow chart.
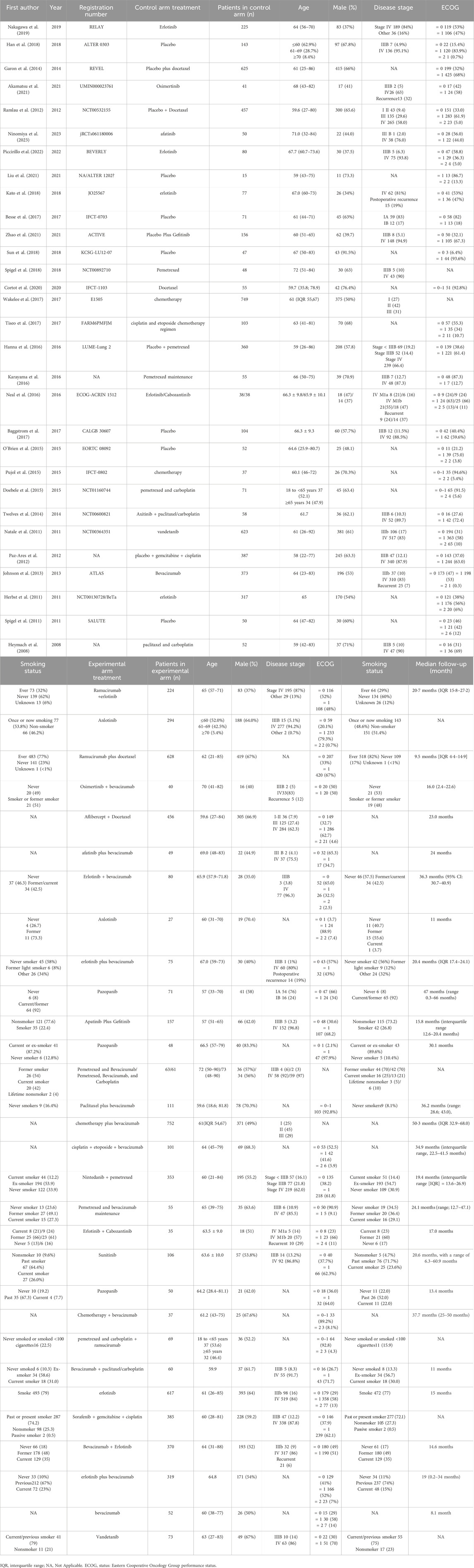
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of included studies.
The drugs analyzed in this meta-analysis include Aflibercept, Anlotinib, Axitinib, Bevacizumab, Cabozantinib, Erlotinib, Pazopanib, Ramucirumab, Sorafenib, Sunitinib, and Vandetanib. Most patients had a history of smoking, and the control groups were predominantly placebo.
Bias risk assessmentBias risk was evaluated using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Most studies clearly described random sequence generation, had no incomplete data, and showed no selective reporting, thus being assessed as having a low risk of bias. Two studies exhibited incomplete outcome data and were categorized as having a high risk of bias; one also displayed selective reporting. Overall, the quality of the included RCTs was deemed high (Supplementary Figure 1).
Network meta-analysisSeventeen treatment regimens were analyzed for the risk of hypertension during vascular-targeted drug therapy (Figure 2). Erlotinib exhibited the lowest risk of hypertension, with a surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) of 91.1%. Anlotinib had the highest risk of hypertension (SUCRA = 11.5%), significantly greater than that associated with Erlotinib (HR: 53.79, 95% CI: 1.62–1600.19). Chemotherapy was the next highest in risk after Erlotinib (HR: 1.24, 95% CI: 0.07–17.59, SUCRA = 88.8%). Sorafenib combined with chemotherapy ranked third, with a risk ratio of 0.31 compared to Erlotinib (95% CI: 0.01–8.62, SUCRA = 67.5%). Axitinib combined with chemotherapy had a higher risk of hypertension compared to chemotherapy alone (HR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.28–60.97). Cabozantinib had a significantly higher risk of hypertension compared to Erlotinib (HR: 8.02, 95% CI: 1.19–61.83) (Figure 3). The cumulative ranking probability graph in Figure 4 shows that treatments with higher SUCRA values have a lower probability of inducing hypertension, with Erlotinib, chemotherapy, and Sorafenib combined with chemotherapy being the top three treatments with the lowest hypertension risk.
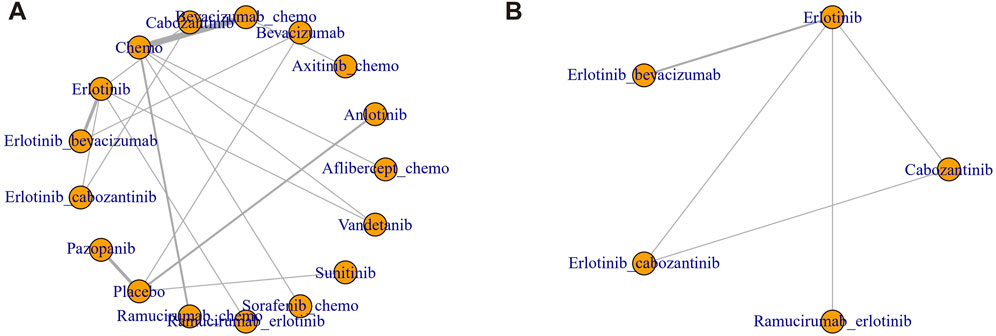
Figure 2. Network diagram of RCT. (A) Hypertension (B) Thrombosis. Each node represents one treatment. The size of the node is proportional to the number of participants randomized to that treatment. The edges represent direct comparisons. The width of the edge is proportional to the number of trials.
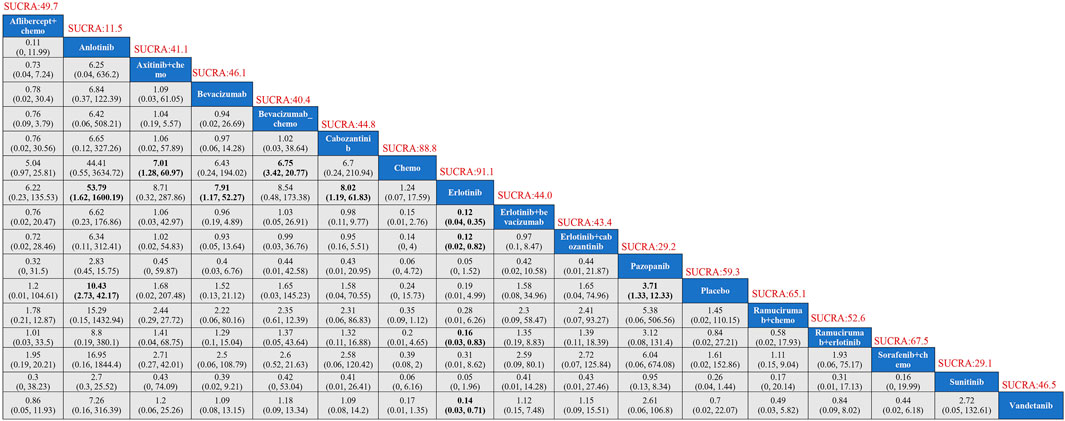
Figure 3. Results of TKIs compared with adverse reactions of hypertension. SUCRA, Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve.
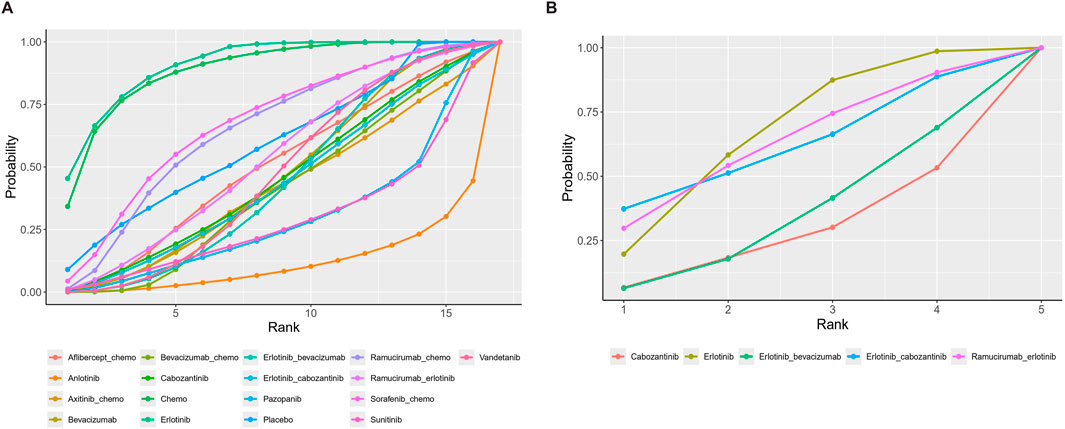
Figure 4. Cumulative ranking probability diagram. (A) Hypertension (B) Thrombosis. Each curve represents a treatment. The larger the area under the curve, the greater the probability of being the best treatment.
In terms of adverse thrombotic outcomes, four RCTs were analyzed, covering five treatment regimens. Erlotinib showed the lowest risk of thrombosis, with a SUCRA of 66.0%. Ramucirumab combined with Erlotinib had the second lowest risk (HR: 0.99, 95% CI: 0.26–3.74, SUCRA = 62.1%). Erlotinib combined with Cabozantinib ranked third (SUCRA = 61.3%). Cabozantinib had the highest risk of thrombosis, with a ratio of 2.27 compared to Erlotinib (95% CI: 0.31–22.89, SUCRA = 26.9%) (Figure 5).
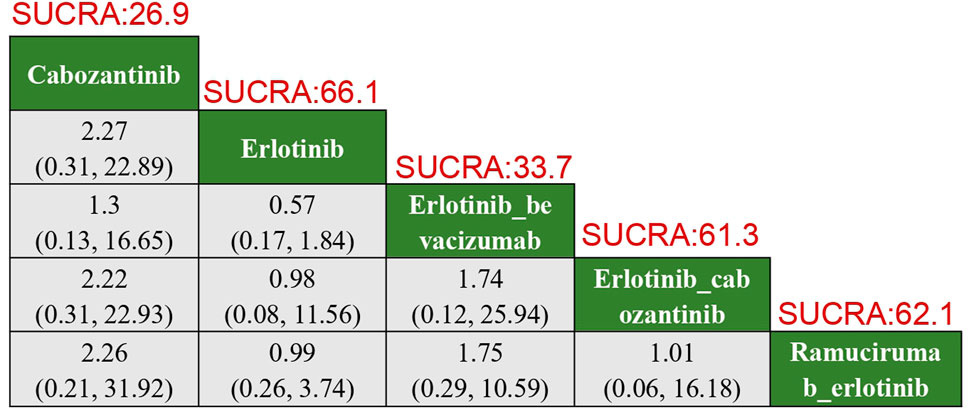
Figure 5. Results of TKIs compared with adverse reactions of thrombosis. SUCRA, Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve.
Heterogeneity and sensitivity analysesWe observed moderate heterogeneity in the hypertension network (I2 = 45%, p = 0.03) and low heterogeneity in the thrombosis network (I2 = 20%, p = 0.25). Sensitivity analyses excluding high-risk-of-bias studies did not significantly alter our main findings, confirming the robustness of our results. Subgroup analyses revealed that EGFR mutation status and treatment duration did not significantly impact the relative safety rankings of the TKIs.
Publication biasFunnel plots for both hypertension and thrombotic outcomes appeared roughly symmetrical (Figure 6), indicating no significant publication bias. This suggests that the results are reliable and not significantly influenced by the selective reporting of outcomes.
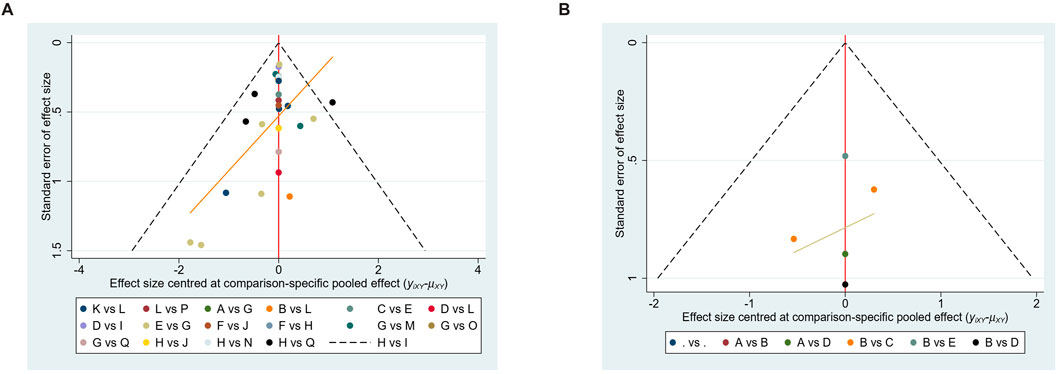
Figure 6. Funnel plot of network meta-analysis. (A) Hypertension (B) Thrombosis.
DiscussionKey findingsThis study provides a comprehensive comparison of the cardiovascular safety profiles of various Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) used in the treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Our network meta-analysis revealed that Erlotinib is associated with the lowest risks of both hypertension and thrombotic events among the evaluated treatments. In contrast, Anlotinib and Cabozantinib were associated with significantly higher risks of these adverse events.
To sustain their high proliferation rate, cancer cells require tumors to rapidly develop new vascular networks. However, the vasculature within tumors is often underdeveloped, which impairs its functionality (Carmeliet and Jain, 2011a). Abnormalities in tumor vascular development are partially due to irregular levels of growth factors secreted by tumor and stromal cells, with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) playing a pivotal role (Carmeliet and Jain, 2011b). The poor functionality of tumor vasculature profoundly affects the tumor microenvironment, leading to hypoxia, reduced immune cell infiltration and activity, and an increased risk of metastatic dissemination. It has been proposed that antiangiogenic therapies could potentially correct these structural and functional defects in tumor vasculature (Carmeliet and Jain, 2011b; Viallard and Larrivée, 2017).
VEGF primarily interacts with two main receptors: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1), also known as fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (Flt-1), and VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2). VEGFR-1 is the exclusive receptor for other VEGF family members (Papetti and Herman, 2002; Ceci et al., 2020) and is essential for hematopoiesis, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activation, and the migration of monocytes and other immune cells into the tumor microenvironment (TME) (Ferrara et al., 2003). In contrast, VEGFR-2 is critical for angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. VEGF binding to VEGFR-2 activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) via the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) pathway (Zachary, 2003). This signaling pathway results in the release of vasodilators such as nitric oxide (NO), which increases vascular permeability (Lal et al., 2001). Upregulation of VEGF has been documented in various benign and malignant tumors, including melanoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, and ovarian cancer. In the tumor environment, the activation of the VEGF/VEGFR signaling axis ultimately leads to increased vascular density, invasiveness, immune evasion, and, in some cases, enhanced metastatic capacity (Jinnin et al., 2008).
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a member of the ERBB family of cell surface receptor tyrosine kinases, is implicated in cancer progression. The binding of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to EGFR triggers phosphorylation of the receptor and other ERBB family members, leading to cell proliferation. EGFR signal transduction also contributes to tumor cell proliferation, resistance to apoptosis, angiogenesis, and metastasis (Chong and Jänne, 2013).
Recent molecular and clinical investigations have revealed intricate interactions between hypertension and VEGF signaling pathways. Specifically, hypertension-induced microvascular disruption may trigger elevated plasma VEGF expression, as evidenced by increased VEGF levels observed in patients with essential hypertension (EH) (Yang et al., 2017). This relationship appears bidirectional, with epidemiological data demonstrating significant associations between blood pressure dynamics and cancer risk (Radišauskas et al., 2016; Schairer et al., 2017).
In the context of cancer-associated complications, venous thromboembolism (VTE) emerges as a principal cause of mortality. The administration of anti-VEGF therapies has been correlated with increased VTE incidence (Posch et al., 2016), though the precise molecular mechanisms underlying this association remain to be fully elucidated. Mechanistic studies have revealed that bevacizumab administration significantly enhances plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) expression across multiple compartments, including tumor tissue, plasma, and thrombi. This observation has been further validated in mouse human lung cancer xenograft models, where bevacizumab-induced PAI-1 upregulation promotes VTE formation. Clinical validation through randomized controlled trials has consistently identified a characteristic adverse event profile associated with bevacizumab, predominantly comprising hypertension, proteinuria, hemorrhagic complications, and thrombotic events (Sandler et al., 2004).
Notably, geriatric populations demonstrate heightened susceptibility to thromboembolic and hypertensive complications during anti-angiogenic therapy (Boehm et al., 2010). This vulnerability becomes particularly relevant in the context of long-term adjuvant or maintenance treatment regimens, where the therapeutic benefits of anti-angiogenic agents must be carefully balanced against their cardiovascular risk profile.
Our analysis supports the implementation of a cardiovascular risk-stratified approach to therapeutic selection. For patients with elevated cardiovascular risk profiles, we advocate for preferential utilization of agents demonstrating superior cardiovascular safety characteristics. This strategy holds the potential to significantly reduce the incidence of thrombotic and hypertensive complications while minimizing mortality risk. Furthermore, our findings provide an evidence-based framework to guide clinical decision-making and inform the development of cardiovascular risk-adapted guidelines for targeted therapy optimization.
In this study, we evaluated these anti-angiogenic drugs to compare their risks of hypertension and thrombosis and identified the drug with the fewest side effects. Clinicians can use this information to select drugs with fewer adverse effects based on the patient’s underlying conditions, thereby improving the management of targeted therapy toxicity.
Our analysis indicates that Erlotinib has the lowest risk of both hypertension and thrombosis among the drugs studied. This conclusion was reached through constructing an indirect drug comparison network, providing highly credible evidence. Chemotherapy ranks second in terms of lowest hypertension risk. Anlotinib is associated with the highest risk of hypertension, suggesting that clinicians should carefully assess patients' baseline blood pressure and cardiovascular health before prescribing this drug. Additionally, Cabozantinib presents the highest risk of thrombosis, indicating that clinicians need to evaluate the risk of thrombosis in multiple organs and consider the prudent use of anticoagulants when administering this drug.
Clinical implicationsThe clinical implications of this study are significant. In treating NSCLC, especially in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, Erlotinib should be considered as a first-line option due to its lower risk of hypertension and thrombotic events. Clinicians should exercise caution when prescribing Anlotinib and Cabozantinib, particularly in patients at high risk for cardiovascular complications. These findings underscore the importance of individualized treatment plans that weigh the benefits of tumor control against the risks of serious side effects.
Additionally, the results of this study suggest that more rigorous cardiovascular monitoring may be warranted for patients receiving high-risk TKIs, such as Anlotinib and Cabozantinib. This could involve regular blood pressure checks, thrombosis risk assessments, and the use of prophylactic measures to mitigate these risks.
Strengths and limitationsThis study has several strengths, including the use of a Bayesian network meta-analysis to integrate data from multiple studies, providing a robust comparative analysis of TKI safety profiles. The large sample size and inclusion of diverse treatment regimens enhance the generalizability of our findings.
However, several limitations of this study and their potential impacts on our findings warrant careful consideration. First, significant heterogeneity was observed across included studies, mainly due to variations in study design, patient characteristics, and outcome definitions. While our random-effects model and subgroup analyses partially addressed this issue, the heterogeneity might have led to either over- or underestimation of treatment effects, particularly in smaller subgroups.
The language restriction to English publications might have resulted in missing valuable data, particularly from Asian countries where TKIs are extensively used. This potential language bias could be especially relevant for newer TKIs that are more commonly studied in non-English speaking regions, possibly affecting our effect estimates.
The varying quality of included studies and limited long-term cardiovascular outcome data represent additional limitations. Although we conducted quality assessment and sensitivity analyses, lower-quality studies might have influenced our estimates, particularly in comparisons with fewer studies. This impact could affect our ability to fully capture the cardiovascular safety profiles of different TKIs, especially for rare adverse events.
Further prospective investigations are warranted to elucidate the cardiovascular safety profiles of combination regimens incorporating targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, with particular emphasis on risk stratification and predictive biomarker identification.
ConclusionIn this study, we conducted a network meta-analysis to compare the cardiovascular safety profiles of various Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) used in the treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Our findings indicate that Erlotinib is associated with the lowest risk of both hypertension and thrombotic events, making it a preferred treatment option, especially for patients with pre-existing cardiovascular risk factors. Conversely, Anlotinib and Cabozantinib were found to carry significantly higher risks of these adverse events, necessitating cautious use and careful monitoring in clinical practice.
The results of this study provide valuable insights for clinicians in selecting appropriate TKIs, balancing the efficacy of cancer treatment with the potential for serious cardiovascular complications. These findings also underscore the importance of individualized treatment strategies, particularly in patients with a higher risk of hypertension or thrombotic disorders.
Data availability statementThe original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributionsMT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Conceptualization, Validation. CP: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. ZW: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing–original draft, Data curation, Project administration, Resources. CJ: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
FundingThe author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s noteAll claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary materialThe Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1491990/full#supplementary-material
ReferencesAhluwalia, A., Jones, M. K., Matysiak-Budnik, T., and Tarnawski, A. S. (2014). VEGF and colon cancer growth beyond angiogenesis: does VEGF directly mediate colon cancer growth via a non-angiogenic mechanism? Curr. Pharm. Des. 20 (7), 1041–1044. doi:10.2174/1381612819999131218175905
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Akamatsu, H., Toi, Y., Hayashi, H., Fujimoto, D., Tachihara, M., Furuya, N., et al. (2021). Efficacy of osimertinib plus bevacizumab vs osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M-mutated non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: west Japan oncology group 8715L phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 7 (3), 386–394. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6758
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Al Kawas, H., Saaid, I., Jank, P., Westhoff, C. C., Denkert, C., Pross, T., et al. (2022). How VEGF-A and its splice variants affect breast cancer development - clinical implications. Cell Oncol. (Dordr) 45 (2), 227–239. doi:10.1007/s13402-022-00665-w
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Baggstrom, M. Q., Socinski, M. A., Wang, X. F., Gu, L., Stinchcombe, T. E., Edelman, M. J., et al. (2017). Maintenance Sunitinib following initial platinum-based combination chemotherapy in advanced-stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study-CALGB 30607 (Alliance). J. Thorac. Oncol. 12 (5), 843–849. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2017.01.022
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Besse, B., Mazières, J., Ribassin-Majed, L., Barlesi, F., Bennouna, J., Gervais, R., et al. (2017). Pazopanib or placebo in completely resected stage I NSCLC patients: results of the phase II IFCT-0703 trial. Ann. Oncol. 28 (5), 1078–1083. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx070
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Boehm, S., Rothermundt, C., Hess, D., and Joerger, M. (2010). Antiangiogenic drugs in oncology: a focus on drug safety and the elderly - a mini-review. Gerontology 56 (3), 303–309. doi:10.1159/000262450
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Carmeliet, P., and Jain, R. K. (2011a). Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10 (6), 417–427. doi:10.1038/nrd3455
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Castel, M., Pathak, A., Despas, F., and Mazières, J. (2011). Adverse effects of new biological therapies for non-small-cell bronchial cancer. Presse Med. 40 (4 Pt 1), 415–419. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.02.004
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ceci, C., Atzori, M. G., Lacal, P. M., and Graziani, G. (2020). Role of VEGFs/VEGFR-1 signaling and its inhibition in modulating tumor invasion: experimental evidence in different metastatic cancer models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (4), 1388. doi:10.3390/ijms21041388
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Chaimani, A., Higgins, J. P., Mavridis, D., Spyridonos, P., and Salanti, G. (2013). Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One 8 (10), e76654. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076654
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cortot, A. B., Audigier-Valette, C., Molinier, O., Le Moulec, S., Barlesi, F., Zalcman, G., et al. (2020). Weekly paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus docetaxel as second- or third-line treatment in advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: results of the IFCT-1103 ULTIMATE study. Eur. J. Cancer 131, 27–36. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2020.02.022
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Daly, C. H., Neupane, B., Beyene, J., Thabane, L., Straus, S. E., and Hamid, J. S. (2019). Empirical evaluation of SUCRA-based treatment ranks in network meta-analysis: quantifying robustness using Cohen's kappa. BMJ Open 9 (9), e024625. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024625
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
David, E. A., Clark, J. M., Cooke, D. T., Melnikow, J., Kelly, K., and Canter, R. J. (2017). The role of thoracic surgery in the therapeutic management of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 12 (11), 1636–1645. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2017.08.008
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Doebele, R. C., Spigel, D., Tehfe, M., Thomas, S., Reck, M., Verma, S., et al. (2015). Phase 2, randomized, open-label study of ramucirumab in combination with first-line pemetrexed and platinum chemotherapy in patients with nonsquamous, advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 121 (6), 883–892. doi:10.1002/cncr.29132
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Garon, E. B., Ciuleanu, T. E., Arrieta, O., Prabhash, K., Syrigos, K. N., Goksel, T., et al. (2014). Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 384 (9944), 665–673. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60845-X
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Han, B., Li, K., Wang, Q., Zhang, L., Shi, J., Wang, Z., et al. (2018). Effect of anlotinib as a third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the ALTER 0303 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 4 (11), 1569–1575. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3039
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Hanna, N. H., Kaiser, R., Sullivan, R. N., Aren, O. R., Ahn, M. J., Tiangco, B., et al. (2016). Nintedanib plus pemetrexed versus placebo plus pemetrexed in patients with relapsed or refractory, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 2): a randomized, double-blind, phase III trial. Lung Cancer 102, 65–73. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.10.011
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Herbst, R. S., Ansari, R., Bustin, F., Flynn, P., Hart, L., Otterson, G. A., et al. (2011). Efficacy of bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of standard first-line chemotherapy (BeTa): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 377 (9780), 1846–1854. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60545-X
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Heymach, J. V., Paz-Ares, L., De Braud, F., Sebastian, M., Stewart, D. J., Eberhardt, W. E., et al. (2008). Randomized phase II study of vandetanib alone or with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (33), 5407–5415. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.17.3138
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Higgins, J. P., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 343, d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Jinnin, M., Medici, D., Park, L., Limaye, N., Liu, Y., Boscolo, E., et al. (2008). Suppressed NFAT-dependent VEGFR1 expression and constitutive VEGFR2 signaling in infantile hemangioma. Nat. Med. 14 (11), 1236–1246. doi:10.1038/nm.1877
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Johnson, B. E., Kabbinavar, F., Fehrenbacher, L., Hainsworth, J., Kasubhai, S., Kressel, B., et al. (2013). ATLAS: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIIB trial comparing bevacizumab therapy with or without erlotinib, after completion of chemotherapy, with bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 31 (31), 3926–3934. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.47.3983
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Karayama, M., Inui, N., Fujisawa, T., Enomoto, N., Nakamura, Y., Kuroishi, S., et al. (2016). Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed and bevacizumab versus pemetrexed monotherapy after induction therapy with carboplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 58, 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.01.013
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Kato, T., Seto, T., Nishio, M., Goto, K., Yamamoto, N., Okamoto, I., et al. (2018). Erlotinib plus bevacizumab phase ll study in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (JO25567): updated safety results. Drug Saf. 41 (2), 229–237. doi:10.1007/s40264-017-0596-0
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Krupitskaya, Y., and Wakelee, H. A. (2009). Ramucirumab, a fully human mAb to the transmembrane signaling tyrosine kinase VEGFR-2 for the potential treatment of cancer. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 10 (6), 597–605.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Lal, B. K., Varma, S., Pappas, P. J., Hobson, R. W., and Durán, W. N. (2001). VEGF increases permeability of the endothelial cell monolayer by activation of PKB/akt, endothelial nitric-oxide synthase, and MAP kinase pathways. Microvasc. Res. 62 (3), 252–262. doi:10.1006/mvre.2001.2338
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Le, X., Nilsson, M., Goldman, J., Reck, M., Nakagawa, K., Kato, T., et al. (2021). Dual EGFR-VEGF pathway inhibition: a promising strategy for patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 16 (2), 205–215. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.10.006
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Liu, Y., Cheng, Y., Wang, Q., Li, K., Shi, J., Wu, L., et al. (2021). Effectiveness of anlotinib in patients with small-cell lung cancer and pleural effusion: subgroup analysis from a randomized, multicenter, phase II study. Thorac. Cancer 12 (22), 3039–3045. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.14176
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., et al. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 4 (1), 1. doi:10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Nakagawa, K., Garon, E. B., Seto, T., Nishio, M., Ponce Aix, S., Paz-Ares, L., et al. (2019). Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20 (12), 1655–1669. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30634-5
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Natale, R. B., Thongprasert, S., Greco, F. A., Thomas, M., Tsai, C. M., Sunpaweravong, P., et al. (2011). Phase III trial of vandetanib compared with erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 29 (8), 1059–1066. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.5981
留言 (0)