With the growing need for industrial and service robots, which need to perform a range of grasping and complex manipulation tasks, the field of robot manipulation has attracted global attention from researchers (Liu et al., 2023a; Fang et al., 2023). The enhancement of a robot's overall operational capability relies on the attainment of stable and dependable grasping capabilities. Consequently, the assessment of grasping outcomes represents a pivotal domain for investigation.
The extensive study of existing computer vision achievements has facilitated the thorough examination of vision-based environmental perception technology. Researchers have achieved a significant number of exemplary works in the areas of slip detection (Mahler et al., 2019; Sundermeyer et al., 2021), material recognition (Liu et al., 2023a; Holm et al., 2020), and so on (Piacenza et al., 2022). In scenes driven by visual perception, computer vision can only acquire a limited amount of information from a single viewpoint. This information mainly includes a complete scene description, which is often affected by exposure and focus problems caused by changes in light and materials. With these limitations, vision-only methods still perform insufficiently in unstructured scenes. In situations where lighting conditions are far from ideal (Yi et al., 2022), unexpected obstructions happen (Phelan et al., 2017), or complex interactions with the target are needed (Wang et al., 2021), indirect measurements like vision are likely to be inadequate, which often lead to task failures.
In contrast, haptic sensing is receiving increasing research attention due to its direct access to interacting information. Vision could provide a comprehensive overview, which acquires generalized sensing, while haptic offers detailed records of contact, haptic acquires detailed and localized information through direct contact, combining the benefits of vision and haptic for detection is a more competitive option. The integration of visual and haptic modalities has been demonstrated to enhance the perception of robots, with related methods exhibiting superior performance in material classification (Xiong et al., 2023b; Yang et al., 2022; Xiong et al., 2023a), object recognition (Xiong et al., 2023c; Tatiya and Sinapov, 2019) and environment exploration (Liao et al., 2024; Luo et al., 2017).
One advantage of utilizing multiple modalities is that the remaining modalities can compensate for and provide information from disparate perspectives, even when some of the other modalities appear to be occluded or noisy. In modal pairing and perceptual tasks, when disparate inputs are encountered, humans employ “causal inference” to ascertain whether the two sensory signals originate from a single source (Ernst and Banks, 2002; Landy et al., 2011). This enables them to select the optimal means of integrating the acquired information. This crucial mechanism in humans has not yet been extensively explored with regard to its potential applications in the domain of visual and haptic fusion.
Concurrently, the data within the unimodal state is frequently heterogeneous. The most common approach is to extract features according to temporal and spatial dimensions, respectively. With regard to space, objects exhibit diverse shapes and materials, which can give rise to notable variations in friction when grasping them in different positions. In the context of time, despite a grasping action being relatively brief, it is a continuous process. The continuity and stability of this process also exert a significant influence on the outcome of the grasping action.
In this paper, we focus on how to learn effective Visual-Haptic features in the task of slip detection. In our approach, we utilize data enhancement and preprocessing techniques to process sequential data comprising visual and haptic images. Next, we extracted temporal and spatial features using self-attention (Vaswani et al., 2017) and Squeeze-and-Excitation attention (Hu et al., 2018), respectively. In the fusion stage, two-step fusion is employed to achieve the integration of visual and haptic features, as well as the fusion of temporal and spatial features, respectively. In each step, gate units are employed to regulate the input signal. After that, fusion feature is sent to a MLP to get the prediction. We validate the performance of the model and compare it with several state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on slip datasets (Li et al., 2018). The experiment results demonstrate that our method exhibits superior performance compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. The visualization of the attention mechanism illustrates that our method is capable of effectively extracting both temporal and spatial feature from visual and tactile information.
The main contributions of the work in this paper can be described as follows:
1. We propose a feature extraction method that combines two attention mechanisms to extract features in spatial and temporal dimensions, improving the model's ability to perceive spatial-temporal feature;
2. Balance and causal inference mechanisms in neurological research are considered in our method, improving the model's ability to adapt to multimodal inputs;
3. A two-step fusion model was employed to enhance the information fusion capability of the method;
4. The experiment results show that our method is superior to other three SOTA methods in terms of the accuracy with 5%;
5. Analysis of the visualization suggest that the Vahagn model can capture position-related features and time-related features that are useful for task.
2 Realated work 2.1 Haptic sensorsA number of haptic sensors have been developed in recent years. Some sensors are designed to capture forces and moments on contact, or data from other sensors such as temperature and vibration directly. BioTac (Wettels et al., 2014) is an excellent example. The sensor has a rigid core and several types of sensors inside, surrounded by a deformable housing. The high-resolution haptic sensors represented by GelSight (Dong et al., 2017) are quite different, as the surface of the sensor is an elastic gel that changes according to the shape of the object in contact. A normal tiny camera is placed under the elastomer, and in order to make the shape changes observed more visible, three LEDs are placed in different directions around the gel. Thanks to the unique design, GelSight could detects three different types of information: movement of the object texture, change of the contact area, and stretching of the sensor surface. An important advantage of using cameras to capture signals is that the data is standardized as images, which allows researchers to use well-established computer vision algorithms to extract the features.
2.2 Slip detectionSlip detection is very important for robotic manipulation. In recent years, various methods have been employed. Liao et al. (2024) attempted to use graph networks to evaluate grasping stability on pressure data obtained from a novel PT-TIP sensor. Liu et al. (2023a) used a triple network to judge the grasping result with haptic images, and they found that haptic can still achieve similar results under different grasping postures. The results demonstrate the importance of combining visual and haptic information for perceiving joint tasks. Li et al. (2018) proposed a DNN based on CNN and LSTM. The model uses pre-trained CNN to extract features from images of vision and haptic. Multiple sets of spliced features are then sent into LSTM (Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997) for fusion, and the grasping stability results are outputted. The experiments result proved the effectiveness of the joint perception of visual and haptic (Wang et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2023; Girbes-Juan et al., 2020). Inspired by the success of attention mechanisms on dependencies between images (Zhao et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2023), words (Yang et al., 2021; Munkhdalai et al., 2024), and audios (Ryan et al., 2023), (Cui et al., 2020) introduced the attention mechanism to the feature fusion process. They proposed the VTFSA model, which uses the self-attention mechanism on the spliced features after extracting the input visual and haptic separately. The comparison results proved its effectiveness. However, this processing does not effectively distinguish the importance of the information from the two sources and underutilizes the information from the time series. Han et al. (2023) introduced a Transformer-based robotic grasping framework for rigid gripper robots, leveraging haptic and visual information to ensure secure object grasping. Evaluation demonstrated that Transformer models exhibit higher grasping accuracy and computational efficiency compared to traditional CNN-LSTM models. Although the methods proposed by these works can reach a decent performance on slip detection, none of them have taken into account the problem of adaptation between visual-haptic information and the spatial-temporal feature of the grasping process in a unified way. Therefore, we proposed a new method involves performing temporal and spatial feature extraction on input visual and haptic sequences in parallel, and get the feature of multi-source and spatial-temporal information with a two-step fusion.
2.3 Attention mechanismsIn recent years, the attention has been widely used in various tasks, including natural language processing (Yang et al., 2021; Munkhdalai et al., 2024), image feature recognition (Zhao et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2023), and so on (Yak et al., 2023; McKinzie et al., 2024). The self-attention (SA) (Vaswani et al., 2017) has been formalized to better capture the interrelationships between input words, resulting in a significant improvement in machine translation performance. To better account for the varying importance of individual channels in image features, Hu et al. (2018) proposed the Squeeze-and-Excitation attention (SEA) mechanism. This mechanism allows the network to focus on specific feature channels by assigning different weights of importance to them or by suppressing channel features that are not useful enough. Here, we adopt ideas from SA mechanism and SEA mechanism into the spatial and temporal feature extraction modules, respectively, so that key spatial locations can be extracted and interrelationships between time series can be recognized.
3 MethodsIn Section 3.1, we introduce the dataset used here in detail. In Section 3.2, we provide a complete description of Vahagn.
3.1 Slip datasetLi et al. (2018) created a multimodal dataset that comprises visual and haptic data. They collected 1102 sets of interaction data from 84 different common objects. The collection experiment employed a UR5 robotic arm equipped with a WSG-50 parallel gripper. To obtain haptic data, a GelSight sensor was added to one side of the gripper. In experiment, a camera was added to the middle of the gripper jaws to capture visual observation. During each execution, the position and strength of the grasp varied, and the data from the camera and haptic sensors were recorded simultaneously. Unlike the Calandra dataset (Calandra et al., 2017), which only collected data at several key moments, Li et al. (2018) collected sequences data of visual and haptic throughout the execution. The results of each grasping were recorded as labels. In the Slip dataset, each set of data comprises two image sequences captured by the camera and the haptic sensor, both with a resolution of 640 × 480. The visual and haptic images are captured simultaneously and are both 21 frames in length. A label is provided for each set, denoting the result of the grip. The value “0” signifies a sliding movement, whereas “1” denotes a stabilizing action.
3.2 The overall frameworkThe model proposed in this paper takes visual and haptic image sequences as inputs and extracts temporal and spatial features using self-attention (SA) and Squeeze-and-Excitation attention (SEA), respectively. In the fusion process, the weights of different features are adjusted with the help of modality gate unit and temporal-spatial gate unit. The attention-based feature extraction module for visual-haptic inputs and the gate-based feature fusion module together constitute the VisuAl Haptic Attention Gate Net (Vahagn), and the overall framework of the model is shown in Figure 1.
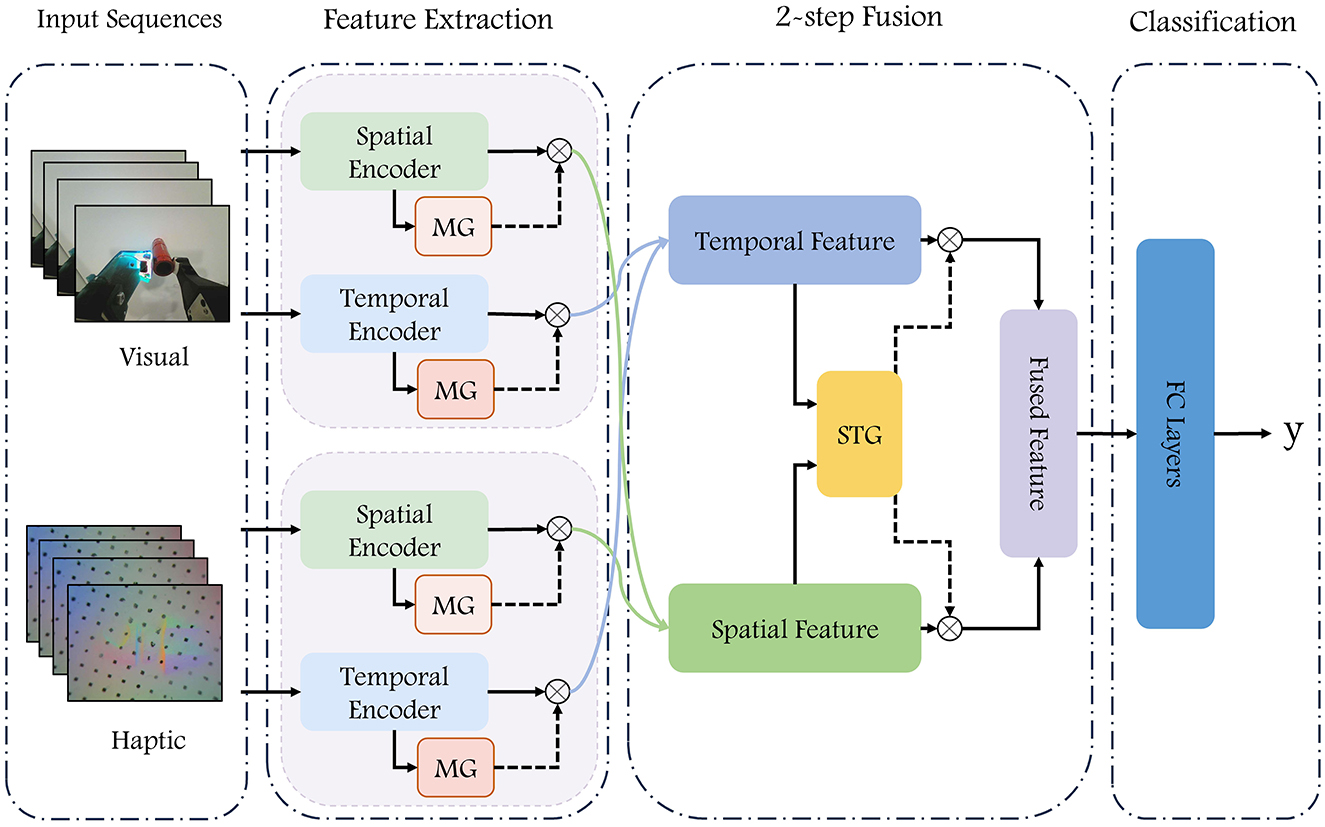
Figure 1. Diagram of our VisuAl Haptic Attention Gate Net (Vahagn) model. The RGB images and the haptic sensors images are fed into a deep neural network to predict whether the grasp is successful. Consecutive N frames of visual and haptic images are inputted into the temporal encoder and spatial encoder, respectively, after which four sets of features from vision and haptic are fused twice to obtain the resulting features, which are concatenated as the input into a fully connected network for prediction.
The proposed network has four main components: data processing, feature extraction, two-step fusion, and classification modules.
3.2.1 Data processingThe stability of the entire grasp is contingent upon the stability of all its constituent segments. Therefore, we propose that the label assigned to a given grasp set can also be applied to the its sub-segments. In accordance with this supposition, we employ N frames of successive visual and haptic images as inputs for a single prediction, here we set N to 8. The Figure 2 illustrates the processing and enhancement performed prior to the input being passed to the network. .
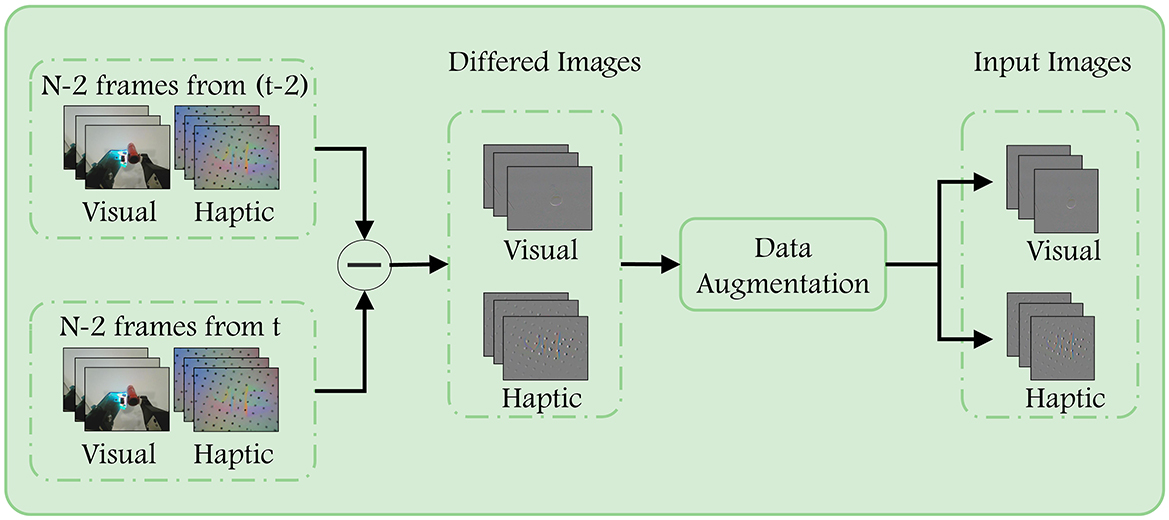
Figure 2. Data preprocessing. First, we subtract the corresponding two frames ago from each of the input images to highlight the regions that have changed due to contact with the target object. After that, we flip the images of the same group using the same probability after resizing to complete the enhancement of the training data.
To emphasize the difference between the current frame image and the previous ones, we first subtract the images across frames. The N−2 images starting from t are differenced from the corresponding images starting from t−2. This helps to eliminate task-irrelevant background in the images that is not necessary for completing the task. We apply the same operation to both the visual images and haptic images. Afterwards, in order to increase the diversity of the data, the image was resized to 224 × 224, and a decision was made as to whether to flip it horizontally or vertically, with a probability of 0.5. The operations performed are consistent across the visual difference image sequence and the haptic difference image sequence, respectively.
3.2.2 Feature extractionWhen performing grasping, the selection of grasping position and the continuity of the action during execution have a great influence on the success of grasping. In this paper, with visual image sequence Xv∈R(N-2)×Hv×Wv and haptic image sequence Xh∈R(N-2)×Hh×Wh as inputs, we constructe a spatial encoder and a temporal encoder, for extracting spatial feature about grasping position and temporal feature about stability information. Here, N, H, and W denote the sequence length, image height, and image width. Following data processing, both H and W yielded a value of 224.
3.2.2.1 Spatial encoderThe purpose of the spatial encoder is to identify and extract features associated with the spatial position of the grasping. From the perspective of visual analysis, our focus is on the relative position of the gripper and the object, as well as the posture of target. In contrast, from the tactile perspective, we place emphasis on the specific details of the contact between the gripper and the target. The structure devised for the spatial encoder is illustrated in Figure 3. The encoder takes a single image as input and outputs the single modal spatial features.
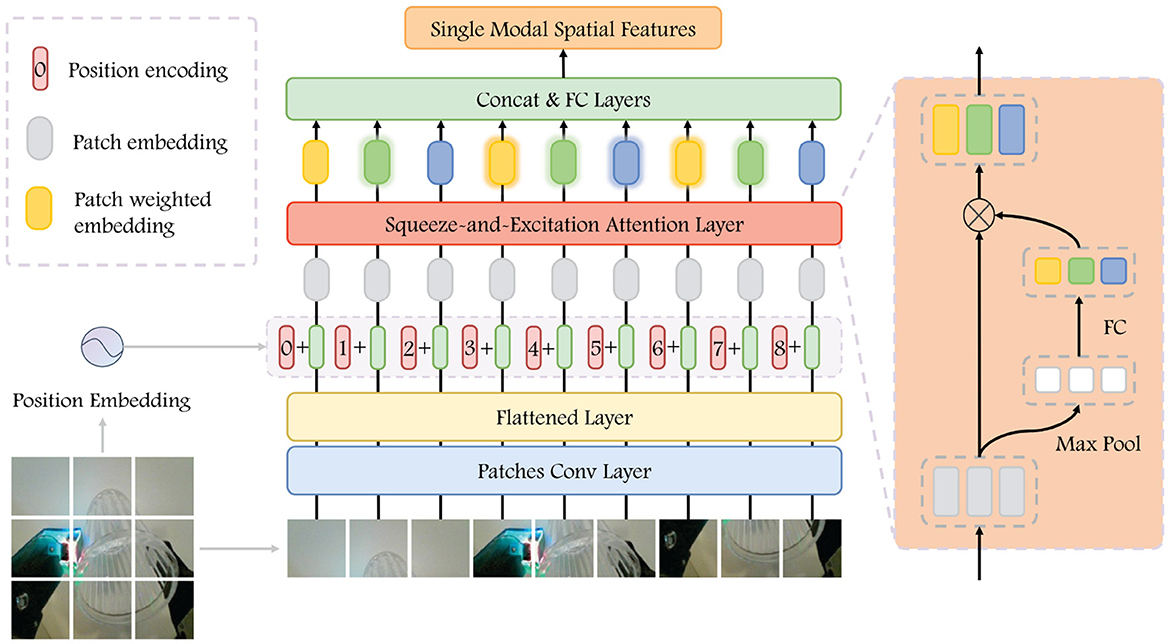
Figure 3. Visualization of Spatial Encoder. The input image is patched to embedding, and we get the patch embedding after adding the space position embedding. After passing it through the SEA, we have weighted features. The single-modal spatial features are obtained after concatenated them as the input into a fully connected network.
In the visual difference image sequence, the final frame is selected to the spatial encoder as input and extracted the patches XpVS∈RpvnS×pvhS×pvwS, where pvhS×pvwS is the resolutions of each patch and pvnS=Hv×WvpvhS×pvwS is the number of patches, which we set to 64. Subsequently, the patches go through a convolutional layer to extract relevant feature. Then, we flatten it and added position embedding to get the patches feature F∈RpvnS×DS, DS denotes the feature length of each patch and takes the value 768. In feature F, each row represents the feature of one patch, which contains information regarding the position within the original image. We then apply the Squeeze-and-Excitation attention (SEA) mechanism on F to extract the relative importance of individual patch. The execution process can be represented as:
F′=F⊙Sig(MLP(Pool(F))), (1)Feature extraction is conducted through the maximum pooling layer and FCN, and then sigmoid activation is applied to obtain importance weights. After that, these importance weights are then multiplied with the original input F to generate the weighted representation of patches feature.
For the haptic sequence, we also use the last frame of the difference image as input and perform the same process. The spatial encoder for haptic utilizes the identical hyperparameters as that for vision, with their parameters updated independently. The spatial encoder provides us with visual spatial features FVS and haptic spatial features FHS.
3.2.2.2 Temporal encoderThe temporal encoder takes a series of difference images as input to obtain continuity and stability during execution. The input visual difference image sequence is denoted as XpVT∈R(N-2)×pvhT×pvwT, where pvhT×pvwT is the resolution of input images. We use a convolutional layer to extract the 2D features, flatten and add them with the time encoding to obtain the temporal feature VT∈R(N−2) × DT, where DT is the feature length of single-frame and is set to 512.
To extract the relationships between frames in the time dimension, a self-attention unit is introduced, inspired by works about natural language processing. The self-attention mechanism can be represented as the process of matching a query (Q) and a set of key (K)-value (V) pairs to an output. In execution, the Q, K, and V matrices are generated by multiplying the input vector with three separate learnable matrices WQ, WK, and WV, respectively:
Q=XWQ,K=XWK,V=XWV, (2)where the vector lengths for Q, K, and V are all set to 128.
The attention scores for different positions are obtained by computing the dot product of Q and K. These scores are then scaled and multiplied with the matrix V to extract a single attention, which is denoted as Attention(Q, K, V). The attention scores could capture the significant relationship between the frames in a continuous sequence. Then the weighted features obtained by multiplying the attention scores with the original inputs are used as the temporal feature, and we denote the temporal features from vision and haptic as FVT and FHT. By focusing on the correlation between the difference images at different locations in the input sequence, one can gain insight into the variability between these images. In turn, such insight facilitates the assessment of the overall process continuity and stability.
3.2.3 Two-step fusionSpatial feature has the information of the location of contact and the posture of the target, while temporal feature focuses on the continuity and stability of the whole process. The input data are derived from both visual and haptic sources, and after feature extraction by the temporal and spatial encoders, we can get a total of four different sets of features. To fully exploit the cross-modal information from both time and space, we employ a two-step feature fusion, which includes Cross-Modality fusion and Spatial-Temporal fusion, as illustrateed in Figure 4, and get a joint feature of the inputs images.
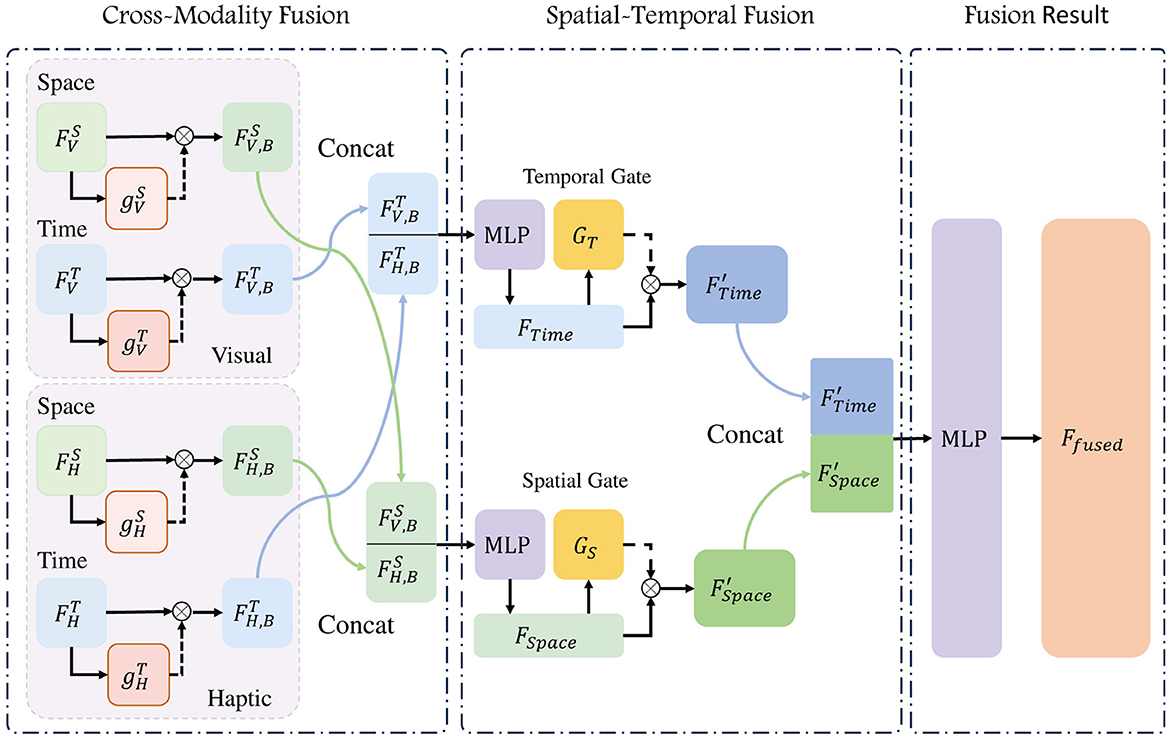
Figure 4. Flowchart of Two-step Fusion. The temporal and spatial features derived from both vision and haptics are integrated through a two-step process: cross-modality fusion and spatial-temporal fusion. In this process, two gates—one for modal fusion and another for spatio-temporal fusion—are employed to regulate the relative weights of the features.
3.2.3.1 Cross-modality fusionWe fused spatial features from vision and haptic, as well as the temporal features from the same sources. Given that the data utilized in this model is derived from both visual and haptic modalities, this fusion process is called Cross-Modality fusion. From haptic images, we can observe the localized pressing situation, but the perception of information such as the gesture of the target is lacking, while the information from vision is more comprehensive, but deficient in detail. When comes to how much each modality could help the prediction, we look at the neurological study for inspiration. Rideaux et al. (2021) mentioned the balance mechanisms and causal inferences processes when they receive information from different sources. Based on this, we put the original features F from visual and haptic into modality gate (MG) units for importance scores g(F), which in turn is multiplied with the original features F for balanced features FB. The gate unit employed in this study is a three-layer fully connected layer, wherein the input length is identical to the output length and is equal to the length of the feature F. The processing of the gate unit can be represented as:
We then concatenate the weighted features and pass them to a FCN and get the temporal feature FTime and spatial feature FSpace with length 1, 024. These two can be expressed as:
FV,BS=FVS⊙gVS(FVS), (4) FH,BS=FHS⊙gHS(FHS), (5) FSpace=MLP(Concat(FV,BS,FH,BS)); (6) FV,BT=FVT⊙gVT(FVT), (7) FH,BT=FHT⊙gHT(FHT), (8) FTime=MLP(Concat(FV,BT,FH,BT)), (9)where we use superscripts to distinguish the encoder, and subscripts to indicate the source of the data, in detail, the superscripts S for spatial encoder and T for temporal encoder, while the subscripts V and H denote features from vision and haptic. The g denotes the modality gate applied on the modality features. The effectiveness of the modality gate will be fully validated in subsequent ablation experiments.
3.2.3.2 Spatial-Temporal fusionSpatial features derived from visual and haptic inputs are integrated in FSpace, and temporal features derived from visual and haptic inputs are integrated in FTime. When temporal and spatial features are fused, a similar three-layer FCN is employed to construct a gated unit G, which serves to adjust the relative weights of temporal and spatial features. In detail, we pass FTime and FSpace through separate spatial-temporal gate G for weighted feature FTime′ and FSpace′. Gate unit G does not change the length of the features. We then concatenate the two feature vectors and mapping it to the fused feature of length 512 use a fully connected network:
FTime′=FTime⊙G(FTime), (10) FSpace′=FSpace⊙G(FSpace), (11) Ffused=Concat(FTime′,FSpace′)WT+b, (12)where Ffused represents the complete fused feature of the current input set. WT is a learnable parameter that performs linear mapping, and b represents another set of learnable parameters used to provide offsets.
3.2.4 ClassificationThe objective of this task is to predict the stability of grasping, indicated by a binary output of either 1 for stable grasping or 0 for slipping. We pass the fused feature Ffused to a three-layer FCN to get a two-dimensional output, which represents the predicted probability at the corresponding label.
4 ExperimentIn this section, in order to verify the validity of the model proposed, we conduct experiments on the dataset proposed in Li et al. (2018). We take haptic and visual images sequences as input, and predict the state of grasping with the output. We compare it with three state-of-the-art methods, CNN-LSTM (Li et al., 2018), VTFSA (Cui et al., 2020), and the TimeSformer (Han et al., 2023). In addition, we conducted a series of ablation experiments and analyzed the results to understand the role of each component. For the encoders, we visualized the attention and analyzed the features obtained from the inputs.
4.1 Implementation detailsWe conduct the experiments on the slip dataset. In the experiments, the dataset is divided into training, validation, and test sets. During training, we increase the diversity of the data with augmentation using the methods described previously. The results were obtained on the test dataset. Three different inputs were tested for each model: vision alone, haptic alone, and vision with haptic.
For the CNN-LSTM model, we follow Li et al. (2018) and choose VGG16 as the backbone of the CNN with pre-trained initialization. After extracting features from visual and tactile images respectively using pre-trained CNN model, the features are concatenated and passed into the LSTM, and then the out features are sent to a FCN to get the prediction. For VTFSA, we follow the description provided by Cui et al. (2020). The input images and haptic signals are processed in discrete encoders to obtain the visual feature, and the haptic feature. These features are then conveyed to the self-attention module after concatenation. Finally, the fused features are subsequently transmitted to the downstream FCN classifier, where the prediction is generated. In regard to TimeSformer, we follow Han et al. (2023). The temporal and spatial features of the visual and haptic sequences are extracted in a sequential manner, using a space-time attention method. The visual and haptic features are then concatenated and passed directly to the downstream prediction FCN model.
In experiments, we took 8-frame vision images and 8-frame haptic images as input. The predicted probabilities and labels were provided to the cross-entropy function to get the loss values. The Adam optimizer was utilized in conjunction with a learning rate of 8 × 10−4. A total of 200 rounds were conducted in batches of 48. The comparison results are displayed in the Table 1.
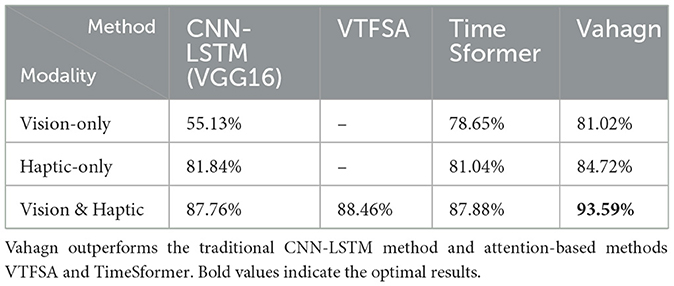
Table 1. Performance comparison of different models with different inputs on slip dataset.
4.2 EvaluationFrom Table 1, we can see that the Vahagn can provide classification results with higher accuracy. For the CNN-LSTM, haptic-only with 81.84% significantly outperforms vision-only with 55.13%, as shown by Liu et al. (2023b), and Transformer models perform similarly for single modality case. For multi-modalities case, Vahagn achieves 93.59% with accuracy, which is +5% higher than VTFSA (88.46%) and +5% higher than TimeSformer (87.88%), similar result was obtained when compared to traditional CNN-LSTM method. Vahagn has better performance than traditional methods and other Transformer models in the slip detection task.
To understand the importance of temporal and spatial information in prediction, we conducted ablation experiments on encoder. The results on accuracy, precision, and recall are shown in Table 2. From the results, we can see that, the accuracy is acceptable for spatial-encoder-only with 81.31%, but the model struggles to provide effective results when spatial encoder is missing. The accuracy is significantly better when the input is jointly encoded with temporal encoder and spatial encoder (93.59%).
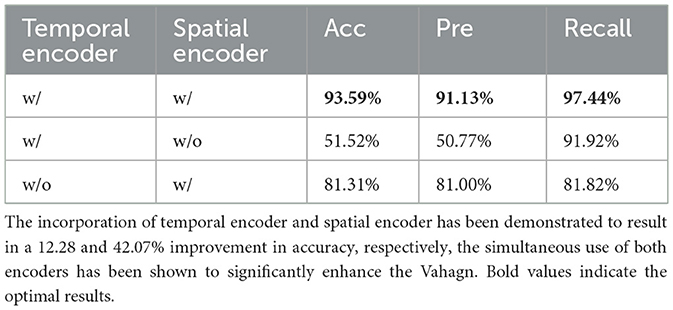
Table 2. Ablation studies results of Vahagn on encoder.
The results show that Vahagn not only outperforms the traditional method of CNN-LSTM, but also compares more favorably with VTFSA, which also adopts the attention mechanism. And Vahagn performs equally well against the TimeSformer, which takes into account the spatial-temporal features.
In comparison with the CNN-LSTM, the Vahagn employs a distinctive design for the extraction of temporal and spatial features. In contrast to VTFSA, Vahagn considered the relative importance between different source and used a gate unit to regulate it, enabling Vahagn to adjust the weight of visual and haptic information. In contrast to the TimeSformer, we distinguished between temporal and spatial feature extraction and the two processes are relatively independent, which helps to preserve deeper features from the input. Furthermore, the ablation experiment on encoder validates the assumption that the input image sequences contain different information about time and space.
In order to validate the veracity of Vahagn's structure and key parameters, we conduct experiments on the length of sequence input into the temporal encoder N and the size of the patches in the spatial encoder. We also perform ablation experiments on several key structural parts of Vahagn.
We firstly test on the length of input sequence N. Table 3 displays the results as the input sequence length N variations. We train the Vahagn with different input lengths (6, 7, 8, 9, and 10) and collected the corresponding accuracy, precision, and recall results. The results show that the best accuracy was obtained when N is 8, accompanied by the best pre and recall, while 10-frame input also showed strong competitiveness.
留言 (0)