 Tomoki Inagaki1‡
Tomoki Inagaki1‡ Yoshitaka Sato1,2*‡
Yoshitaka Sato1,2*‡ Jumpei Ito3§
Jumpei Ito3§ Mitsuaki Takaki4†§
Mitsuaki Takaki4†§ Yusuke Okuno5
Yusuke Okuno5 Masahiro Yaguchi1
Masahiro Yaguchi1 H. M. Abdullah Al Masud1,6
H. M. Abdullah Al Masud1,6 Takahiro Watanabe1
Takahiro Watanabe1 Kei Sato3
Kei Sato3 Shingo Iwami4,7,8
Shingo Iwami4,7,8 Takayuki Murata1,9
Takayuki Murata1,9 Hiroshi Kimura1*
1Department of Virology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan
2Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO), Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi, Japan
3Division of Systems Virology, Department of Infectious Disease Control, International Research Center for Infectious Diseases, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
4Mathematical Biology Laboratory, Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
5Medical Genomics Center, Nagoya University Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
6Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Chittagong, Chattogram, Bangladesh
7Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST), Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi, Japan
8MIRAI, Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi, Japan
9Department of Virology and Parasitology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan
Hiroshi Kimura1*
1Department of Virology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan
2Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO), Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi, Japan
3Division of Systems Virology, Department of Infectious Disease Control, International Research Center for Infectious Diseases, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
4Mathematical Biology Laboratory, Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
5Medical Genomics Center, Nagoya University Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
6Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Chittagong, Chattogram, Bangladesh
7Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST), Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi, Japan
8MIRAI, Japan Science and Technology Agency, Kawaguchi, Japan
9Department of Virology and Parasitology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan
In the published article, there was an error in Table 2 as published. We have carelessly swapped the rows and columns of Table 2. The corrected Table 2 and its caption appear below.
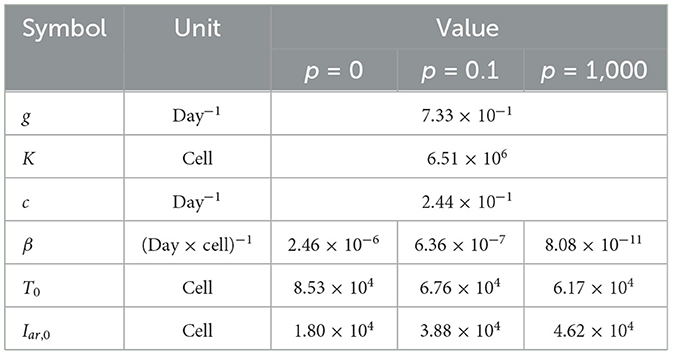
Table 2. Estimated parameters by fitting the mathematical model to experimental data.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: EBV, pre-latent phase, abortive lytic infection, fate mapping, neo virology
Citation: Inagaki T, Sato Y, Ito J, Takaki M, Okuno Y, Yaguchi M, Masud HMAA, Watanabe T, Sato K, Iwami S, Murata T and Kimura H (2024) Corrigendum: Direct evidence of abortive lytic infection-mediated establishment of Epstein-Barr virus latency during B-cell infection. Front. Microbiol. 15:1426311. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1426311
Received: 01 May 2024; Accepted: 13 May 2024;
Published: 23 May 2024.
Edited and reviewed by: Theodoros Kelesidis, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2024 Inagaki, Sato, Ito, Takaki, Okuno, Yaguchi, Masud, Watanabe, Sato, Iwami, Murata and Kimura. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yoshitaka Sato, yssato@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp; Hiroshi Kimura, hkimura@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp
†Present address: Mitsuaki Takaki, Department of Computational Biology and Medical Sciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
‡These authors share first authorship
§These authors share third authorship
留言 (0)