Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), mainly represented as Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), are the most common inflammatory intestinal diseases worldwide, characterized by intermittent chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract [1][2][3]. In contrast to CD – which may affect any part of the intestinal tract – UC causes only localized damage in the colon and the rectum [4]. This chronic disease is manifested by a dysregulated inflammatory process and an altered immune response to yet undefined environmental factors (in genetically predisposed individuals) [5]. As a result, UC patients present inflammatory reactions, erosions of the colonic wall and associated bleeding, thus, the most common UC clinical symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding and weight loss [6][7]. In addition, the accumulation of intestinal contents may lead to the thickening of the intestinal wall; this condition is called a toxic megacolon, and may be responsible for severe, life-threatening complications [8].
–
With the emergence of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, considerable evidence has accumulated regarding the relationship between gut microbiota (GM) composition and the onset, clinical presentation and prognosis of numerous chronic illnesses, including UC [9][10]. While the GM, primarily composed of billions of bacterial species, subspecies, and biotypes, plays a crucial role in maintaining host homeostasis [11][12][13][14][15][16], disease occurrence can also be significantly influenced by environmental factors and genetic predisposition [17]. Significant differences in the representation of individual strains were found in UC patients, with a notable increase in the number of Pseudomonatoda (previously: Proteobacteria), a phylum including SRB [18][19][20].
–
Furthermore, modifications of the GM structure in UC patients have been often associated with alterations in microbial-derived metabolite production [21][22][23][24][25][26]. For instance, the levels of beneficial short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacteria are typically reduced in both mucosal and fecal samples of IBD patients, compared to healthy individuals [27][28][29][30].
–
Moreover, increased concentrations of some bacteria are associated with a higher production of toxic metabolites that favor the onset and progression of intestinal diseases. For example, sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) are anaerobic microorganisms able to produce, by dissimilatory sulfate reduction, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a highly toxic compound to all living organisms [23][24][31][32][33][34][35]. Recently, it has also been hypothesized that H2S is involved in the process of bowel inflammation and UC development, due to its ability to increase mucosal permeability and to block butyrate metabolism [22][33][36][37]. Additionally, it has been recently documented that SRB can also produce biofilm in the gut, along with other pathogenic species (e.g., Bacteroides spp., Pseudomonas spp., Clostridium spp. and Escherichia spp.) and penetrate the blood vessels after damaging the intestinal epithelium [34]. In this context, the objective of this study was to evaluate the composition of the GM in patients with varying degrees of UC severity and activity: i) severe, ii) severe in an active state, and iii) moderate UC. Specifically, our focus was on cultivating SRB in a modified Postgate medium to assess their influence on altering intestinal communities.
RESULTSEnrolled patients
Six patients with UC, comprising five males and one female, were enrolled in the study. The mean age of the participants was 52 years, ranging from 26 to 80 years. Clinical characteristics corresponding to these UC patients are reported in Table 1. Four patients were affected by severe UC and two (samples 5 and 6) were suffering from a moderate form of UC and five out of six patients showed a Mayo score of 12. In addition, only one patient (sample 5) reported both a relapsing active disease refractory to steroids and a family history of IBD.
–
Table 1. Clinical features of the enrolled patients.
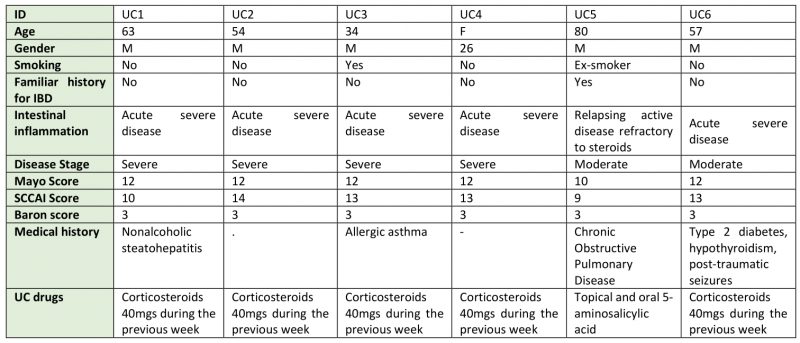
UC: ulcerative colitis, M: male, F: female, SCCAI: Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index
–
Bacterial genera identified in the GM of severe UC patients
The percentage of individual genera in the GM of severe UC patients (samples 1, 2) was different both before cultivation as well as after cultivation in the SRB medium (Figure 1). The intestinal genera diversity in patient 1 (sample 1A) included bacterial species of only three main genera: Escherichia-Shigella (59%), Proteus (30%), Lactobacillus (10%). All other genera were detected at less than 1% (Figure 1). Inoculation of the sample into SRB medium and five days of cultivation led to bacterial compositional changes. We observed a dominance of Bacteroides species (34%) followed by the Proteus genus (28%). The percentage of Proteus spp. did not change significantly compared to the sample without cultivation (Figure 1). Percentage of other genera (Klebsiella, Megasphaera, Escherichia-Shigella, Parabacteroides, Phascolarctobacterium, Prevotellaceae NK3B31 group, Alistipes, Pseudoramibacter, Paraprevotella, Solobacterium, Bilophila and Barnesiella) in sample 1B after cultivation were less than or equal to 8%.
–
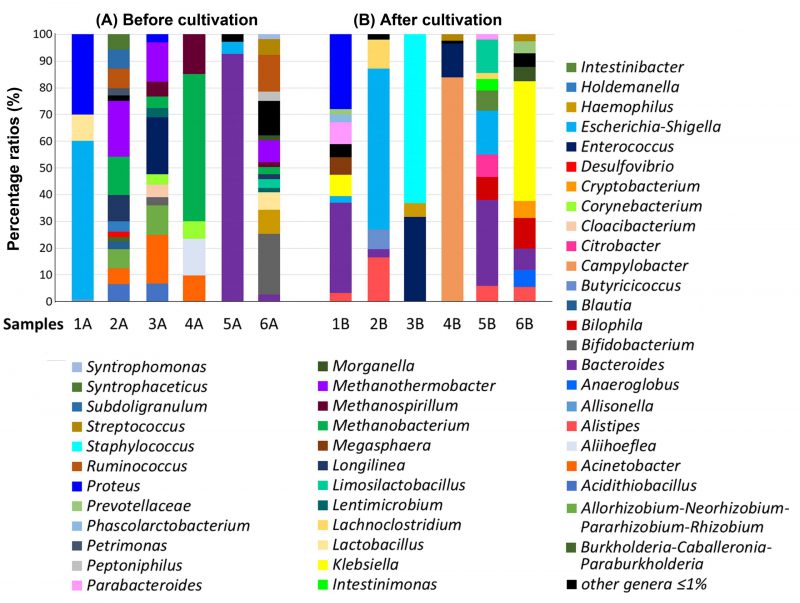
FIGURE 1: Stacked bar plots reporting the percentage of the microbial genera identified in the GM of severe UC patients. (A) Sequencing results of uncultivated stool samples, (B) sequencing results of stool samples after cultivation in SRB medium.
–
The representation of genera in the sample without cultivation taken from patient 2 (sample 2A) was more differentiated than in the sample after culture (sample 2B). The dominant genera in sample 2A were: Methanothermobacter (21%), Methanobacterium (14%) and Longilinea (10%). Other genera, including Allorhizobium-Neorhizobium-Pararhizobium-Rhizobium, Ruminococcus, Subdoligranulum, Holdemanella, Acidithiobacillus, Acinetobacter, Syntrophaceticus, Blautia, Petrimonas, Desulfovibrio, Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia, Porphyromonas and Actinomyces were represented in percentage by less than 8%. The representation of genera in sample 2B exhibited less diversity compared to sample 2A, with Escherichia-Shigella (61%) identified as the predominant genus. Other relatively dominant genera were Alistipes (17%) and Lachnoclostridium (11%). Butyricicoccus (7%) and Bacteroides (3%) were also detected, while under-represented genera accounted for the remaining 2%.
–
Bacterial genera identified in the GM of patients with severe UC in active state
The percentage of individual genera in the GM of patients with severe UC in active state (samples 3, 4) was also considerably different. In the uncultivated sample from patient 3 (sample 3A), we observed a higher diversity of genera compared to the cultivated counterpart (Figure 1). The dominant microbial genera were Enterococcus (21%), Acinetobacter (18%), Methanothermobacter (15%) and Allorhizobium-Neorhizobium–Pararhizobium-Rhizobium (11%). Other detected microorganisms included Methanobacterium spp., Acidithiobacillus spp., Methanospirillum spp., Cloacibacterium spp., Corynebacterium spp., Lentimicrobium spp., Bifidobacterium spp. and Proteus spp. Contrastingly, the sample cultured in SRB medium (sample 3B) showed a completely different microbial pattern with Staphylococcus spp. (63%), Enterococcus spp. (32%) and Haemophilus spp. (5%) making up the majority of the sample. In this case, the cultivation likely resulted in the significant increase of the Staphylococcus spp. and a subsequent reduction in bacterial diversity.
–
In sample 4, more than half of the GM of the sample without cultivation (sample 4A) consisted of the genus Methanobacterium (55%) with Aliihoeflea spp. (14%), Methanospirillum spp. (15%), Acinetobacter spp. (10%) and Corynebacterium spp. (7%) also being documented. The cultivation of sample 4B presumably supported the thriving of Campylobacter spp. which accounted for up to 84% of the detected organisms. Most of the remaining sample species were made up of Enterococcus spp. (13%) and Streptococcus spp. (2%).
–
Bacterial genera identified in the GM of moderate UC patients
Regarding the samples of patients with moderate UC (Figure 1), sample 5 without cultivation (sample 5A) showed a high abundance of Bacteroides spp. (93%) and lower levels of Escherichia-Shigella spp. (5%) and others (2%). The sample from the same patient, but after cultivation (sample 5B), showed remarkable diversity. In particular, the dominant genera were found to be Bacteroides (32%), Escherichia-Shigella (16%), Limosilactobacillus (12%) and Bilophila (9%). Other detected genera were: Citrobacter (8%), Intestinibacter (8%), Alistipes (6%), Intestinimonas (4%), Parabacteroides (2%) and Lachnoclostridium (2%).
–
The most abundant genera in the sample 6 without cultivation (sample 6A) were Bifidobacterium (23%), Ruminococcus gnavus (14%), Haemophilus (9%) and Methanothermobacter (8%), while other genera represented by an abundance lower than 8% were Lactobacillus (7%), Streptococcus (6%), Bacteroides (3%), Peptoniphilus (3%), Limosilactobacillus (3%), Methanobacterium (3%), Syntrophomonas (2%), Morganella (2%), Methanospirillum (2%), Longilinea (2%) and Lentimicrobium (2%).
–
Klebsiella spp. (45%) and Bilophila spp. (12%) were predominant in the same sample, but after cultivation (sample 6B). Additional genera in sample 6B were Bacteroides (8%), Cryptobacterium (6%), Anaeroglobus (6%), Morganella (5%), Prevotella (5%), Alistipes (5%), Streptococcus (3%), all accounting for 8% or less.
–
To compare the ratios of SRB genera in the feces of all studied patients, the percentage of these microbial communities was calculated. Among all SRB, the genus Desulfovibrio was detected directly only in the feces of sample 2A (a patient with acute UC without cultivation). A completely different SRB genus, Bilophila, was revealed only after the cultivation in patients' samples 6B (patient with acute UC), 5B (patient with chronic UC) and 1B (patient with acute UC); in these patients, the genus Desulfovibrio was not detected.
–
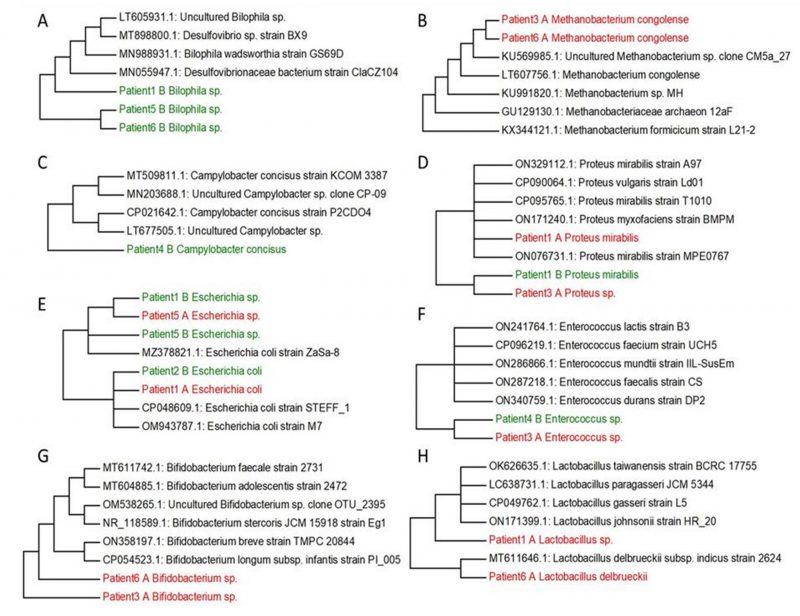

FIGURE 2: Phylogenetic trees created based on identified genera from patients with UC and the comparison of their sequences from GeneBank. Bilophila (A), Methanobacterium (B), Campylobacter (C), Proteus (D), Escherichia (E), Enterococcus (F), Bifidobacterium (G), Lactobacillus (H). Non-cultured samples are marked by red A, cultured samples are coloured by green B.
–
Based on our research and research of other authors [38][39][40][41][42][43][44] we decided to select the main genera, that have often been associated with UC (Bilophila, Methanobacterium, Campylobacter, Proteus, Escherichia, Enterococcus, Bifidobacterium, Lactobacterium) and create phylogenetic trees, aiming to compare the genetic conformity of these genera in patients with severe, severe in active state or moderate UC patients (Figure 2). The experiment was focused on SRB which usually colonize anaerobic areas of soil, wetlands, fresh waters and marine waters, but are also known to be associated with UC development through the induction of a GM dysbiosis caused by their ability to produce high concentrations of H2S [5]. Recognizing the significant role of Bacteroides genus species in IBD, we opted to focus on key species within this genus, frequently linked to UC, and constructed phylogenetic trees. The goal was to compare the genetic conformity of these species among patients with severe, severe in active state, or moderate UC (Figure 3).
–
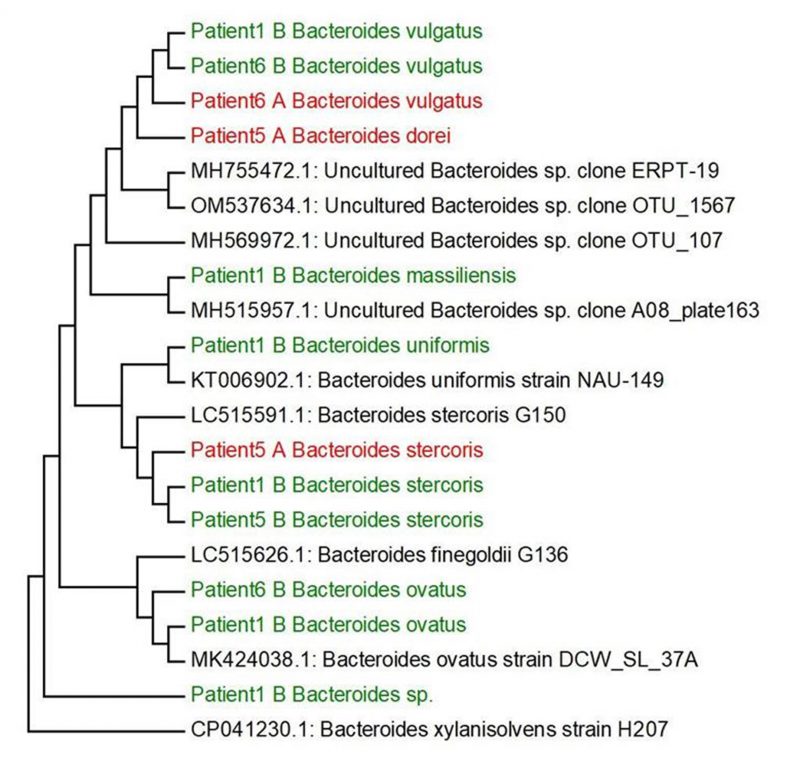
FIGURE 3: Phylogenetic trees created based on identified Bacteroides spp. from patients with UC and the comparison of their sequences from GeneBank. Non-cultured samples are marked by red A, cultured samples are coloured by green B.
DISCUSSIONThe etiology of UC involves microbial, genetic, and environmental factors and its incidence has been increasing worldwide. Currently, the effects of UC are primarily investigated in animal models, offering various advantages. This approach allows for the exploration of the detrimental effects of this inflammatory disease and enables the assessment of the role of intestinal microorganisms in the initiation and progression of UC [45]. However, the molecular mechanisms by which gut microorganisms cause UC are yet not fully understood. Even so, a strong association between high indices of clinical activity and the presence of members of the Enterobacterales order (Gram-negative gut bacteria), Clostridium perfringens type E, Desulfovibrio spp. and Enterococcus faecalis have been found. In contrast, an association among low indices of clinical activity and Clostridium butyricum and Ruminococcus albus presence has been observed. These findings suggest that the GM composition is related to the disease severity and, furthermore, that microbial metabolites could influence UC progression. For example, SRB play a crucial role in IBD development, especially in UC, because of their ability to produce toxic compounds such as H2S and acetate [5][23][24][34].
–
In general, a strong association between UC and Clostridium difficile, Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli and Phocaeicola vulgatus infections have been documented [20]. Moreover, UC patients also reported a reduced number of bacterial species belonging to the phylum Bacillota (previously Firmicutes) and a considerable increase of Actinomycetota (previously Actinobacteria) and Pseudomonatoda, a phylum including SRB [19].
–
Following the cultivation of fecal samples from specific patients (1, 5, and 6) in SRB medium, only one SRB genus, namely Bilophila spp., was identified. The sequences of this bacterial genera formed one cluster (patient 5 and patient 6), connected with patient 1, that was genetically similar to other SRB genera, including mucin-producing Bilophila spp. and Desulfovibrionaceae members. In particular, hydrogenotrophic and mucolytic genera, such as Desulfovibrio, Desulfobacter, Desulfobulbus and Bilophila have all been associated with UC. Additionally, their secreted metabolites' mucolytic activity can be utilized by other intestinal bacteria with the consequent production of H2S. This in turn can directly increase gut inflammation as well as inhibit butyrate metabolism [38]. Butyric acid is a crucial SCFA with well-known and potent anti-inflammatory properties, that plays a crucial role as a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, an energy metabolite to produce ATP and a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) activator. In relation to gut dysbiosis, certain studies have documented variations in the composition of the GM and the associated microbial metabolism, including differences in SCFA levels, depending on CD activity. [46][47].
–
Within the Methanobacterium genus, Methanobacterium congolense formed one cluster with uncultured Methanobacterium sp. clone CM5a_27 and other methanogenic archaea (methanogens) (access numbers: KU569985.1, LT607756.1, KU991820.1, GU129130.1, KX344121.1). The only samples where Methanobacterium congolense was not detected were from samples three and six after cultivation in SRB medium. Methanogens were initially isolated in the human intestinal tract by Miller et al., and they typically characterize a healthy and mature anaerobic GM [39]. However, the role and relevance of methanogens (and other archaea) in the human intestinal microbiome are still not well investigated and not yet fully understood [48]. A recent report has hypothesized that bacterial dysbiosis in the intestine of patients with IBD may contribute to an elevated abundance of methanogen species. Methanogens might potentially enhance the production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and activate dendritic cells, thus significantly contributing to the inflammatory state of the mucosa [49].
–
In general, the unresolved question still remains as to whether chronic and recurrent inflammation arises from persistent infection with a specific pathogen, overexposure to normal luminal bacterial products due to increased intestinal permeability, or an abnormally aggressive immune response to luminal components [47].
–
Another genus which can be isolated from the stool of patients with UC is Campylobacter. Campylobacter spp. are commensal bacteria found in cattle, sheep, pigs and birds while in humans (especially C. jejuni and C. coli) they are associated with several gastrointestinal conditions and non-intestinal manifestations including bacteremia, brain abscesses, meningitis, and reactive arthritis. Moreover, Campylobacter spp. and Salmonella gastroenteritis are associated with IBD development [40]. Only C. concisus was detected after the cultivation and this species has been formed with two clusters including cultured and uncultured species (access numbers: MT509811.1. MN203688.1. CP021642.1. LT677505.1)
–
UC patients reported the presence of Proteus spp., a genus comprising microorganisms that has been associated with a sharp decline in absorption processes on the small intestinal mucosa. This genus may be isolated from the oral cavity, stomach, small intestinal mucosa and, most commonly, from the stool. In recent years, a primary focus has been the interrelationships between microbial quantitative and qualitative composition. This includes opportunistic pathogenic bacteria from the genus Proteus, which are seen to increase in patients with UC [41]. In this study, P. mirabilis was identified after cultivation only in patient 1, while other species of this genus have been detected in fecal samples of patient 3, but before cultivation in SRB medium. Both sequences related to a cluster, including P. vulgaris, P. myxofaciens and other strains of P. mirabilis from GenBank.
–
The association of E. coli with UC etiology has also been investigated and it has been reported that these bacteria could be found in only a small number of patients. The mucosal adhesion of these isolates was much higher compared to physiological samples or samples from patients with infectious diarrhea. The most virulent E. coli strains have adhesive properties, suggesting that these strains could play an impacting role in UC pathogenesis. In conclusion, there is no complete information on the role of intestinal E. coli, and its association with the pathogenesis of UC is controversial.
–
In the study conducted by Seishima et al. [43], metagenomic analysis of the fecal microbiota of IBD patients and fecal transplantation from responding patients to genetically susceptible animals was performed. The authors confirmed a causal relationship between inflammatory strains of E. faecium and UC. By sequencing multiple strains isolated from UC patients, the genotype of E. faecium, presumably responsible for inflammation, was identified. Thus, a causal relationship between bacterial strains and inflammation of the colon has been clearly shown [43].
–
As previously mentioned, patients suffering from UC have a different proportion of symbiotic or potentially pathogenic microorganisms in comparison to healthy. This difference is characterized by the expansion of members of the Enterobacterales order at the expense of beneficial genera, such as Fusobacterium, Clostridium/Clostridioides, Ruminococcus, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. are prominent bacteria found in commercially available probiotic preparations commonly employed in the treatment of IBD. Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. work to counteract the virulence mechanisms of harmful bacteria and the ensuing inflammatory response, which is closely linked to the pathogenesis of IBD. We selected these probiotic bacteria because they are an important part of the normal human intestinal microbiota; they are very well biologically characterized and are widely used in the treatment of dysbiosis [44].
–
A causative role for Bacteroides species in experimental UC was suggested in a study by Campieri and Gionchetti, (2001). In this study, the role of bacteria in UC pathogenesis was shown in animal models [50]. In a carrageenan guinea pig model of experimental colitis, germ-free animals did not develop colitis until after monoassociation with P. vulgatus [51]. Subsequently, it was suggested that different strains of P. vulgatus led to considerable differences in the inflammatory response without a correlation between the sources of strains and the severity of carrageenan-induced lesions. In this model, pretreatment with metronidazole prevented colitis, while administration of Gram-positive bacteria or coliforms was not effective. These data suggest the need for interaction between bacteria sensitive to metronidazole and dietary sulfate. More recently, the degree of cecal inflammation in HLA-B27 transgenic rats was shown to be correlated with levels of isolates on Bacteroides selective medium and increased anaerobic/aerobic and Bacteroides/aerobic ratios [52]. Indirect evidence for the interaction between the luminal microbiota and the immune system exists from studies using animal models with disruptions in immunoregulatory molecules. It was reported that spontaneous colitis, which consistently develops in knockout and transgenic murine models, does not occur when these mice are maintained in germ-free conditions [53][54][55][56]. Furthermore, it should be noted that only two genera of the Desulfovibrionaceae family (Desulfovibrio and a taurine-respiring sulfite-reducing Bilophila) were detected in the feces of the various patients before and after cultivation in the SRB medium. However, it should be noted that the members of the genera Bilophila are unable to use sulfate as an electron acceptor [57]. The species of Bilophila (in particular, the human stool-derived B. wadsworthia) caused systemic inflammation in specific-pathogen-free mice [58]. Bilophila members are classified as a taurine-respiring sulfite-reducing bacteria (sulfite is an intermediate reduced by dissimilatory sulfite reductase) and an H2S-producing bacterium [59][60].
–
B. wadsworthia, a strictly anaerobic, sulfite-reducing bacteria and a common member of the human GM, has been associated with appendicitis and colitis [61]. H2S production (mostly from B. wadsworthia) pathways were expressed abundantly across various health states, demonstrating that these microbial functions are core attributes of the human gut [62]. Therefore, the findings documented in this study – obtained through the characterization of the GM composition of UC patients using the latest molecular methods and comparing the results with data available in publicly available databases – aimed to provide a better understanding of the course and development of this disease, paving the way for new personalized treatments of this condition in the future.
–
In conclusion, although UC is a chronic inflammatory condition of the colon, affecting a growing number of patients worldwide and substantially decreases their quality of life, insights can be gained from the GM of moderate and severe cases. Despite certain limitations in our study, such as the limited number and demographic heterogeneity of participants, the absence of healthy controls, the cross-sectional design, and the lower taxonomic resolution of 16S rRNA sequencing, our findings provide valuable insights into the compositional changes of the GM in patients with UC. The study presented here uses current sequencing technologies and complementary culture methods (to allow for the more effective detection of pro-inflammatory SRB) were used to identify the relevant bacterial genera in the GM of patients with UC. The results obtained do not establish a causal relationship between the presence of SRB and the onset or severity of UC. Instead, the findings highlight, among other observations, significant variations in the gut microbial composition among patients with varying disease severity and activity. Different bacterial genera were found to be dominant in each of these cases. In addition, with the use of an SRB-specific medium before sequencing, considerable changes were noted in the microbial composition of the samples (either by decreasing or increasing bacterial diversity). In particular, this increased detection of characteristic Desulfovibrionaceae members [68], such as Desulfovibrio spp. and Bilophila spp.
–
These insights contribute to a better understanding of the disease's pathogenesis and may inform the development of novel therapeutic strategies, including probiotic preparations containing beneficial bacterial communities, to counteract the virulence mechanisms of harmful bacteria and mitigate the ensuing inflammatory response.
MATERIAL AND METHODSCollection of stool samples of UC patients
Patients affected by UC were enrolled at the Careggi University Hospital (Florence, Italy), after obtaining written informed consent. The description of the patients is given in Table 1. This study included adult (>18 years) patients affected by active UC, requiring hospitalization, while subjects were excluded if they were taking antibiotics or probiotics and similar products (prebiotics or symbiotics) four weeks before sample collection, were pregnant or lactating, were affected by other known organic gastrointestinal disease (such as, but not limited to, malignancy, chronic diarrhea; celiac disease and/or important food intolerance (e.g., lactose) and travelled to exotic areas in the last six months.
–
The severity of the disease has been assessed through the Baron score, the Mayo score and the Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index (SCCAI) score.
–
At the moment of the hospitalization, two fecal samples for each patient were collected and immediately frozen at -20°C; one was not cultivated in SRB medium, while the other was incubated in the modified SRB medium (Figure 4). Notably, samples 1 and 2 were taken from patients affected by severe UC, while samples 3 and 4 were taken from patients with severe UC in active state and samples 5 and 6 belonged to men with a moderate UC (Table 1).
–
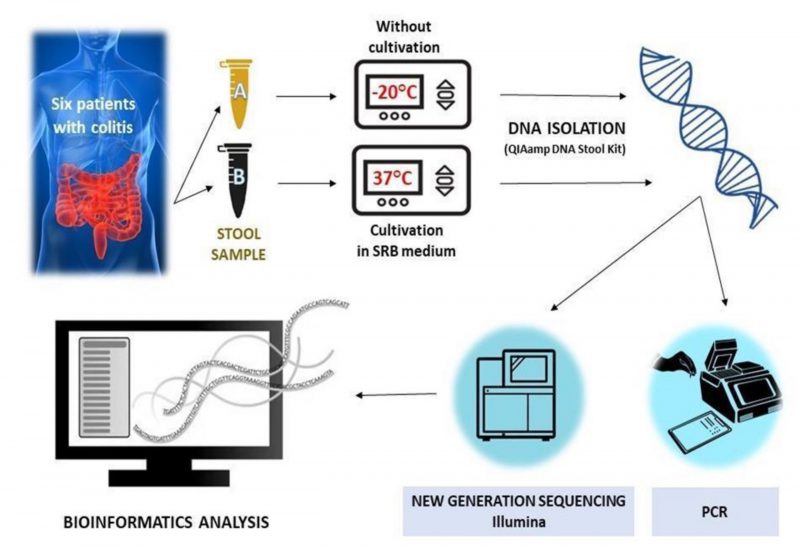
FIGURE 4: Experimental workflow without (Eppendorf tube A) or with cultivation (Eppendorf tube B) in SRB medium.
–
All methods have been performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations included in the statement approved by the local Ethics Committee of the Tuscany Region (study 118 n°2016.0842), Careggi University Hospital and followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
–
Medium for intestinal SRB cultivation
All samples for the cultivation were collected in sterile Eppendorf tubes full of the liquid medium that was bubbled with molecular nitrogen gas to attain anaerobic conditions. The composition of modified medium for intestinal SRB cultivation was as follows (grams per liter): Na2SO4 (3), KH2PO4 (0.3), K2HPO4 (0.5), NH4Cl (1), CaCl2 × 6H2O (0.06), yeast extract (1), sodium citrate (0.3), sodium lactate (6), MgSO4 × 7H2O (0.1), ascorbic acid (0.1) and (NH4)2SO4 (0.2). Potential of hydrogen (pH) range in the large intestine of humans and animals is limited (5.5–8) and it depends on many factors, including the composition and enzymatic activity of intestinal microorganisms, substrates they are able to use, the process of digestion and the quality of consumed food. As people's constant body temperature is around 37°C, cultivation was performed in a thermostat set at the same temperature, during 5 days. By respecting these conditions and creating the optimal pH and redox potential, the gut environment was simulated. This medium incorporates various organic components, thereby facilitating the growth of other anaerobic bacteria present in the human gut as well [63].
–
Isolation of DNA
Total DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Stool Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) from frozen (-20°C) stool samples according to the manufacturer's instructions, with minor modifications, as described below.
–
Firstly, 180 mg of each stool sample was mixed with 1.4 mL Buffer ASL and homogenized. The suspension was incubated at 95°C for 5 min and then centrifuged at 10.000 rpm. An InhibitEX tablet was added to the supernatant to remove impurities and PCR inhibitors. After the next centrifugation step, 200 μL of the supernatant was added to 15 μL of proteinase K solution and 200 μL of buffer AL. The mixture was incubated at 70°C for 10 min, cooled and added with 200 μL of ethanol 96%. Next, the supernatant was centrifuged through the QIAamp kit column and then washed with 500 µL of AW1 and AW2 buffers. Finally, DNA was eluted with 200 μL of AE elution buffer and stored at -20°C.
–
Amplification and sequencing
Universal primers were used for the amplification of the V4 variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene [64][65]. The primers were marked by molecular barcodes for sample identification and adapter sequences for flow cell hybridisation. Platinum\™ II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA) at 0.8× was used for the PCR reaction. Cycling conditions were the following: 94°C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of incubation at 94°C for 45 s, 52°C for 1 min (50% thermal ramp) and 72°C for 90 s, and a final extension step at 72°C for 10 min. PCR products were purified using Agencourt AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, Brea, USA), quantified and normalized using dsDNA HS assay with a Qubit 4 fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA), and their quality was checked using DNF-474 HS NGS kit with Fragment Analyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, USA).
–
Purified amplicons were paired-end sequenced using a Mid Output Kit (2×150 bp) with the MiniSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, USA). Raw FASTQ reads were processed using the DADA2 package (version 1.16.0) [66], in R (version 4.0.0). Then, reads were filtered, trimmed, de-replicated and de-noised according to the standard operating procedure [67]. Afterwards, forward and reverse reads were merged, chimeras were removed, and the taxonomy was assigned by the RDP naive Bayesian classification [68] against the Silva database v138 [69].
–
The relative abundance of the taxonomic groups was calculated for the microorganisms detected in this study. Sequences were compared using the BLAST feature (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/about/) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) [70]. The sequences were uploaded to the Mega7 software [71] for comparative phylogenetic analyses and clustering was performed by the neighbor-joining method [72][73].
–
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
–
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The patients affected by UC were enrolled at Careggi University Hospital (Florence, Italy) after obtaining informed consent and approval of the local Ethics Committee (study 118 n°2016.0842). This research was also approved by the Bioethics Committee at the Faculty of Science at Masaryk University (EKV-2021-060).
REFERENCES Boirivant M, and Cossu A (2012). Inflammatory bowel disease: Inflammatory bowel disease. Oral Dis 18(1): 1–15. 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2011.01811.x Head K, and Jurenka JS (2004). Inflammatory bowel disease. Part II: Crohn's disease–pathophysiology and conventional and alternative treatment options. Altern Med Rev J Clin Ther 9(4): 360–401. 15656711 Rubin DC, Shaker A, and Levin MS (2012). Chronic intestinal inflammation: inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon cancer. Front Immunol 3: 107. 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00107 Vilela EG (2012). Evaluation of inflammatory activity in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 18(9): 872. 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.872 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, and Vít\ězová M (2020). Possible synergy effect of hydrogen sulfide and acetate produced by sulfate-reducing bacteria on inflammatory bowel disease development. J Adv Res 27: 71-78. 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.007 Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB, Peyrin-Biroulet L, and Colombel J-F (2017). Ulcerative colitis. The Lancet 389(10080): 1756–1770. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32126-2 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, and Vít\ězová M (2019). Toxicity of hydrogen sulfide toward sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7. Arch Microbiol 201(3): 389–397. 10.1007/s00203-019-01625-z Stange EF (2013). Inflammatory bowel diseases. Preface. Dig Dis 31(3–4): 269–269. 10.1159/000354674 Sanchez-Morate E, Gimeno-Mallench L, Stromsnes K, Sanz-Ros J, Román-Domínguez A, Parejo-Pedrajas S, Inglés M, Olaso G, Gambini J, and Mas-Bargues C (2020). Relationship between Diet, Microbiota, and Healthy Aging. Biomedicines 8(8): 287. 10.3390/biomedicines8080287 Fontana A, Manchia M, Panebianco C, Paribello P, Arzedi C, Cossu E, Garzilli M, Montis MA, Mura A, Pisanu C, Congiu D, Copetti M, Pinna F, Carpiniello B, Squassina A, and Pazienza V (2020). Exploring the Role of Gut Microbiota in Major Depressive Disorder and in Treatment Resistance to Antidepressants. Biomedicines 8(9): 311. 10.3390/biomedicines8090311 Macfarlane, M. J. Hopkins, G. T. Ma S (2000). Bacterial Growth and Metabolism on Surfaces in the Large Intestine. Microb Ecol Health Dis 12(2): 64–72. 10.1080/089106000750060314 Cummings JH, and Macfarlane GT (1997). Colonic microflora: Nutrition and health. Nutrition 13(5): 476–478. 10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00114-7 Macfarlane S, Steed H, and Macfarlane GT (2009). Intestinal bacteria and inflammatory bowel disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 46(1): 25–54. 10.1080/10408360802485792 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, and Kollár P (2019). Analysis of physiological parameters of Desulfovibrio strains from individuals with colitis. Open Life Sci 13(1): 481–488. 10.1515/biol-2018-0057 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, and Vít\ězová M (2019). Analysis of pH dose-dependent growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Open Med 14(1): 66–74. 10.1515/med-2019-0010 Kushkevych I, Kollar P, Ferreira AL, Palma D, Duarte A, Lopes MM, Bartos M, Pauk K, Imramovsky A, and Jampilek J (2016). Antimicrobial effect of salicylamide derivatives against intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Appl Biomed 14(2): 125–130. 10.1016/j.jab.2016.01.005 Öhman F, Hassenstab J, Berron D, Schöll M, and Papp KV (2021). Current advances in digital cognitive assessment for preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement Diagn Assess Dis Monit 13(1): e12217. 10.1002/dad2.12217 Ahmed EA, Ahmed SM, Zakaria NH, Baddour NM, and Header DA (2022). Study of the gut microbiome in Egyptian patients with active ulcerative colitis. Rev Gastroenterol México Engl Ed 88(3): 246-255. 10.1016/j.rgmxen.2022.07.006 Barberio B, Facchin S, Patuzzi I, Ford AC, Massimi D, Valle G, Sattin E, Simionati B, Bertazzo E, Zingone F, and Savarino EV (2022). A specific microbiota signature is associated to various degrees of ulcerative colitis as assessed by a machine learning approach. Gut Microbes 14(1): 2028366. 10.1080/19490976.2022.2028366 Carbonnel F, Jantchou P, Monnet E, and Cosnes J (2009). Environmental risk factors in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: an update. Gastroentérologie Clin Biol 33: S145–S157. 10.1016/S0399-8320(09)73150-1 Dai Z, Ramesh V, and Locasale JW (2020). The evolving metabolic landscape of chromatin biology and epigenetics. Nat Rev Genet 21(12): 737–753. 10.1038/s41576-020-0270-8 Kushkevych I, Castro Sangrador J, Dordević D, Rozehnalová M, Černý M, Fafula R, Vít\ězová M, and Rittmann SK-MR (2020). Evaluation of Physiological Parameters of Intestinal Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Isolated from Patients Suffering from IBD and Healthy People. J Clin Med 9(6): 1920. 10.3390/jcm9061920 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, Kollar P, Vít\ězová M, and Drago L (2019). Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and its Role in IBD Development. J Clin Med 8(7): 1054. 10.3390/jcm8071054 Kushkevych I, Kotrsová V, Dordević D, Bu\ňková L, Vít\ězová M, and Amedei A (2019). Hydrogen Sulfide Effects on the Survival of Lactobacilli with Emphasis on the Development of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Biomolecules 9(12): 752. 10.3390/biom9120752 Kováč J, Vít\ězová M, and Kushkevych I (2018). Metabolic activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria from rodents with colitis. Open Med 13(1): 344–349. 10.1515/med-2018-0052 Kushkevych I, Cejnar J, Treml J, Dordević D, Kollar P, and Vít\ězová M (2020). Recent Advances in Metabolic Pathways of Sulfate Reduction in Intestinal Bacteria. Cells 9(3): 698. 10.3390/cells9030698 Parada Venegas D, De la Fuente MK, Landskron G, González MJ, Quera R, Dijkstra G, Harmsen HJM, Faber KN, and Hermoso MA (2019). Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front Immunol 10: 277. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00277 LeBlanc JG, Chain F, Martín R, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Courau S, and Langella P (2017). Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb Cell Factories 16(1): 79. 10.1186/s12934-017-0691-z Deleu S, Machiels K, Raes J, Verbeke K, and Vermeire S (2021). Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 66: 103293. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103293 Massier L, Blüher M, Kovacs P, and Chakaroun RM (2021). Impaired Intestinal Barrier and Tissue Bacteria: Pathomechanisms for Metabolic Diseases. Front Endocrinol 12: 616506. 10.3389/fendo.2021.616506 Abdulina D, Kováč J, Iutynska G, and Kushkevych I (2020). ATP sulfurylase activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria from various ecotopes. 3 Biotech 10(2): 55. 10.1007/s13205-019-2041-9 Kushkevych I, Fafula R, Parák T, and Bartoš M (2015). Activity of Na+/K+-activated Mg2+-dependent ATP-hydrolase in the cell-free extracts of the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7 and Desulfomicrobium sp. Rod-9. Acta Vet Brno 84(1): 3–12. 10.2754/avb201585010003 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, Vít\ězová M, and Rittmann SK-MR (2021). Environmental Impact of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Their Role in Intestinal Bowel Diseases, and Possible Control by Bacteriophages. Appl Sci 11(2): 735. 10.3390/app11020735 Dordević D, Jančíková S, Vít\ězová M, and Kushkevych I (2020). Hydrogen sulfide toxicity in the gut environment: Meta-analysis of sulfate-reducing and lactic acid bacteria in inflammatory processes. J Adv Res 27: 55-69. 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.003 Kushkevych I, Vít\ězová M, Fedrová P, Vochyanová Z, Paráková L, and Hošek J (2017). Kinetic properties of growth of intestinal sulphate-reducing bacteria isolated from healthy mice and mice with ulcerative colitis. Acta Vet Brno 86(4): 405–411. 10.2754/avb201786040405 Kushkevych I, Dordević D, Vít\ězová M, and Kollár P (2018). Cross-correlation analysis of the Desulfovibrio growth parameters of intestinal species isolated from people with colitis. Biologia 73(11): 1137–1143. 10.2478/s11756-018-0118-2 Kushkevych I, Vít\ězová M, Kos J, Kollár P, and Jampílek J (2018). Effect of selected 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxanilides on viability and sulfate metabolism of Desulfovibrio piger. J Appl Biomed 16(3): 241–246. 10.1016/j.jab.2018.01.004 Earley H, Lennon G, Coffey JC, Winter DC, and O'Connell PR (2021). Colonisation of the colonic mucus gel layer with butyrogenic and hydrogenotropic bacteria in health and ulcerative colitis. Sci Rep 11(1): 7262. 10.1038/s41598-021-86166-6 Chaudhary PP, Conway PL, and Schlundt J (2018). Methanogens in humans: potentially beneficial or harmful for health. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(7): 3095–3104. 10.1007/s00253-018-8871-2 Akar M, Aydin F, Yurci MA, Abay S, Ateş \İ, and Deniz K (2018). The possible relationship between Campylobacter spp./Arcobacter spp. and patients with ulcerative colitis: Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 30(5): 531–538. 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001095 Kanareykina SK, Misautova AA, Zlatkina AR, and Levina EN (1987). Proteus dysbioses in patients with ulcerative colitis. Food Nahr 31(5–6): 557–561. 10.1002/food.19870310570 Kushkevych I (2014). Etiological Role of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in the Development of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Ulcerative Colitis. Am J Infect Dis Microbiol 2(3): 63–73. 10.12691/ajidm-2-3-5 Seishima J, Iida N, Kitamura K, Yutani M, Wang Z, Seki A, Yamashita T, Sakai Y, Honda M, Yamashita T, Kagaya T, Shirota Y, Fujinaga Y, Mizukoshi E, and Kaneko S (2019). Gut-derived Enterococcus faecium from ulcerative colitis patients promotes colitis in a genetically susceptible mouse host. Genome Biol 20(1): 252. 10.1186/s13059-019-1879-9 Leccese G, Bibi A, Mazza S, Facciotti F, Caprioli F, Landini P, and Paroni M (2020). Probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Strains Counteract Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) Virulence and Hamper IL-23/Th17 Axis in Ulcerative Colitis, but Not in Crohn's Disease. Cells 9(8): 1824. 10.3390/cells9081824 Harris KG, and Chang EB (2018). The intestinal microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases: new insights into complex disease. Clin Sci 132(18): 2013–2028. 10.1042/CS20171110 Forbes JD, Van Domselaar G, and Bernstein CN (2016). Microbiome Survey of the Inflamed and Noninflamed Gut at Different Compartments Within the Gastrointestinal Tract of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Inflamm Bowel Dis 22(4): 817–825. 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000684 Russo E, Cinci L, Di Gloria L, Baldi S, D'Ambrosio M, Nannini G, Bigagli E, Curini L, Pallecchi M, Andrea Arcese D, Scaringi S, Malentacchi C, Bartolucci G, Ramazzotti M, Luceri C, Amedei A, and Giudici F (2022). Crohn's disease recurrence updates: first surgery vs. surgical relapse patients display different profiles of ileal microbiota and systemic microbial-associated inflammatory factors. Front Immunol 13: 886468. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.886468 Borrel G, Brugère J-F, Gribaldo S, Schmitz RA, and Moissl-Eichinger C (2020). The host-associated archaeome. Nat Rev Microbiol 18(11): 622–636. 10.1038/s41579-020-0407-y Houshyar Y, Massimino L, Lamparelli LA, Danese S, and Ungaro F (2021). Going Beyond Bacteria: Uncovering the Role of Archaeome and Mycobiome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Physiol 12: 783295. 10.3389/fphys.2021.783295 Campieri M (2001). Bacteria as the cause of ulcerative colitis. Gut 48(1): 132–135. 10.1136/gut.48.1.132 Onderdonk AB, Bronson R, and Cisneros R (1987). Comparison of Bacteroides vulgatus strains in the enhancement of experimental ulcerative colitis. Infect Immun 55(3): 835–836. 10.1128/iai.55.3.835-836.1987 Rath HC, Ikeda JS, Linde HJ, Schölmerich J, Wilson KH, and Sartor RB (1999). Varying cecal bacterial loads influences colitis and gastritis in HLA-B27 transgenic rats. Gastroenterology. 116(2): 310–319. 10.1016/S0016-5085(99)70127-7. Ehrhardt RO, Lúdvíksson BR, Gray B, Neurath M, and Strober W (1997). Induction and prevention of colonic inflammation in IL-2-deficient mice. J Immunol Baltim Md 1950 158(2): 566–573. 8992969 Kühn R, Löhler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, and Müller W (1993). Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75(2): 263–274. 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80068-P LeBlanc J-F, Segal JP, de Campos Braz LM, and Hart AL (2021). The Microbiome as a Therapy in Pouchitis and Ulcerative Colitis. Nutrients 13(6): 1780. 10.3390/nu13061780 Sankarasubramanian J, Ahmad R, Avuthu N, Singh AB, and Guda C (2020). Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Specificity in Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease. Front Med 7: 606298. 10.3389/fmed.2020.606298 Kuever J, Rainey FA, and Widdel F (2005). Class IV. Deltaproteobacteria class nov. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, editors Bergey's Manual® Syst. Bacteriol. Springer US, Boston, MA; pp 922–1144. Feng Z, Long W, Hao B, Ding D, Ma X, Zhao L, and Pang X (2017). A human stool-derived Bilophila wadsworthia strain caused systemic inflammation in specific-pathogen-free mice. Gut Pathog 9(1): 59. 10.1186/s13099-017-0208-7 Laue H, Denger K, and Cook AM (1997). Taurine reduction in anaerobic respiration of Bilophila wadsworthia RZATAU. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(5): 2016–2021. 10.1128/aem.63.5.2016-2021.1997 Laue H, Smits THM, Schumacher UK, Claros MC, Hartemink R, and Cook AM (2006). Identification of Bilophila wadsworthia by specific PCR which targets the taurine:pyruvate aminotransferase gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 261(1): 74–79. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00335.x Burrichter AG, Dörr S, Bergmann P, Haiβ S, Keller A, Fournier C, Franchini P, Isono E, and Schleheck D (2021). Bacterial microcompartments for isethionate desulfonation in the taurine-degrading human-gut bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia. BMC Microbiol 21(1): 340. 10.1186/s12866-021-02386-w Hanson BT, Dimitri Kits K, Löffler J, Burrichter AG, Fiedler A, Denger K, Frommeyer B, Herbold CW, Rattei T, Karcher N, Segata N, Schleheck D, and Loy A (2021). Sulfoquinovose is a select nutrient of prominent bacteria and a source of hydrogen sulfide in the human gut. ISME J 15(9): 2779–2791. 10.1038/s41396-021-00968-0 Kovac J, and Kushkevych I (2019). New modification of cultivation medium for isolation and growth of intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. In: MendelNet 2017. Mendel Univ Brno, Fac AgriSciences, Brno, Brno; pp 702–707. Pichler M, Coskun ÖK, Ortega-Arbulú A, Conci N, Wörheide G, Vargas S, and Orsi WD (2018). A 16S rRNA gene sequencing and analysis protocol for the Illumina MiniSeq platform. MicrobiologyOpen 7(6): e00611. 10.1002/mbo3.611 Nossa CW (2010). Design of 16S rRNA gene primers for 454 pyrosequencing of the human foregut microbiome. World J Gastroenterol 16(33): 4135. 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4135 Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, and Holmes SP (2016). DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7): 581–583. 10.1038/nmeth.3869 Callahan BJ, Sankaran K, Fukuyama JA, McMurdie PJ, and Holmes SP (2016). Bioconductor Workflow for Microbiome Data Analysis: from raw reads to community analyses. F1000Research 5: 1492. 10.12688/f1000research.8986.2 Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, and Cole JR (2007). Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16): 5261–5267. 10.1128/AEM.00062-07 Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, and Glöckner FO (2012). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1): D590–D596. 10.1093/nar/gks1219 Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, and Lipman DJ (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3): 403–410. 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 Kumar S, Stecher G, and Tamura K (2016). MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7): 1870–1874. 10.1093/molbev/msw054 Kushkevych I, Vít\ězová M, Vít\ěz T, and Bartoš M (2017). Production of biogas: relationship between methanogenic and sulfate-reducing microorganisms. Open Life Sci 12(1): 82–91. 10.1515/biol-2017-0009 Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, and Higgins DG (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21): 2947–2948. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404–
All authors of this paper contributed, K.M., L.M. and I.K. analyzed and interpreted data from Illumina; I.K., F.G., S.B., A.A. conceptualization, methodology, and investigation of this study; I.K., D.N., S.K-M.R.R., and M.V. data curation and investigation, K.M., L.M., I.K., M.G., S.B., A.A. and M.V. writing original draft preparation, writing manuscript and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Open access funding was provided by the University of Vienna. Logan Hodgskiss is greatly acknowledged for proof reading and for providing criti-cal comments.
This research was supported by the Grant Agency of Masaryk University (MU-NI/A/1280/2022). M.G. would like to acknowledge the support of ESCMID’s “30 under 30” Award.

Comparison of microbial communities and the profile of sulfate-reducing bacteria in patients with ulcerative colitis and their association with bowel diseases: a pilot study by Kushkevych et al. is licensed under a
留言 (0)