Leprosy is a chronic granulomatous infectious disease caused by M. leprae and M. lepromatosis, and its clinical presentations exhibit widely varying morphological characteristics. Dermatoscopy is a non-invasive examination tool which can help in diagnosis and categorising leprosy into various sub-groups.1
MethodologyThis multi-centre cross-sectional study of leprosy patients was conducted from November 2021 to April 2022. After a thorough cutaneous and neurological evaluation followed by histopathological confirmation of diagnosis, representative skin lesions from the study patients were photographed and the most representative skin lesions were chosen for dermatoscopic evaluation.
Dermatoscopic evaluation was performed using a hand-held DL4 DermLite dermatoscope at 10x magnification in polarised contact mode, and photographs were captured and archived. The archived dermatoscopic images were analysed by the authors BA and KV for a set of pre-decided dermatoscopic features as listed in Table 1. Discrepancy in opinions, if any, were sorted by personal discussions. Any new dermatoscopic features observed were also documented. The histopathological specimen was obtained prior to treatment initiation from the most downward leprosy spectrum as per the standard practice and did not always correlate with the dermatoscopic lesion. Skin biopsy was also repeated at the end of treatment as part of the standard of care.
Table 1: Frequency of dermatoscopic features in study population
Dermatoscopic finding Percentage of patients exhibiting the finding n = 53 Distorted pigment network 48 (90.6%) Focal white areas 40 (75.5%) Reduced follicular and eccrine openings 43 (81.1%) Widened skin lines 28 (52.8%) Brownish background 24 (45.3%) Linear vessels 26 (49.0%) Branching vessels 16 (30.2%) Milky red globules 16 (30.2%) Dotted vessels 2 (3.8%) Pinkish hue 22 (41.5%) Circle hairs 15 (28.3%) Broken hairs 17 (32.1%) White rosettes 2 (3.8%) Follicular plugs 3 (5.7%) White shiny streaks 17 (32.1%) Whitish-yellow globules 27 (50.9%) Scales 16 (30.2%) Bluish area due to clofazimine 2 (3.8%) Serocrusts 1 (1.9%) ResultsA total of 53 patients aged between 14 and 80 years were included. Of these, there were 33 (62.3%) males and 20 (37.7%) females. The median duration of symptoms at presentation was 10.5 months (1–120 month range). The spectrum of leprosy as per Ridley–Jopling classification at diagnosis was indeterminate in 1 (1.9%), tuberculoid (TT) in 1 (1.9%), borderline tuberculoid (BT) in 25 (21.5%), borderline lepromatous (BL) in 9 (17%), lepromatous (LL) in 14 (26.4%) and histoid in 3 (5.7%). There were no defaulters and only one relapse case. Reactions were seen only in 9 (17%) patients, of which 4 (7.5%) were type 1 reactions (T1R) in BT spectrum and 5 (9.4%) were type 2 reactions (T2R) in LL spectrum. Slit skin smear (SSS) was positive in 38 (71.7%) patients. The mean bacteriological index (BI) at baseline was 2.02 ± 1.86. Fifteen out of 38 patients had a BI > 1. The majority of the patients received the World Health Organization (WHO) multi-drug therapy (MDT) multibacillary regimen (WHO MDT-MBR). Of the 53 patients, 19 (35.8%) had type IV, 31 (58.5%) had type V and 3 (5.7%) had type VI Fitzpatrick skin phototype.
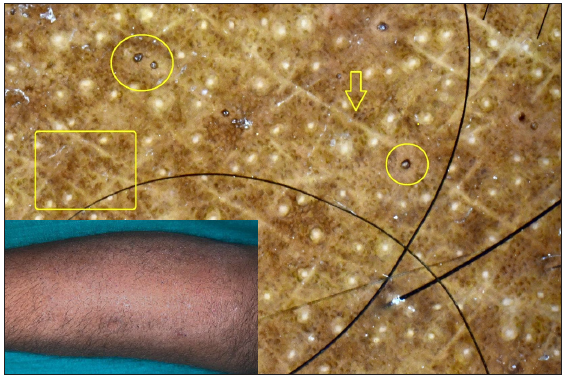
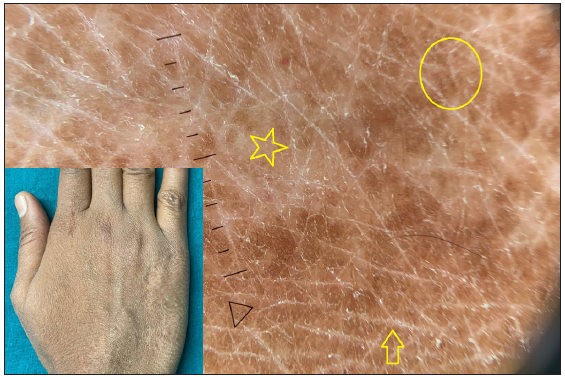
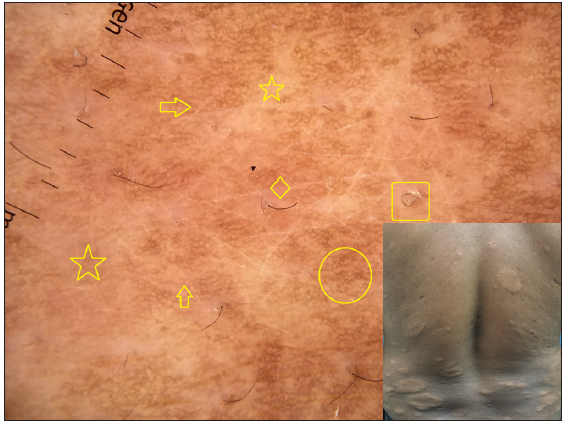
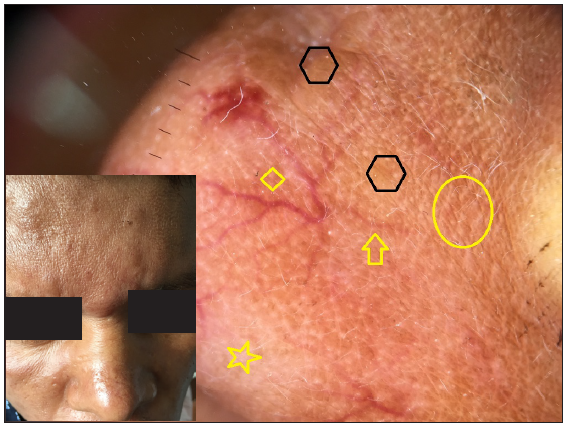
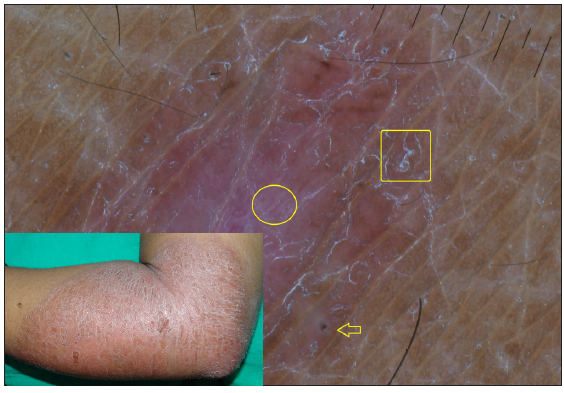
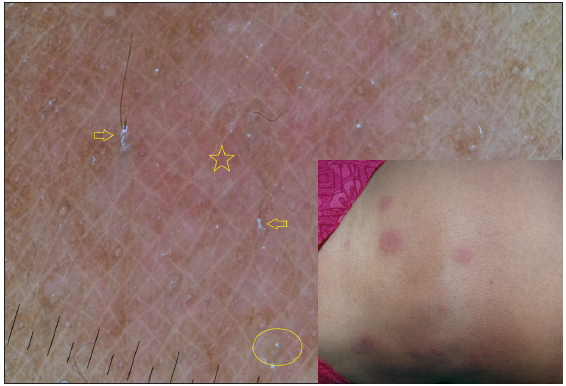
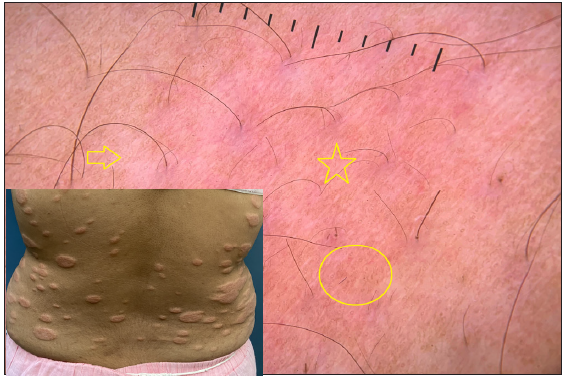
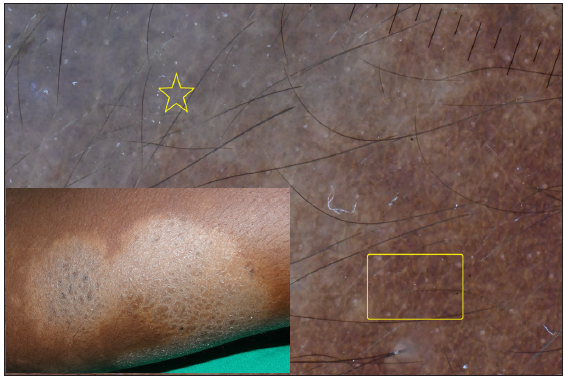
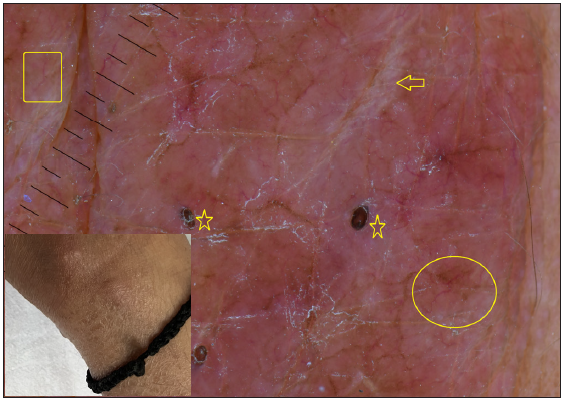
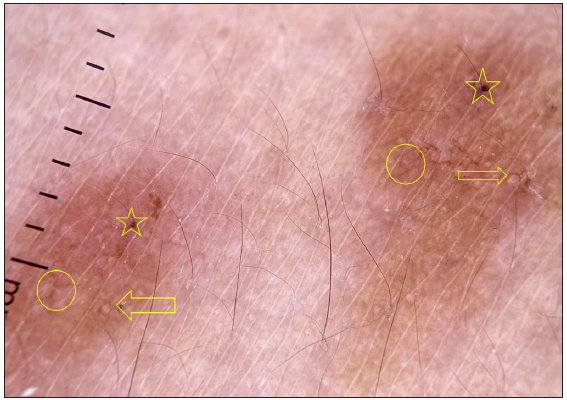
Dermatoscopic evaluation of all patients was done, the results of which are summarised in Table 1 and Figures 1, 2 and 3. Brownish background was fairly well represented in non-reactive lesions [Figure 1]. The various dermatoscopic features found were widened skin lines [Figures 1a, 1b and 1c], focal white areas [Figures 1b, 1c and 1d] and distorted pigment networks [Figures 1a–1d and 2c]. Other features included and circle hairs [Figures 1a, 1c and 2b], follicular plugs [Figures 2a and 3a] and white rosettes [Figure 3b]. Only two patients showed bluish pigmentation due to clofazimine [Figure 2d] Vascular changes consisted of linear [Figures 1d, 3a and 3b], branching [Figures 1d, 3a and 3b], globular and linear blurry vessels [Figure 2a]. Whitish-yellow globules [Figure 1d] and white shiny streaks [Figures 2c and 3a] were also noted.
Export to PPT
Export to PPT

Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Dermatoscopic features based on BIThere was no statistically significant difference in the dermatoscopic features across the spectrum (p > 0.05) [Table 2]. In the tuberculoid spectrum with BI 0/1, pigmentary and follicular changes were seen more commonly, whereas vascular changes and whitish-yellow globules were prominent in lesions with BI > 1.
Table 2: Frequency of dermatoscopic features in leprosy spectrum based on bacteriological index, duration of disease and site of involvement
Bacteriological index:
BI = 0/1
(n-16)
DPN FWA RFEO WSL BB CH BH WR FP LV BV MBG DV PH WSS WYG ScInd
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
TT
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
BT
(n = 7)
6
(85.7%)
7
(100%)
5
(71.4%)
3
(42.9%)
2
(28.6%)
1
(14.3%)
3
(42.9%)
5
(71.4%)
5
(71.4%)
3
(42.9%)
6
(85.7%)
6
(85.7%)
3
(42.9%)
BL
(n = 4)
4
(100%)
4
(100%)
4
(100%)
4
(100%)
3
(75%)
1
(25%)
2
(50%)
1
(25%)
1
(25%)
2
(50%)
3
(75%)
2
(50%)
1
(25%)
LL
(n = 3)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
T2R
(n = 2)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
Bacteriological index:
BI => 1
(n-37)
DPN FWA RFEO WSL BB CH BH WR FP LV BV MBG DV PH WSS WYG ScBT
(n = 18)
14
(77.8%)
13
(72.2%)
15
(83.3%)
12
(66.7%)
8
(44.4%)
8
(44.4%)
2
(11.1%)
3
(16.7%)
2
(11.1%)
1
(5.6%)
1
(5.6%)
2
(11.1%)
3
(16.7%)
BL
(n = 5)
4
(80%)
4
(80%)
3
(60%)
2
(40%)
1
(20%)
2
(40%)
1
(20%)
2
(40%)
2
(40%)
2
(40%)
2
(40%)
2
(40%)
1
(20%)
2
(40%)
LL
(n = 11)
5
(45.5%)
3
(27.3%)
2
(18.2%)
1
(9.1%)
3
(27.3%)
1
(9.1%)
5
(45.5%)
2
(18.2%)
1
(9.1%)
3
(27.3%)
7
(63.6%)
5
(45.5%)
1
(9.1%)
HL
(n = 3)
3
(100%)
2
(66.7%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
2
(66.7%)
2
(66.7%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
2
(66.7%)
3
(100%)
T1R
(n = 4)
4
(100%)
2
(50%)
4
(100%)
2
(50%)
2
(50%)
2
(50%)
4
(100%)
1
(25%)
3
(75%)
1
(25%)
3
(75%)
1
(25%)
2
(50%)
3
(75%)
T2R
(n = 3)
3
(100%)
2
(66.7%)
2
(66.7%)
2
(66.7%)
2
(66.7%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
Disease duration: < 6 months (n-23) DPN FWA RFEO WSL BB CH BH WR FP LV BV MBG DV PH WSS WYG ScBT
(n = 13)
11
(84.6%)
10
(76.9%)
11
(84.6%)
9
(69.2%)
5
(38.5%)
6
(46.2%)
1
(7.7%)
5
(38.5%)
2
(15.4%)
3
(23.1%)
1
(7.7%)
3
(23.1%)
3
(23.1%)
2
(15.3%)
BL
(n = 2)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
LL
(n = 6)
2
(33.3%)
1
(16.7%)
1
(16.7%)
4
(66.7%)
2
(33.3%)
1
(16.7%)
5
(83.3%)
3
(50%)
HL
(n = 2)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
T1R
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
T2R
(n = 2)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
1
(50%)
2
(100%)
2
(100%)
1
(50%)
Disease duration: < 6 months (n-30) DPN FWA RFEO WSL BB CH BH WR FP LV BV MBG DV PH WSS WYG ScInd
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
TT
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
BT
(n = 12)
9
(75%)
10
(83.33%)
9
(75%)
6
(50%)
5
(41.7%)
3
(25%)
2
(16.7%)
3
(25%)
3
(25%)
1
(8.3%)
4
(33.3%)
5
(41.7%)
5
(41.7%)
BL
(n = 7)
6
(66.7%)
6
(66.7%)
6
(66.7%)
5
(55.6%)
4
(44.4%)
1
(11.1%)
3
(33.3%)
1
(11.1%)
2
(22.2%)
2
(22.2%)
1
(11.1%)
3
(33.3%)
4
(44.4%)
2
(22.2%)
3
(33.3%)
LL
(n = 8)
4
(50%)
3
(37.5%)
2
(25%)
1
(12.5%)
4
(50%)
1
(12.5%)
2
(25%)
1
(12.5%)
1
(12.5%)
3
(37.5%)
3
(37.5%)
3
(37.5%)
1
(12.5%)
HL
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
T1R
(n = 3)
3
(100%)
1
(33.33%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
2
(66.7%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
2
(66.7%)
3
(100%)
T2R
(n = 3)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
1
(33.3%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
2
(66.7%)
1
(33.3%)
2
(66.7%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
Site of involvement: Facial
(n-12)
DPN FWA RFEO WSL BB CH BH WR FP LV BV MBG DV PH WSS WYG ScBT
(n = 8)
4
(50%)
4
(50%)
3
(37.5%)
1**
(12.5%)
1
(12.5%)
1
(12.5%)
2
(25%)
4
(50%)
3
(37.5%)
3
(37.5%)
1
(12.5%)
4
(50%)
3
(37.5%)
2
(25%)
LL
(n = 4)
1
(25%)
1
(25%)
T2R
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
Site of involvement: Extra-facial
(n-41)
DPN FWA RFEO WSL BB CH BH WR FP LV BV MBG DV PH WSS WYG ScInd
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
TT
(n = 1)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
1
(100%)
BT
(n = 17)
16
(94.1%)
16
(94.11%)
17
(100%)
14
(82.4%)
8
(47.1%)
8
(47.1%)
3
(17.6%)
1
(5.9%)
4
(23.5%)
3
(17.6%)
3
(17.6%)
4
(23.5%)
5
(29.4%)
6
(35.3%)
BL
(n = 9)
8
(88.9%)
8
(88.9%)
7
(77.77%)
6
(66.7%)
4
(44.4%)
1
(11.1%)
4
(44.4%)
3
(33.3%)
3
(33.3%)
2
(22.2%)
4
(44.4%)
5
(55.6%)
3
(33.3%)
3
(33.3%)
LL
(n = 10)
6
(60%)
4
(40%)
3
(30%)
1
(10%)
5(50%)1
(10%)
5
(50%)
1
(10%)
4
(40%)
7
(70%)
6
(60%)
1
(10%)
HL
(n = 3)
3
(100%)
2
(66.7%)
3
(100%)
1
(33.3%)
2
(66.7%)
2
(66.7%)
1
(33.3%)
留言 (0)