A 59-year-old man presented with an asymptomatic nodule over the right jaw of two years’ duration. On examination, there was a slightly protuberant intracutaneous nodule, 1cm in diameter with a bluish appearance overlying the right jaw [Figure 1]. No similar lesions were noted anywhere on his body. There was no prior history of trauma, no significant past history and no family history of similar lesions. A skin biopsy was done.
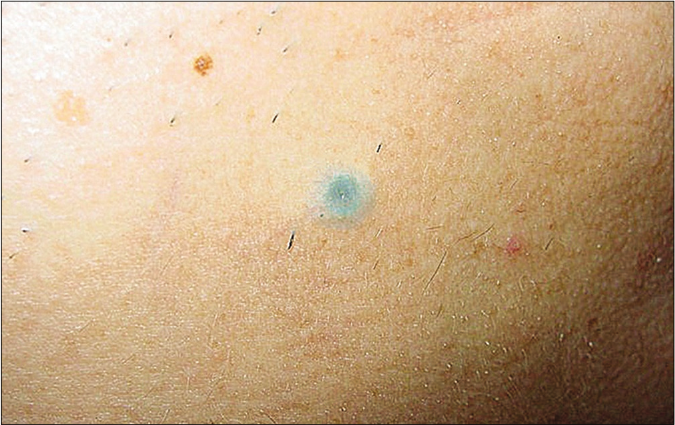
Figure 1:: A slightly protuberant subcutaneous nodule, 1cm in diameter, with a bluish appearance over the right jaw
Export to PPT
QuestionWhat is the diagnosis?
AnswerPigmented follicular cyst
DiscussionThe nodule was totally resected under local anaesthesia. Histological examination revealed a cyst located in the mid-dermis, surrounded by loose fibrous connective tissue [Figure 2a]. The cyst wall comprised stratified squamous epithelium exhibiting epidermoid keratinization which consisted of stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale from inside to outside. The cavity was filled with abundant keratinous material and some cross-sections of thick and deeply pigmented hair shafts which were composed of an eosinophilic medulla and numerous melanin granules [Figure 2b]. No sebaceous lobules were noted within the cyst wall.
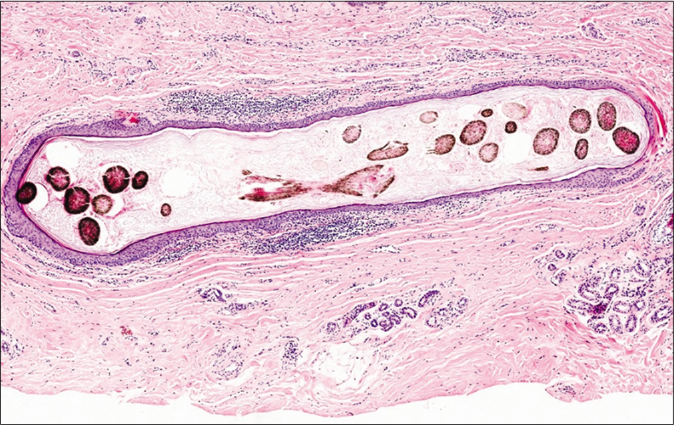
Figure 2a:: A cyst located in the mid-dermis with wall demonstrating epidermoid keratinization (H and E, ×100)
Export to PPT
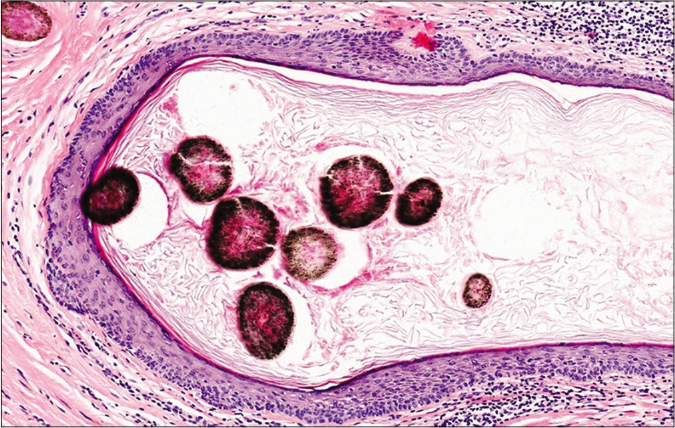
Figure 2b:: Cyst cavity shows cross-sections of thick and deeply pigmented hair shafts composed of an eosinophilic medulla and melanin granules (H and E, ×200)
Export to PPT
Pigmented follicular cyst, first described by Mehregan and Medenica about 40 years ago, is a rare variant of epithelial cysts with characteristic histology.1 The entity is most commonly described in men between 20 and 63 years of age and is mostly located on the upper body, especially the head and neck region.1
Clinically, the entity is typically characterized by a single, 0.4–1.5 cm, deep brown or bluish intracutaneous nodule or dome-shaped papule which often resembles a blue nevus, a melanocytic nevus, a histiocytoma, or a dermatofibroma.1 Multiple pigmented follicular cysts have been also described.2-4 In some rare cases, some patients with multiple lesions have a familial association.2 More infrequently, a pigmented follicular cyst can present as a pigmented ring-shaped lesion as opposed to a papule or nodule.5
Histopathologically, the entity shows a retention cyst within the mid-dermis which is lined by stratified squamous epithelium that resembles the epidermis, occasionally with some dermal papillae and rete ridges present in the cyst wall, usually in the vicinity of a hair follicle.3 Many melanin-pigmented hair shafts are observed in the cyst cavity, characterizing the microscopic appearance, and are responsible for the pigmented clinical appearance of this entity. Sometimes the cyst has a pore-like opening to the epidermis and the cyst wall presents some anagen follicles.1 On occasion, there is a degeneration of hair shafts in a pigmented follicular cyst that can be easily overlooked, leading to a misdiagnosis as an epidermal cyst.6 In some cases, a sebaceous gland can be visualized in the cyst wall, suggesting that the entity should be considered as a continuum of pilosebaceous cysts.3
The differential diagnoses of pigmented follicular cysts include vellus hair cysts, pigmented epidermal cysts and dermoid cysts. Vellus hair cysts are most often multiple 1-4 mm sized, dome-shaped skin colored to pigmented papules located on the anterior chest of young individuals (4-18 years old) without sex predilection.3,7 These cysts may be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.7 These can be differentiated from pigmented follicular cysts based on the content of the cysts, and vellus hair cysts contain abundant vellus hairs. Pigmented epidermal cysts are epidermal cysts with a black-brown or bluish appearance, most frequently occurring in dark-skinned races, characterized histopathologically by rich pigment granules in the cyst walls or pigmentophages in the surrounding stroma.8 Dermoid cysts typically manifest at birth, most commonly around the eyes.7 These histologically demonstrate a deep dermal or subcutaneous cyst with an epidermoid wall to which hair follicles and sebaceous glands are connected.1,7
Pigmented follicular cysts are benign cutaneous tumors, and complete excision is recommended for solitary lesions while multiple lesions can be successfully ablated by a continuous-wave CO2 laser or electrosurgery followed by curettage.4
留言 (0)