Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cutaneous malignancy worldwide, accounting for nearly 80% of all non-melanoma skin cancers.1 While they have low metastatic potential, BCCs are locally invasive. Risk factors include radiation exposure, human papillomavirus infections, immunosuppression, and genetic predisposition.2 BCCs are more common in older individuals and often affect men more than women.3
A skin biopsy is essential to confirm the diagnosis, although dermoscopy can aid in clinical diagnosis.4 Most primary BCCs are managed with surgical excision. Destructive measures and topical treatments are alternatives for low-risk patients or when surgery is impractical.5 Prognosis is excellent with low recurrence rates, but regular follow-up is vital. Around 50% of recurrences appear within 2 years and 80% within 5 years post-treatment.6
Incidence rates of BCC are rising in Caucasians and Asians alike.7–9 Aggressive subtypes are rising, highlighting the need for early diagnosis.10 Most BCC literature concentrates on phototypes I and II, which are common in Caucasians. However, BCC in the skin of colour often presents differently, being pigmented and prone to misdiagnosis, which requires a high index of suspicion among clinicians.11
While prior Indian studies have covered BCC demographics and clinical features, data on long-term follow-up and treatment outcomes are lacking.12–15 This retrospective study aimed to investigate the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical and pathological aspects, and treatment outcomes of BCC in North Indian patients.
MethodologyThis retrospective study, conducted at a North Indian tertiary care centre, focused on patients diagnosed with BCC at the dermatosurgery clinic from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2022. Inclusion criteria comprised a confirmed clinical and histopathological diagnosis of BCC, along with the availability of detailed clinical history, dermoscopic features, and histopathology findings. Demographic parameters (age, gender, Fitzpatrick skin type) and potential risk factors (chemical exposures, genodermatoses, smoking, personal/family history of skin cancers, use of photoprotective measures, comorbidities, and prior treatments) were systematically collected.
Clinical examination recorded details about BCC lesions, including location, size, number, and morphology. Treatment modalities, such as standard surgical excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, topical agents (5-fluorouracil, imiquimod), curettage, and radiofrequency ablation, were chosen based on clinical features, risk assessment, and patient preferences. Surgical options were provided for patients fit for surgery, with Mohs micrographic surgery preferred in sensitive areas or cases with aggressive subtypes or recurrence. Patients with multiple lesions or compromised health were directed toward topical or locally destructive therapies.
We adhered to evidence-based guidelines for BCC management. Histopathological and dermoscopic findings were extracted from records. Only participants with complete details were included, excluding those with missing data. For follow-up, we specifically considered patients with a minimum follow-up duration of 6 months. Patients were informed about potential BCC recurrence and encouraged to report any symptoms promptly, even if they occurred between scheduled follow-up visits conducted every 6 months.
We employed SPSS version 23 for data analysis, expressing qualitative data as percentages and quantitative data as medians and ranges. Pairwise comparisons utilised Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test for qualitative data and Mann–Whitney U test for skewed quantitative data. Analyses were two-sided with p = 0.05 significance. Survival analysis used Kaplan–Meier curves and the Cox proportional hazards regression model assessed predictor variables’ impact on recurrence risk.
Results Population demographics and risk factorsOut of 83 confirmed cases, 47 (56.6%) were females. The median age was 62 years (6–85). Nearly one-third were in their seventh decade of life. Median age at presentation showed no statistically significant gender difference (p = 0.865). Mean (SD) symptom duration was 46.6 (51.3) months (1–360) and was similar for males and females (p = 1.00). Excluding the patient with oculocutaneous albinism, all patients were Fitzpatrick skin types III, IV, or V. Table 1 presents an overview of the demographic characteristics of the study population, encompassing associated genodermatoses, comorbidities, and diverse risk factors.
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of the study population
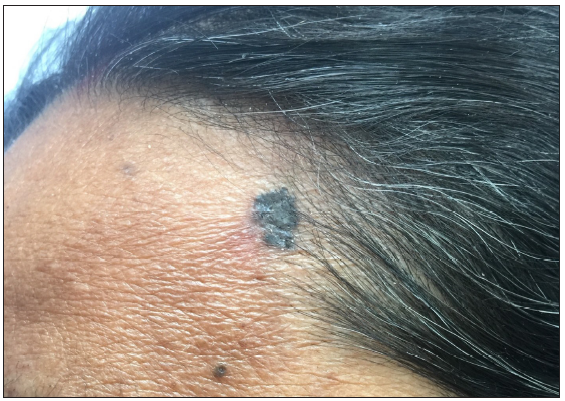
Characteristics Value Total confirmed cases 83 Females (%) 47 (56.6%) Median age in years (Range) 62 (6–85) Mean (SD) symptom duration in months (Range) 46.6 (51.3) (1–360) Genodermatoses (%) 8 (9.6%) - Xeroderma pigmentosum 5 - Gorlin syndrome 2 - Albinism 1 - Epidermodysplasia verruciformis 1 Common comorbidities - Hypertension 17 - Diabetes 16 Prior malignancies - Squamous cell carcinomas 2 - Laryngeal carcinoma 1 - Hepatocellular carcinoma 1 Concurrent premalignant lesions - Bowen’s disease 2 - Actinic keratosis 1 Fitzpatrick skin types - III, IV or V All patients (excluding albinism) Photoprotective measures (%) 8 (9.6%) Risk factors - Smoking 6 (7.2%) - Family history of BCC 3 (3.6%) - Exposure to ionising radiation 2 (2.4%) - Iatrogenic immunosuppression 1 (1.2%) Regular daily outdoor activities (%) Around 70% Clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathologic characteristicsThe majority (81.9%) had a single lesion, while 15 had multiple lesions, including six with genodermatoses and one who was a liver transplant recipient on immunosuppressants. Table 2 summarises the clinical details of the study population. In total, 126 lesions were assessed. The median size at presentation was 1.90 cm (0.2 cm–7 cm). Patients with lesions exceeding 2 cm had a significantly longer median duration of illness (48.0 (60.0) vs 24.0 (49.5) months, p = 0.048). Among 126 examined lesions, 104 (82.5%) were present on the head and neck. The most common site of involvement was the malar region, with right and left cheeks [Table 3]. Pigmentation was clinically evident in 57/126 patients (45.2%). The most common dermoscopic features observed were crusting (n = 71, 56.3%), arborising telangiectasias (n = 69, 54.7%), and blue-grey dots (n = 65, 51.5%) [Table 4].11 Of the 88 lesions for which clinico-histopathological typing could be done, the most common subtype was nodular BCC in 35 patients (39.7%). Other observed clinico-histopathological variants included nodulocystic (n = 21, 23.8%), micronodular (n = 17, 19.3%), superficial (n = 7, 7.95%), basosquamous (n = 6, 6.8%), morpheaform BCC (n = 1, 1.14%) and infiltrative BCC (n = 1, 1.14%).
Table 2: Lesional characteristics of included patients
Lesion Characteristics Details Number of lesions 126 Clinically evident pigmentation 57/126 patients (45.2%) Lesion margins Rolled: 72 (57.1%), raised: 48 (38.1%) and depressed: 6 (4.7%) Lesion surface Ulcerated: 46 (36.5%), crusted: 44 (34.9%), smooth: 14 (11.1%), telangiectatic: 9 (7.1%), verrucous: 7 (5.5%) and gritty: 6 (4.8%) Lesion size (Median) 1.90 cm (Interquartile range (IQR): 1.82 cm) Lesion size range 0.2 cm–7 cm Symptoms Asymptomatic: 58 patients (69.9%), bleeding: 21 patients (25.3%) and pain: 8 patients (9.6%) Recurrent lesions 5 patients (3.97%) Treatment of recurrent lesions Surgical treatment: 2 patients, electrosurgery: 1 patient, topical 5-Fluorouracil: 1 patient, radiotherapy: 1 patient Duration of illness (Median) Exceeding 2 cm: 48.0 (60.0) months, not exceeding 2 cm: 24.0 (49.5) months, p = 0.048Table 3: Distribution of basal cell carcinomas as per site
Site Number of lesions (n = 126) Malar region 33 (26.1%) Nose 26 (20.6%) Periocular 11 (8.7%) Periauricular 10 (7.9%) Forehead 7 (5.5%) Temple 5 (3.9%) Chin 5 (3.9%) Neck 5 (3.9%) Scalp 2 (1.6%) Lip 2 (1.6%) Other (trunk and limbs) 20 (15.8%)Table 4: Dermatoscopic features of the study population
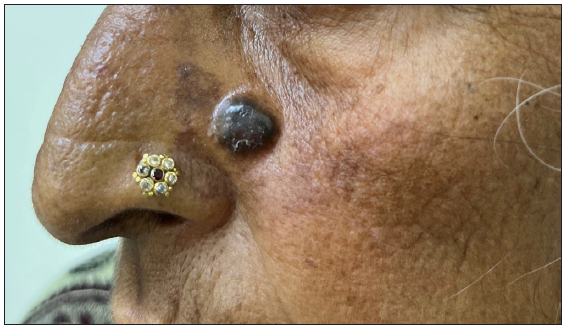
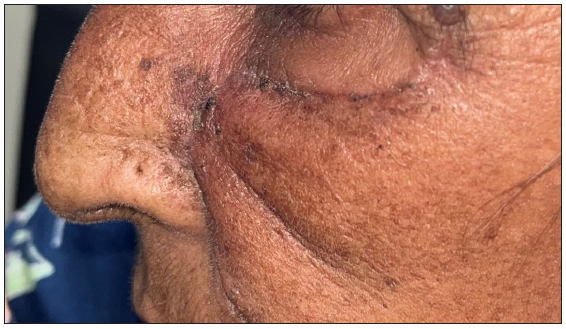
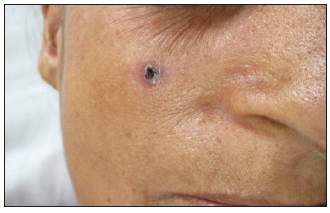
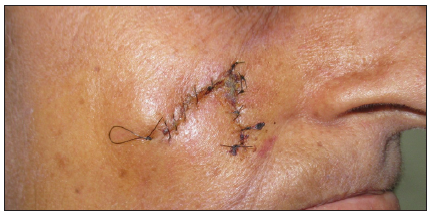
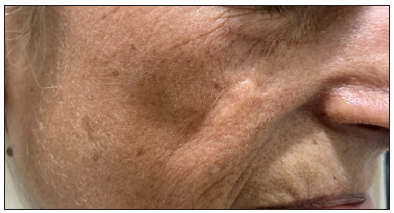
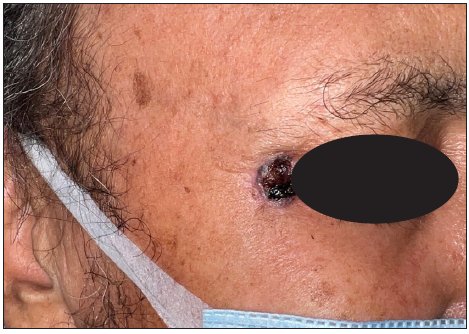
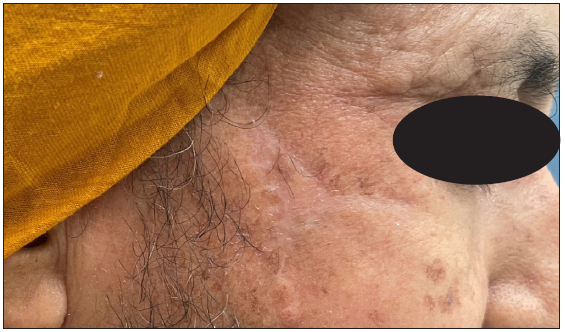
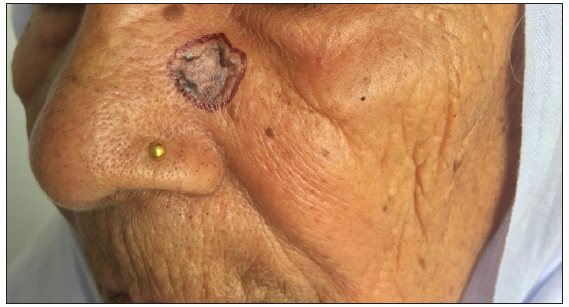
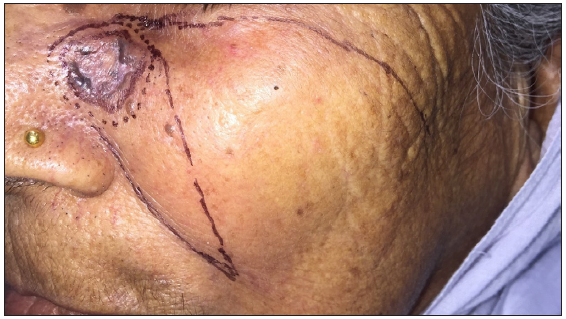
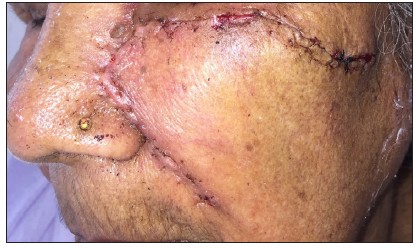
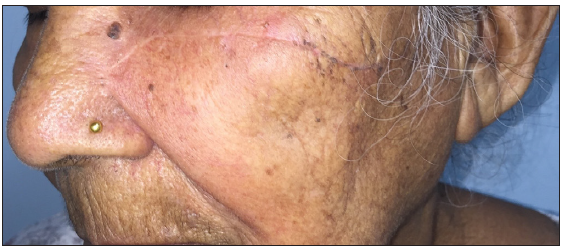
Dermoscopic changes Number of lesions (n = 126) Surface changes Scaling/crusting 71 (56.3%) Ulceration 51 (40.4%) Erosions 38 (30.1%) Pigmentary changes Blue-grey dots 65 (51.5%) Blue-white veil 62 (49.2%) Maple leaf-like areas 59 (46.8%) Blue-grey globules 53 (42.1%) Spoke wheel areas 8 (6.3%) Regression structures Yellow-white structureless areas 31 (24.6%) Short white streaks 15 (11.9%) Vascular changes Arborising vessels 69 (54.7%) Linear telangiectasias 41 (32.5%) Hairpin vessels 10 (7.9%) Glomerular vessels 14 (11.1%) Special signs Adherent fibre sign 27 (21.4%) Rainbow effect 34 (26.9%) Management, complications, and long-term follow-upModes of management included surgical excision in 59 patients (71.1%, [Figure 1]) and Mohs micrographic surgery in four patients (4.8%, [Figure 2]). Six patients received topical therapy, including 5-fluorouracil (n = 5, 7.2%) and imiquimod (n = 1,1.2%). Radiofrequency ablation and curettage were employed in two patients each (2.4%). Three patients denied intervention, and seven patients were referred to the oculoplastic/plastic surgery department for management. Surgical excision was performed with a margin of 3–4 mm and reconstruction was performed by various methods including primary closure (n = 26, 44.1%), advancement flap (n = 15, 25.4% [Figures 1 and 2]), rotation flap (n = 8, 13.5%, [Figures 3 and 4]), transposition flap (n = 6, 10.2%, [Figure 5]) and bilobed flap (n = 4, 6.7%). Short-term complications included local site infection (n = 8), wound gaping (n = 6) and flap necrosis (n = 2). Over the long term, two patients developed hypertrophic scarring.
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
Export to PPT
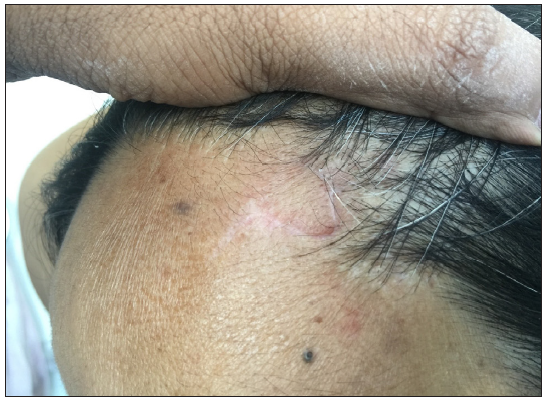
Export to PPT
Of the 70 patients with available follow-up (median: 40 months, range: 6–57 months), five (7.1%) had recurrences, comprising two surgical excision patients, two treated with 5-fluorouracil, and one with curettage [Table 5]. An additional 7.1% developed new BCCs at different sites, which included two who also had xeroderma pigmentosum. Three patients died, one from lung cancer, another from erythroderma secondary to pityriasis rubra pilaris, and the third from multiorgan failure.
Table 5: Characteristics of patients who experienced a recurrence of basal cell carcinoma during follow-up
S. no. Age in years/gender Duration of disease at presentation in months Risk factor(s) Site of lesion Size of lesion (in cm) Clinico-histological subtype Initial management Time to recurrence (in months) Management of recurrent lesion 1. 21/M 7 Xeroderma pigmentosum, recurrent lesion Temple 0.5 × 0.5 Basosquamous Surgical excision with primary closure 46 Re-excision 2. 47/F 48 None Chin 3×2 Micronodular Surgical excision with advancement flap 40 Denied intervention 3. 47/F 12 Epidermodysplasia verruciformis Nose 4×3 Superficial Topical 5-fluorouracil 26 Denied intervention 4. 65/M 36 Photo damage, including multiple actinic keratoses Pre-auricular 5×2 Nodulocystic Topical 5-fluorouracil 32 Surgical excision 5. 6/M 2 Xeroderma pigmentosum Malar 1×1 Nodular Curettage 42 Surgical excisionAmong surgical excision patients (n = 59), follow-up data was available for 49 (median: 40 months, range: 6–57 months). Of these, 45 remained recurrence-free, two experienced site-specific recurrences and two died of causes unrelated to the disease or intervention. Mohs micrographic surgery patients (n = 4) had no recurrences but had shorter follow-up (median: 9.5 months, range: 8–10 months). Mean disease-free survival favoured surgery (55.58 ± 0.98 months) over medical or destructive therapies (43.6 ± 3.482 months, p = 0.003, [Figure 6]). The medical/destructive group however had more patients with multiple lesions (p = 0.003) and associated genodermatoses (p < 0.001).
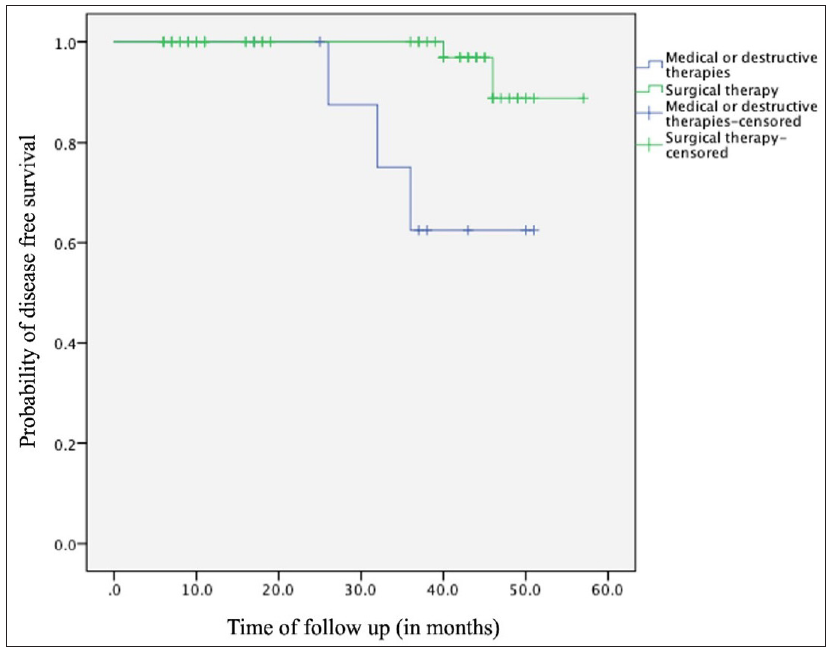
Export to PPT
We used Cox proportional hazards regression to assess the impact of various factors on recurrence risk. None of these variables, including age (HR: 0.97, p = 0.219), gender (HR: 0.39, p = 0.388), lesion duration (HR: 0.99, p = 0.822), size (HR: 5.27, p = 0.197), number (HR: 1.28, p = 0.844) and treatment type (medical/destructive or surgical) (HR: 0.19, p = 0.263), were statistically significant. This suggests their limited influence on recurrence risk, possibly due to the small number of recurrences observed.
DiscussionBCC has seen rising incidence due to factors like an ageing population, increased sun exposure, and lifestyle changes. Asian BCC tends to differ from the Western type with lower incidence, older age at first lesion, fewer total lesions, and more pigmented lesions.16–18
In our study population, the age and gender distribution aligned with prior Indian studies.11–15 BCC was most common in the seventh decade of life, with only three patients younger than 20, all having Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP). A female predominance was noted, possibly due to intermittent sun exposure. The infrequent use of sun protection measures in our study highlights the need for enhanced sun safety awareness and education.19
Our results show that BCC primarily affects the cheeks, followed by the nose and periorbital region, consistent with prior studies from India, Korea, and Japan.11,20,21 Nodular BCC was the predominant subtype in patients with darker skin phototypes, in line with prior research on BCC in this population.11,15,18
In a systematic review examining dermoscopy in BCC cases, pigment structures were observed in only 36% of the cases.22 In our study, focusing on phototypes III, IV, and V, over half the patients exhibited pigment structures, with clinical pigmentation observed in 45.2% of cases, aligning with prior research in Asian populations with consistent presence of pigment structures.11,23 Pigment structures enhance the sensitivity and specificity of dermoscopy in pigmented BCC cases.24 Further, pigmented BCCs have a lower risk of recurrence following surgical excision since the tumour margins are better delineated.25
During follow-up, five of seventy patients developed new BCCs at different sites, including two XP patients. The recurrence of primary lesions was observed in five cases, including two that managed with surgical excision. Notably, patients experiencing a recurrence of lesions had high risk factors, including lesions on H areas [high risk for recurrence: “mask areas” of face (central face, eyelids, eyebrows, periorbital, nose, lips, chin, mandible, preauricular and postauricular skin/sulci, ear, temple), genitalia, hands and feet], basosquamous histopathological subtypes, or prior recurrence [Table 3].
Strengths of this study include extensive data collection, robust inclusion criteria, utilisation of dermoscopy and histopathology for accurate diagnosis, and availability of follow-up information. Limitations include retrospective study design, potential for incomplete data, selection bias, and relatively small sample size. Follow-up duration was short, however, as nearly two-thirds of recurrences are evident in the first 3 years after the intervention,6 a significant proportion of recurrences was likely recorded.
ConclusionThe lack of sun protection and delayed attention highlight the need for heightened awareness of BCC among individuals with darker skin tones. Treatment outcomes are positive, with rare recurrences in the absence of high-risk factors. Vigilant follow-up is crucial, particularly for those with prior malignancies or sun exposure. Surgical excision remains the primary treatment, with customisation based on lesion characteristics recommended. Patients with genodermatoses or immunosuppression require specialised care.
留言 (0)